Today is acute enough for anyoneeconomic entity is the question of improving the efficiency of an individual employee. This can be achieved by applying various forms and systems of remuneration. In this article, their types will be considered, the characteristics and differences are given.
Classification
Consider the existing forms of wage systems.
Among them there are two main: piecework and time-based.
Piece, in turn, is divided into types, which are called systems. They contain the keyword of the form name in their name:
- piecework bonus;
- straight piecework;
- piece-progressive;
- indirectly piecework.
This also includes the lump sum wage system.
In turn, the time-based wage system (COT) is also subdivided into the time-based, simple and premium-time-based.
Besides the fact that systems are called varietiesforms, they also include independent concepts. Among them, there is a new tariff system developed by the Government of the Russian Federation. Detailed description of the forms and systems of remuneration will be given below.
Piece shape
In this form, the wage depends onhow many products were made, what quality, how difficult the work was, and what the conditions of work were. This form is tied to the tariff COT.
Расценка за выполняемую работу определяется путем relationship of the tariff rate, which is assigned to a particular job, to the rate of output. These two indicators are taken into account for the same time period. In addition, it can be determined by the product of the rate of time to perform a particular job.
With a direct piece-rate system, the salary increases in direct proportion to the number of products manufactured by the employee and work performed, depending on the piece-rates.
In case of overfulfilment of the norms in excess of the planned amount, the absence of marriage and complaints from buyers, bonuses can be applied, in this case they are talking about piece-bonus COT.
In case of payment for the manufacture of products withinplan for the calculated rates and their application increased for each product made above the norm, use the piece-progressive type of the described form.

Under the lump sum payroll systemcarried out for the whole range of work carried out, while taking into account the deadline for their implementation. It is used, as a rule, to pay for the work of the brigade. Wages can be calculated using labor participation rates (CTS).
Indirect piece of the consideredthe form is used for the purpose of remuneration of workers serving the production process. Their salary directly depends on the number of products produced by the main employees. For this category of workers and there are indirect-piece rates.
Payroll
Consider the examples of piecework wages.
Допустим, что в каком-либо хозяйствующем субъекте for workers employed in primary production, a simple piece-rate form is used. The price per unit of manufactured products is set at 500 rubles. With the release of the main employee 100 units of this product for the month of his salary will be
500 x 100 = 50,000 rubles.
These rates can differentiate independing on the quality gradation of manufactured products. For example, for goods of the first grade rate is 500 rubles., And the second - 300 rubles. The worker manufactured 40 units of production of the 1st grade and 60 units of the second. Then his salary will be
500 x 40 + 300 x 60 = 38,000 rubles.
When applying a piece-rate COT to an employeethe main production is paid, in addition to the basic salary, the premium for over-fulfillment of the planned indicators, and this product must be of high quality. For example, in an economic entity a piece rate is set at 500 rubles. per unit of production. At the same time, the rate of production (manufacturing) was established - 3 pcs / day. The wage regulation states that if the output is carried out with a plan exceeding 10% or more, the main production worker is paid a premium of 10% of the salary. For example, in the month of 20 working days. In this case, the number of manufactured products for this period of time should be 20 x 3 = 60 units. And the worker made 70 units. There is an excess of 16.7% for the release. Thus, the condition for the accrual of the premium is present. Wages will consist of two components:
- Piece (for the work done) - 60 x 500 = 30 000 rubles.
- And premium (for overfulfilment) - 30,000 x 10% = 3,000 rubles.
The total salary will be:
30,000 + 3,000 = 33,000 rubles.
Consider the example of payment for piece-progressive COT.
We accept the conditions of the previous example with the exceptionbonus provisions. From the data it follows that the employee released 10 pieces of products more compared to the plan (70-60 = 10). Suppose that each subsequent unit of the product, manufactured above the plan, is charged at a rate of 600 rubles per unit. Thus, his salary will be:
500 x 60 + 600 x 10 = 36,000 rubles.
Более сложен расчет заработка при использовании chord system. For example, the team carries out construction work. It includes the brigadier, his assistant and three workers. Works are performed within 20 days. The total cost of the work is 500,000 rubles. Different KTUs have been established for different positions: for the foreman - 1.5, his assistant - 1.3, workers - 1.0. Suppose that the work was carried out within the working day, the norm was fully implemented. First you need to calculate the total KTU brigade, which in our example will be
1,5x1 people + 1.3x1 + 1.0x3 = 5.8.
Further the salary according to posts is calculated:
- the foreman - 500 000: 5,8 x 1,5 = 129 310,3 rub.
- Assistant - 500,000: 5.8 x 1.5 = 112,069.0 rubles.
- each worker - 500,000: 5.8 x 1.0 = 86,206.9 rubles.
Consider an example of using indirect-piecework wages.
Suppose the employee’s wage rate,employed in the service industry, is 1,500 rubles. It is auxiliary for two main employees, one of which produces 50, and the second - 100 parts per day. Thus, with a month of 20 working days, the first will produce 1,000, and the second, 2,000 parts. The indirect rate will be:
- for the main employee No. 1 - 1 500: (50 x 2 people) = 15 rubles.
- for the main employee No. 2 - 1 500: (100 x 2) = 7.5 rubles.
Salary of an employee engaged in service production:
15 x 1 000 + 7.5 x 2 000 = 30 000 rubles.
It can also be calculated on the basis of the average percentage of compliance by the main employees.
Time form

In this case, employees receive a salary depending on the performance of standardized tasks. Allocate:
- simple time-based wage system, which is used for a specific number of hours worked, regardless of the amount of work performed;
- time-premium variety, which provides for prizes for high-quality performance of work.
This form involves accountingworking time. Both the piecework discussed earlier and the time-based wage system can be applied to specific employees or to collectives as a whole. Both systems include premium forms of pay.
Application of piecework system
Effective use of piecework is possible in the following cases:
- accounting of labor results is quantitative, that is, it can be accurately determined;
- workers on the COT under review may produce products in excess of the plan;
- there is an opportunity to carry out labor regulation.
Sladelnuyu system is best used in cases of the need to encourage workers to increase the volume of manufactured products.
However, it is not recommended to use it in cases where there are critical values for:
- deterioration in the quality of manufactured products;
- deterioration of maintenance used in the manufacture of equipment;
- violations of technological regimes;
- violation of labor protection service requirements;
- waste of materials and components.
Time-based system

This method of calculating wages should be used in the following situations:
- there is no possibility to increase production volumes;
- if it is, then there may be a deterioration in product quality;
- the production process must be regulated;
- the employee is only required to monitor the process;
- Production is carried out on a conveyor or flow type with a certain rhythm.
Tariff wage system
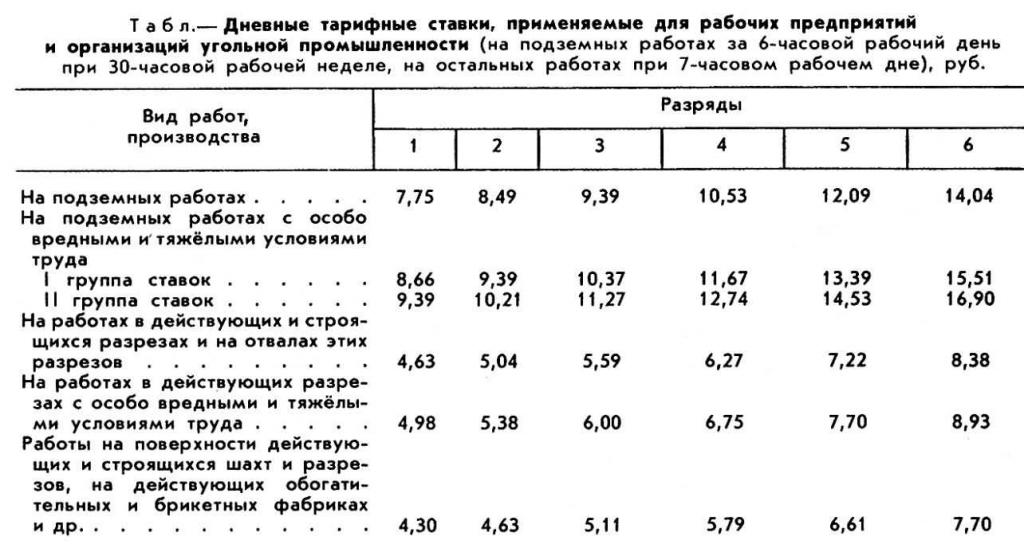
The time form suggests that the salaryemployee is charged for the time worked. In order to take into account the nature and qualifications of the employee, apply the tariff wage system. In this case, the tariff rate is used, which shows the amount of payment for a certain temporary unit. At the same time, they distinguish the minimum of these rates, corresponding to the first category.
There are daily and hourly wage rates.Their combination, together with the assigned coefficients, forms the tariff grid. The coefficient corresponding to the first digit is equal to one. It is the base for the next and shows how much the tariff rate of the category under consideration is higher than the first.
With a simple time-based COT salarycalculated as the product of the hourly wage rate (or daily), corresponding to this category, and the time worked (usually takes the period for which the salary is calculated).
On average, the number of digits in one business entity does not exceed 6-8. Their tariff coefficients are fixed in a collective agreement.
The basis of a single tariff system (ETS) isdistrict coefficients and surcharges for work in adverse conditions. The first one shows how much the wage increases, depending on the location of the economic entity. Their value ranges from 1 to 2. And the introduction is mainly due to the fact that prices in different regions may vary significantly. In addition, in different subjects different food products, and especially non-food cycle, are required, due to the different climatic conditions.
As a base when building a tariff COTan economic entity in a collective agreement must fix its minimum level in the performance of labor duties, which will be the starting point for the tariff rate.
Thus, this system assumes the obligatory accounting of working hours.
Staffing system
Managers of the business entity are mainlywork on the above system. Its essence comes down to the fact that the personnel department makes up the staff list, which indicates the list of positions working in a particular organization, gives the number of employees for each position and determines the size of their salaries.
By analogy with the tariff system and itsqualification reference books developed classifiers with which the attestation commission assigns employees a specific qualification category.
Both are recommended.character for business entities. They can take its position, and they can change it. The procedure for certification and its frequency are determined by the organization itself.
Tariff-free system

Tariffs lead to the fact that there is a leveling between employees who occupy the same positions. An alternative option is considered a tariff-free payment system.
Salary of all employeeseconomic entity is determined by the wage fund (pay) the entire organization or a separate unit. Here, the full monthly payment to the employee is determined by his qualifications, KTU and time worked. For all workers, the qualification level is calculated by the ratio of the actual salary for a certain past period of time to its minimum size for the same period. In total there are ten qualification groups that have their own levels.
The tariff system does not imply an increase in the qualifications of the employee upon reaching the last tariff level. With the system under consideration, the qualification level can increase infinitely.
The inclusion of workers in a certainthe qualification group is exercised by the work collective council. The use of the described system assumes the determination at the first stage of the salary of each employee, and at the second - the salary of individual employees included in the units. As a result of the introduction of this system, the distribution of payroll funds between specialists with equal qualification and rank changes.
Contract wage system isderived tariff system. It involves the conclusion of an employment contract, in which the wages, rights and obligations of the employee and the employer are prescribed.
New system

It involves the division of salaries into two parts.The first is guaranteed and paid for the fact that the employee performs the duties that act as officials. The second part is stimulating. Its size depends on the end result of labor. Also allocate a compensation part in which various extra charges carry.
Thus, the use of the described system assumes that the salary is charged on the piece-time basis.
Введение новых систем оплаты труда базируется на the same principles that were discussed earlier. In particular, the qualification level of the employee, the volume and complexity of the work are taken into account. According to the tariff rate, the basic part of the salary can be determined, which is constant. In contrast, the compensation part is variable and is determined by several factors, first of all, by region and work conditions. The stimulating part contributes to the high-quality performance of work by a certain employee. It is also not guaranteed and is not equalized for all categories of workers.
This system has been implemented since the end of 2008 inall budgetary institutions of the federal level. For them, base salary rates and base salaries were determined by the Government of the Russian Federation. If a subject of the federation has the means that can contribute to raising these rates, he is entitled to do so. In addition, the authorities of the subjects may establish them for those positions that are absent in the Government Decree.
Finally
В данной статье мы рассмотрели формы и системы wages. The main ones described are piecework and time-based, which include a number of varieties. Currently, a new wage system is being applied. The above, with the exception of piecework, are based on a tariff system with certain categories and rates. There are also tariff-free systems based on the distribution of payroll groups by qualification groups.


