Sometimes insects can deliver to humans.quite serious trouble. One of them is Chagas disease, or Chagas, caused by bloodsucking bugs. More than 100 years ago, it was described by Carlus Ribeiro Chagas, a Brazilian physician, than he immortalized himself. The name of the disease sounds differently, depending on the pronunciation of the name of its discoverer. Is Chagas disease dangerous and how serious is it? The answer to this question is positive. Yes, it is dangerous, although there are people who have been living with this disease for many years without even knowing that they are infected. But this is the exception rather than the rule. A more common outcome of the disease is sad: patients die within the first months after infection. How and where can I catch this infection and why do people have such a different reaction to it? Let's try to answer.

Chagas disease: geographical location
For Russians, fortunately, while this ailment isexotic. But once AIDS was far away from us, somewhere in overseas America. The same situation is currently demonstrated by Chagas disease. Where is it spread now? Among people in large numbers it is registered in the South American continent and in some countries of the Caribbean, in Brazil, Venezuela, Panama, Mexico, Peru, Argentina, Guatemala, Colombia, Ecuador, Costa Rica, Paraguay, Bolivia, Suriname, El Salvador, French Guiana , Belize, Nicaragua, Honduras. As for wild animals that also become infected with Chagas disease (squirrels, rats, opossums, cats, dogs and others, only 150 species), the infection is noticed much further north. This gives rise to fears that the disease will soon spread deep into the North American continent. Already, there are cases in Texas, Arizona, southern California and Maryland. The advancement of American trypanosomiasis on the planet is facilitated by the migration of the population in the last 15–20 years taking place on a scale that is no longer controllable. Residents of Latin American countries travel around the world in search of a better life, tourists - in search of adventure. Another reason for the spread of infection is that the poor from the above-mentioned regions not only grabs at any job, but donates blood for money and even sells their organs (kidneys, eyes, etc.). When checking at some blood transfusion sites in the United States of America, it was found that there is more donor material with Chagas disease than with hepatitis and AIDS. And when opening deaths from heart attacks or acute heart failure to persons from the Latin American region, it turned out that every second person suffers from the same disease, only suffers from it in a chronic form. So in the near future, the boundaries of the range of Chagas disease are likely to disappear.

Causative agents of the disease
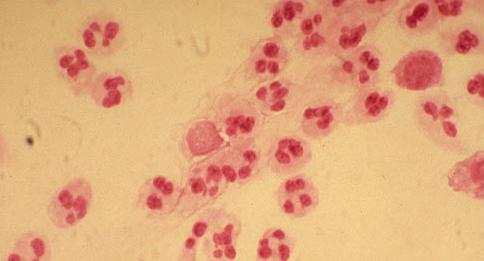
Little-known while Chagas disease isinfection with microscopic unicellular live parasites - cruz trypanosomes (Trypanosoma cruzi). So they called Carlos Shagas in honor of the Institute Osvalda Cruz. These creatures are colorless (in the photo they are shown in the patient's blood, stained with a marker), with an elongated body that looks like a spindle. At one end there is a flagellum that helps the trypanosomes to travel through the victim's body (mainly by blood). Reaching the organ they need, they penetrate through the membranes into the cells and form an eggless form of an egg-like form (amastigote). In cells, trypanosomes actively proliferate, re-forming spindle-shaped "babies" with flagella, which penetrate the victim's blood for further settlement throughout the body. A very bad feature of these microscopic killers is that they are able to influence the victim’s immunity, forcing him to give up the fight. Trypanosomes are exclusively parasitic way of life, making the path: man (animal) - bug - man (animal). In these circles of the life cycle, changes of their forms occur: from the egg to the adult. They also actively proliferate in the stomachs of bugs, which are used for relocation into the bodies of healthy people.

Ways of infection
Chagas disease, a carrier of which is a special typebloodsucking triatom bugs, picked up mainly at night, during sleep in the rooms where these insects live. Someone called them “kissing” for fun, because they prefer to bite mainly on the lips. The name stuck. True, not everywhere. In Chile and Argentina they are called uncomplicated - vinchuca, which means an insect, and in Brazil - a barber-bug. In total, among the large army of triatomid bugs, numbering 130 species, only in America alone have found more than 10 species that are carriers of such a microorganism as the causative agent of Chagas disease. In addition to insects, you can become infected from a sick person through close contact if his blood enters the body of a healthy contactee through wounds on the skin. What is not new AIDS? Therefore, infection often occurs in hospitals during blood transfusions or organ transplants. Infants are still infected in the womb, if it is the carrier of the disease. The most peaceful way to catch the infection is through food that has got the bug feces. This can occur if people who are infected with Chagas' disease are not cooked. Therefore, traveling to countries unsuccessful in relation to triatom bugs, it is advisable to choose a more civilized place to sleep (a better hotel), wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly, and refrain from home meals, helpfully offered by local merchants.

How does the infection occur?
Many people think that Chagas disease is picked up,when the bug bites through the skin and starts drinking blood. In fact, it is not. You can be bitten ten times and stay healthy. And all because the infection occurs when the victim makes a trypanosome cruz, located in the faeces of the bug, in their skin or mucous membranes. These insects are individuals who eat where they are there and crap. A man in a dream involuntarily scratches (and the animals lick) a bitten place. So parasites get into the body of their new owner. By itself, a healthy bug is not dangerous. But, biting infected people, it almost completely becomes infected with trypanosomes, and with the following bites, it transmits new victims to Chagas disease. The pathogen lives and multiplies in the insect's stomach. Contagious bug remains all his life (about 2 years). Matured parasites are localized in the intestines of the victim and are excreted with feces. Once in the human body, the trypanosomes multiply first in blood and then settle in the muscles (mainly in the heart and in the gastrointestinal epithelium). Poor people in Latin America live in crowded, large families, in dilapidated houses, where there are many secluded nooks for bedbugs. Often, Chagas disease infects all family members and even entire neighborhoods. Information for consideration: laboratory animals were infected with trypanosomes even when there was no damage on their skin.

Acute form of the disease
It is noted that the moment of biting by a bug by the skinpainless and imperceptible. Subsequently, a slight redness appears in that place (and sometimes there is nothing), in some people there is swelling and itching. The latent (incubation) period, while the parasite in the victim’s blood is diligently reproducing, can take from a couple of days to 10 days, depending on the strength of the patient’s body and its tendency to allergies. Then comes the so-called acute form. It was during this period that the death of Chagas disease was extremely dangerous. Symptoms are as follows:
- a sharp rise in temperature to critical levels;
- fever;
- severe headaches;
- problems with breathing;
- malfunctions of the heart;
- significant soreness of the abdomen, chest, all muscles;
- adrenal gland damage;
- an increase in the thyroid gland, spleen, and lymph nodes.
When parasites are introduced into nerve fibers, Chagas disease is especially difficult. Symptoms in this case are:
- paralysis;
- speech impairment;
- athetosis
- impaired intelligence.
External manifestations:
- swollen lips;
- swelling of the eyes;
- the acquisition of leather bronze.
The acute form can last two months, overwhich many (especially children) die. In survivors of the crisis, the main symptoms disappear, and the disease proceeds to the next stage. An infected person becomes contagious 10-11 days after a bite.

Chronic form
At this stage, Chagas disease can lasttime does not manifest itself at all, which is observed in approximately 80% of patients. Trypanosomes in the blood no longer dominate, but settle in the tissues and cells of the patient and gradually destroy them. In "chronicles" periodically exacerbations are observed, followed by complete remission. Chagas identified the following types of chronic disease:
- pseudomyxedematous;
- myxedema;
- nervous;
- hearty
The pseudo-myxedematous type is noted in children in15 years old and younger. It is characterized by a slight increase in the thyroid gland and lymph nodes. During periods of exacerbation in children, fever begins, fever rises, and tachycardia is observed. Parasites infiltrate into the subcutaneous tissue, which especially disfigures the face. By characteristic edema and redness, you can visually recognize Chagas disease. Photos presented in a wide assortment on specialized medical-related resources cause, to put it mildly, unpleasant sensations.
The myxedematous type differs from the previous one in much larger disorders in the thyroid gland.
The nervous type is fraught with a delay in the development of children and infantilism.
Cardiac leads to pericarditis, bradycardia, and other heart problems.
When localization trypanosomes Cruz in the wallsorgans of the gastrointestinal tract there are achalasias of the cardia, that is, disorders of the peristalsis of the muscles of these organs. This leads to obstruction of the esophagus and an increase in the departments of the stomach and intestines. Patients have pain when swallowing food and passing through the esophagus, vomiting, belching, weight loss, despite a satisfactory appetite. These symptoms do not depend on the consistency of food and appear even on liquid food.
Diagnostics
Chagas disease is established by externalsigns during clinical examination of the patient and by further laboratory blood tests under the microscope and serological tests. However, with a chronic form of the disease, there are few trypanosomes in the blood, and therefore it becomes more difficult to detect them.
When parasites cannot be isolated in a blood sample, their presence is checked in the lymph nodes (biopsy is done).
Xenodiagnostics is also used.It lies in the fact that laboratory healthy bugs are planted on a sick person, and subsequently (after 14 days) they are examined whether parasites appeared in their intestines or not.

Another test is sowing blood and inoculating it with experimental animals.
At blood transfusion sites, methods based on reactions of fluorescent antibodies, as well as inhibition of gammaglutination, which are more sensitive, although not so specific, are used.
Good results and testMashad Guerreiro. It is based on the compliment binding reaction, that is, on the detection of antibodies to the parasite antigen. This analysis is extremely valuable in the chronic stage of the disease, when other methods are not particularly strong.
Treatment
Currently, such drugs already exist,with which you can completely defeat Chagas disease. Unfortunately, treatment is effective only at the initial stage, until trypanosomes penetrate vital organs. These are Nifurtimox and Benznidazole. They can be purchased in the USA and Latin America strictly according to the prescription. Prescribe these medications to patients with an acute form of the disease, children, during relapses, if the chronic form of the disease is not running. In the later stages, it does not help at all. Therefore, all the actions of doctors are focused on the treatment of complications - diseases of the heart, gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, thyroid gland and other organs.

Forecast
Many people, especially those with acutethe forms appeared apparent recovery, do not think about how dangerous Chagas disease. Meanwhile, about 50 thousand inhabitants of the planet die from it every year. At present, according to various estimates, from 15 to 20 million people are infected, but these figures are not entirely reliable, since the poor, among whom Chagas / Chagas disease is especially widespread, turn to doctors extremely rarely. The prognosis for this disease is favorable only in cases of early correct diagnosis and treatment. At the initial stage, if measures are taken in time, an absolute recovery is possible. It is no longer possible to recover in the later ones. It is also impossible to restore organs affected and destroyed by parasites. In the presence of a chronic disease, many patients die every year from acute heart failure, heart attacks, strokes, and other health problems caused by cruzi trypanosomes.
Prevention
To bypass Chagas disease, prevention is extremely important, since there is no vaccine against cruzi trypanosomes. For residents of dangerous regions, it is as follows:
- as closely as possible to inspect their homes for the detection of nests of bugs, if possible, sanitize insecticides in houses;
- if possible, erect canopies over the beds;
- observe hygiene.

- avoid visiting the jungle, especially in open summer clothes;
- critical approach to choosing a place to sleep;
- Do not be tempted by the overseas goodies for a snack offered by street and market traders (if you are not sure that the food was prepared in compliance with hygiene standards).
For sanitary and epidemiological services:
- to examine infants and older children whose mothers have had Chagas disease;
- reconstruction of dilapidated buildings;
- regularly carry out sanitation with insecticides of residential premises of citizens;
- screen blood donors and carefully examine donors.
There is a proposal to examine all emigrants,arriving from epidemic countries, which should prevent the spread of Chagas disease in other regions. However, given the high infection of animal Cruzi trypanosomes, the problem with the disease in the coming years is unlikely to be resolved.