Under the abbreviation OS it is common to understand twocompletely different concepts: fixed assets and operating systems. Since the title of the article does not specify something definite, we will consider both of them within its framework. Thus, the classification of the OS will be different depending on the object under consideration.
Criteria for classification of fixed assets
Let's start our article with the classification of the OS, which includes buildings, structures, machinery, inventory and other funds called basic.

The group division of the funds in question is used for the use and composition. Classification of the OS by groups is performed according to the following indicators:
- kinds;
- age and period of operation;
- branch belonging;
- functional purpose;
- ownership of property;
- influence on the subject of labor;
- degree of use.
Each classification group has an independent structure, in which the relevant subgroups are distinguished. Let us consider them in more detail.
Types of fixed assets
These include:
- buildings - buildings in which the activities of economic entities are carried out;
- structures - engineering structures with special. functions;
- machines and equipment - various devices belonging to an economic entity;
- tools - are the means of labor with the help of which the direct impact on the subject of labor;
- transfer devices are objects whose purpose is to transport or transfer the necessary energy, gas, suspensions, liquid and solid substances;
- transport means - the whole complex of equipment belonging to an economic entity;
- Inventory and supplies are necessary to provide the necessary labor conditions;
- other - all that is not included in the previous groups.

This is 1 classification of the OS by types. There is another subdivision of them - by depreciation groups, which will be considered below.
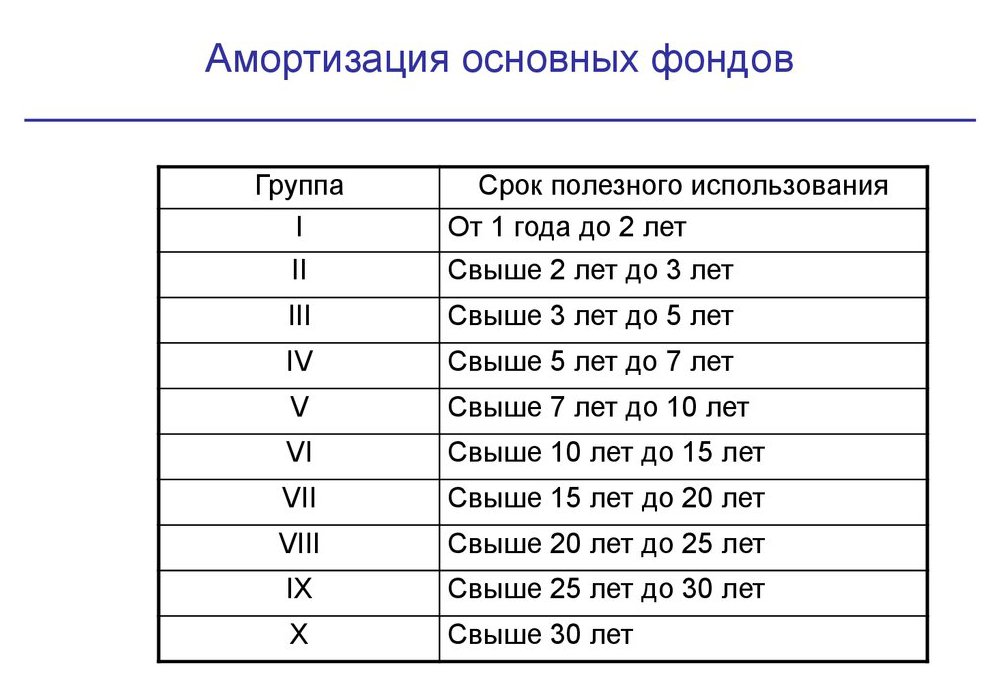
Classification by the period of exploitation
The above division of fixed assets into species is the main classification of the OS, on the basis of which others are built.
According to the section indicated in the section header, 5 groups of similar funds are singled out:
- up to 5 years;
- 5-10;
- 10-15;
- 15-20;
- more than 20 years.
The first two groups include machines and variousmechanisms belonging to an economic entity. The third of them includes special. facilities, as well as equipment and machines designed for long-term use. The last two groups include buildings and structures.
Classification by industry
OS refer to the industry as the products,produced with their use. So, motor transport can be used in various spheres of industry, and therefore its classification should be carried out within the framework of a specific economic entity.
Subdivision of performed functions
It includes the classification of the OS by designation. Within its framework, two groups are distinguished:
- Production, involved in the processproduction, through which the necessary conditions for its implementation are provided. They, in turn, are divided into 2 subgroups: agricultural and non-agricultural.
- Non-productive - employees to provide social and cultural infrastructure.
Classification by ownership of property
It can be owned and rented.The latter is taken into account separately, and there are also features of its operation. The first requirement is due to the fact that it is necessary to take into account the interests of the lessor, and the second - the fact that in the event of their breakdown, it is necessary to design repair and modernization procedures that are not necessary for own funds.

Classification of the impact on the subject of labor
Here, all fixed assets are divided intoactive, which directly affect the manufactured products, forming an assortment, quality and volume of production, and passive. They create conditions for it, but not directly involved in it. The same OS in some industries can act as active, and in others - passive.
Classification by degree of use
By this principle, all operating systems are divided into operating and non-operating. The former take part in the process of manufacturing products, while the latter do not, while they may be:
- for idle time;
- in the reserve - is typical for continuous production in order to quickly replace the failed equipment;
- at the stage of completion - typical for large structures;
- for conservation - for long-term storage of equipment, which can be put into operation immediately after withdrawal from this state;
- ready for start-up - those fixed assets that have completed acceptance tests that can be put into operation after carrying out preparatory work;
- decommissioned;
- intended for implementation.
Classification by depreciation groups
For all fixed assets on the balance sheeteconomic entity, it is envisaged to write off their value as they become depreciated by the value of the goods produced. There is a special document called "Classification of the OS, included in the depreciation groups." It is carried out by the useful life, the rate and its amount. Such a document was approved by the government of the Russian Federation in 2002.
Proceeding from this classification, the profit tax for economic entities is charged.
The classifier includes 10 depreciationgroups, for each of which the code of OKOF and its name is indicated, as well as notes, in which the purpose of the constituent OS is deciphered. Within their limits, subgroups are distinguished, which differ somewhat from the previously given division of the OS by species. These include:
- building;
- dwellings;
- constructions and transfer devices;
- means of transport;
- cars and equipment;
- cattle worker;
- perennial plantations.
Consider the depreciation groups within this classification (terms in months):
- This includes machines and equipment with a useful life of 13-24.
- This includes machinery and equipment, vehicles, household and production equipment, perennial plantations with a period of 25-36.
- This includes the same OS, except for perennial plantations, instead of which structures and transfer devices with a term of 37-60 are introduced.
- The perennial plantations are returned to this group, all are the same ones that were in the third group, additional buildings and working cattle with a term of 61-84 are added.
- Hence the exclusion of working cattle and perennial plantations, the rest are left unchanged, added to the OS, which are not included in other groups with a period of 85-120 months.
- This includes dwellings, vehicles, economic and production equipment, perennial plantations, structures and transfer devices with a period of 121-180.
- Hence, houses are excluded, buildings are returned, and OSs not included in other groups with a period of 181-240 are included.
- These include the same groups, among others, with a period of 241-300.
- Hence the inventory is excluded, the term is 301-360.
- This includes buildings, and dwellings, and perennial plantations, and structures with transfer devices, and vehicles, and machines with equipment, a period of more than 360 months.
Not all objects are included in this classification. More detailed levels are considered in the OKOF. Therefore, when using such a classifier, you first need to use the last document.
Have you made any changes?Until January 1, 2017, this classification could be used by the accounting department of economic entities. However, from that date such a model was excluded, therefore it is necessary to be guided by regulatory enactments in the field of accounting.
Thus, we considered all the main types of classification of the OS as fixed assets.
The concept of operating systems
In most cases, computers thatare established at the concrete economic subject, concern to the basic means. They can not work on their own. Provide their work, in addition to the technical stuffing, the appropriate operating systems. Therefore, consider the concept and classification of the OS, and now we will understand them as shells for PCs.

Under the operating system is understood the complexSoftware tools that have a specific interface to facilitate the interaction between the hardware of the computer and the user. First of all, let's look at the classification and functions of the OS.
The latter include:
- management of running applications;
- Data management;
- management of external devices;
- the organization of an interface that provides user interaction with the computer.
Thus, we have considered the concept of the operating system. To the OS classification we will pass below.
Indications of division
Classification of operating systems (OS) is carried out on the following grounds:
- By the features of the sequence of actions in the management of resources - network and local. The first take part in the management of network, and the second - the resources of the individual computer.
- By the number of users performingsimultaneous work - single and multi-user. Currently, the bulk of the OS refers to the latter form, which allows you to protect the information of individual users from others by distinguishing rights.
- For tasks performed simultaneously - one andmultitasking. With this software, not only the user interacts with the computer, files and peripherals through a user-friendly interface, which is typical for the first type, but also controls the resources used together.
- How to allocate time for workprocessor between several processes running in the system - not displacing and replacing multitasking. In the first case, action planning takes place in the OS. They function until they themselves transfer to the management system the right to choose another process, which is already ready for work. In the second - it is located between the OS and programs of an applied nature. The question of switching between processes is adopted by the system.
- By the kind of hardware they use - OS desktop (PC), clusters, servers, mainframes.

- By the presence or absence of multiprocessorprocessing - single- and multi-processor. The latter in the classification of operating systems (OS) are divided into asymmetric and symmetric, depending on the way the organization of the calculation processes. The first OS is completely executed on one processor, and the application tasks - on others. Symmetric systems are fully decentralized. In this case, all tasks are distributed among all processors.
- If possible, parallel computations in the performance of one task - the support of multi-threadedness.
- Depending on the respective platforms -mobile and dependent. In the first transfer to the new platform provides rewriting only dependent places. Mobile OS - in machine-independent languages.
- By the features of the spheres of application - the OS of real andtime sharing, and batch processing. The latter are used in such calculations, which do not require an instantaneous result, but have a high throughput. In OS with time sharing, each user has his own terminal for dialogue with a certain application. A small piece of CPU time is allocated to a particular task. Therefore, users who perform simultaneous work for such a computer, it seems that each of them works alone. The real-time OS is used when the execution of an object management program is limited in time.
- By construction, based on the use of the object-oriented approach.
- By the method of building the nucleus - micronuclear and witha monolithic nucleus. The first perform a minimum of administrative functions in the administrative regime. All other actions are performed in user mode. The system runs more slowly, but it is more flexible with the ability to modify functions. While monolithic systems operate in an administrative mode, performing quick transitions from different procedures, without requiring switching modes.
- On available application environments in one system. As a result, various programs that were developed for different operating systems can execute.
- By the distribution of functions among the networkcomputers. If the OS is distributed, then the user sees the network as a uniprocessor computer. The distribution system includes: the availability of help, which is unified in relation to the time service and shared resources, calling remote procedures for distribution on computers, multithread processing, and others.

Finally
Thus, the classification of the OS, whereThe latter are understood as the basic means, which are simpler than those with respect to operating systems. In either case, a multi-level subdivision is envisaged for different groups. However, the classification of operating systems is carried out on the basis of established characteristics. At the same time, with respect to fixed assets, one more classification is applied, defined by regulatory enactments.



