Structural features of the columnar leaf tissuedetermine the performance of its most important functions. Due to this, the vital activity of the whole plant organism is realized. In our article we consider the distinctive features of the anatomy and physiology of the columnar tissue.
Features of the internal structure of the sheet
In the plant, the columnar tissue is located in the leaf.How does this body work? Outside it is covered in skin. This type of integumentary tissue consists of densely adjacent living cells, among which are the stomata. Due to these structures, molecules of gaseous substances are introduced: oxygen - into the plant, and carbon dioxide and water vapor - in the opposite direction.
Under the skin are the main cellsphotosynthesizing tissue. They are large, loosely arranged, therefore, form the basis of the sheet. The conductive and supporting function is performed by the veins - a set of elements of conductive and mechanical tissue. Together they form vascular fibrous bundles.

Main leaf fabric
Основная ткань состоит из клеток двух типов:columnar and spongy. The latter are oval in shape, and in between the intercellular spaces are located. These structures take up to a quarter of a sheet. Elements of the main fabric with intercellular spaces form the basis of the sheet, store various substances, participate in gas exchange. The structural features of the columnar tissue make it the main photosynthetic leaf structure.
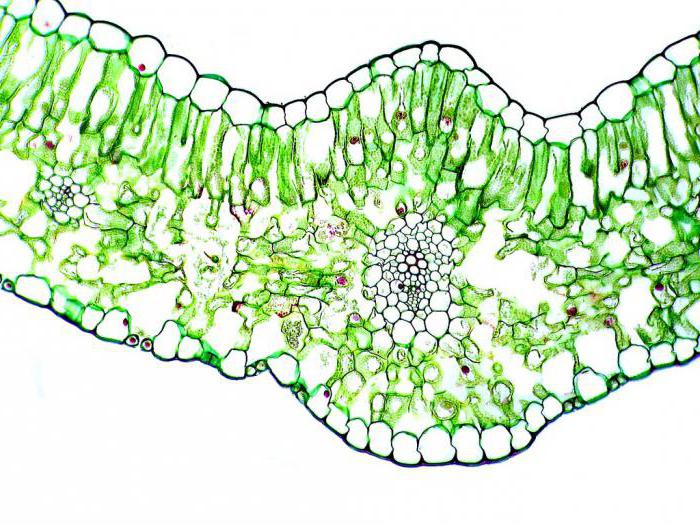
Pillars: Location
Picture of a columnar cell of leaf tissueillustrates the features of its location. It is located directly under the skin on the upper side of the leaves. The cells of this tissue, really resembling columns, can be placed in one or several rows. This arrangement is due to its main function - the implementation of photosynthesis. It is optimal for absorption of oxygen and sunlight.
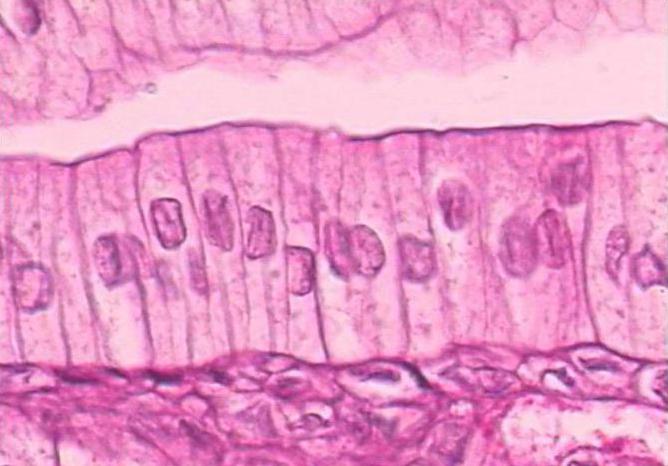
Features of the structure of the columnar fabric
Columnar is a type of primary tissue.plants. Its cells have a cylindrical shape, arranged vertically and tightly adjacent to each other. The number of layers of columnar tissue is directly dependent on the intensity of solar radiation. So, in the leaves of plants that grow in the light, there may be several of them. And in shade-tolerant species, this fabric is poorly developed.
Picture of a columnar cell of leaf tissuedemonstrates its main structures. This is a thin shell, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi complex, EPS. The central position and the main volume of the cell is occupied by the vacuole. This cavity, filled with cell sap, is a kind of reservoir for the supply of water and substances dissolved in it. Due to the presence of chloroplasts, the cells of the columnar tissue have a green color, giving it and the whole leaf.
Photosynthesizing may be different parts.plants. For example, in cacti, the leaves of which are reduced in the thorns, this function is performed by a fleshy stem. Many single-celled organisms are also capable of photosynthesis: chlamydomonad, euglena green, cyanobacteria.

Columnar: Functions performed
Columnar cells contain the greatest amountchloroplasts compared with other elements of the main tissue. Therefore, their main function - the implementation of photosynthesis. Its value is difficult to overestimate, so its scale is often called planetary.
This photochemical process takes place onthe inner membrane of chloroplasts, subject to the availability of sunlight, carbon dioxide and water. The products of this reaction is the monosaccharide glucose. His plant uses as a source of energy necessary for its growth and development. Connecting in chains, glucose forms a complex carbohydrate starch. Its granules are deposited in the cytoplasm in the form of inclusions.
The second product of the photosynthesis reaction isoxygen. This gas is a necessary condition for aerobic respiration, which is the main feature of all life on the planet. The essence of this process is the oxidation of organic substances with the release of the energy of their chemical bonds. The structural features of the columnar tissue provide the orientation of chloroplasts, which allows them to capture sunlight as efficiently as possible.
So, columnar fabric is a typemain. Its cells have an elongated cylindrical shape and are vertically arranged under the upper skin of the leaf. The function of the columnar tissue is due to the peculiarities of the structure: its cells contain green plastids and chloroplasts and allow photosynthesis to occur. This process of planetary value provides the main conditions of life. As a result, plants are provided with organic substances, due to which they feed, and all other organisms - with oxygen, necessary for respiration.