Each type of fabric has many characteristicsigns. They consist in the features of the structure, the set of functions performed, the origin, the nature of the updating mechanism. It is possible to characterize these tissues by several criteria, but the most common is morpho-functional belonging. Such a classification of tissues makes it possible to most fully and substantially characterize each type. Depending on the morphofunctional signs, the following types of tissue are distinguished: epithelial (integumentary), musculoskeletal muscular and nervous.
Structural features of epithelial tissue: common morphological and functional signs
To epithelium include a group of tissues, widelycommon in the body. They can differ in origin, that is, evolve from the ectoderm, mesoderm, or endoderm, and also perform different functions.
The list of common morphofunctional signs characteristic of all epithelial tissues:
1.They consist of cells called epithelial cells. Between them there is a thin intermembrane gap, in which there is no intercellular substance. It, in turn, contains a supramembrane complex (glycocalyx). It is through it that substances enter the cells and through it are removed from the cells.
2The cells of epithelial tissues are very densely located, which causes the formation of layers. It is their presence that allows the fabric to perform its functions. Methods of connecting cells with each other can be different: using desmosomes, gap or tight contacts.
3.The connective and epithelial tissues, which are located one under the other, are separated by a basement membrane consisting of proteins and carbohydrates. Its thickness is 100 nm - 1 micron. Inside the epithelium there are no blood vessels, and therefore, their nutrition is carried out diffusely, using the basement membrane.
four.Epithelial cells are characterized by morphofunctional polarity. They have a basal and apical pole. The nucleus of epithelial cells is located closer to the basal, and almost the entire cytoplasm is located at the apical. There may be clusters of cilia and microvilli.
5. Epithelial tissues have a pronounced ability to regenerate. They are characterized by the presence of stem, cambial and differentiated cells.
Different classification approaches
С точки зрения эволюции клетки эпителия formed before the cells of other tissues. Their primary function was to delimit the body from the external environment. At the present stage of evolution, epithelial tissues perform several functions in the body. According to this characteristic, these types of tissue are distinguished: cover, suction, excretory, secretory and others. The classification of epithelial tissues by morphological features takes into account the shape of epithelial cells and the number of their layers in the reservoir. So, single and multilayer epithelial tissues are isolated.

Characteristics of single-layer epithelium
Features of the structure of the epithelial tissue, whichcalled single-layered, are that the reservoir consists of a single layer of cells. When all cells of the reservoir are characterized by the same height, they are talking about a single-layer single epithelium. The height of epithelial cells determines the subsequent classification, according to which one speaks of the presence of flat, cubic and cylindrical (prismatic) single-layer single-row epithelium in the body.

Places of localization of single-layer cubicepithelium are ducts of the glands and tubules of the kidneys. The height and width of the cells are about the same, the nuclei are round and located in the center of the cells. The origin may be different.
Такой тип однослойной однорядной эпителиальной tissue, as a cylindrical (prismatic) epithelium, is located in the gastrointestinal tract, ducts of the glands, the collecting tubules of the kidneys. The height of the cells is much greater than the width. It has a different origin.

Characteristics of a single-layer multi-row ciliated epithelium
If a single layer of epithelial tissue formsa layer of cells of different heights, they are talking about a multi-row ciliated epithelium. This tissue lines the surface of the airways and some parts of the reproductive system (vas deferens and egg ducts). The structural features of this type of epithelial tissue are that its cells are of three types: short intercalated, long ciliary and goblet. All of them are located in a single layer, but the intercalated cells do not reach the top edge of the reservoir. When growing, they differentiate and turn into ciliate or goblet. A feature of the ciliary cells is the presence of a large number of cilia at the apical pole, the goblet cells are able to produce mucus.
Classification and structure of multilayered epithelia
Клетки эпителия могут образовывать несколько layers. They are located on top of each other, therefore, only the deepest, basal layer of epithelial cells has direct contact with the basement membrane. It contains stem and cambial cells. When they differentiate, they move to the outside. The criterion for further classification is the shape of the cells. This is how a multi-layered flat keratinizing, multi-layered flat non-keratinizing and transient epithelium is isolated.
Characteristics of multilayer flat keratinizing epithelium
Formed from the ectoderm.This tissue consists of the epidermis, which is the surface layer of the skin, and the final section of the rectum. Features of the structure of the epithelial tissue of this type are in the presence of five layers of cells: basal, spinous, granular, brilliant and horny.

The function of this fabric is to protect deep-lying tissues from external damage.
Features of the structure of multilayer flat nonthorogenous epithelium
Formed from the ectoderm.Localization sites are the cornea of the eye, the oral cavity, the esophagus and part of the stomach of some animal species. It has three layers: basal, prickly and flat. The basal layer is in contact with the basement membrane, consists of prismatic cells with large oval nuclei, slightly shifted to the apical pole. The cells of this layer, while sharing, begin to move upward. Thus, they no longer come into contact with the basement membrane and pass into the spinous layer. These are several layers of cells that have an irregular polygonal shape and an oval core. Spike layer goes into the surface - a flat layer, the thickness of which is 2-3 cells.

Transitional epithelium
Classification of epithelial tissuesprovides for the presence of the so-called transitional epithelium, which is formed from the mesoderm. Locations - the renal pelvis, ureters and bladder. The three layers of cells (basal, intermediate, and integumentary) vary greatly in structure. The basal layer is characterized by the presence of small cambial cells of different shapes lying on the basement membrane. In the intermediate layer, the cells are light and large, and the number of rows may be different. It directly depends on how full the body is. In the top layer, the cells are even larger, they are characterized by multi-core, or polyploidy, able to secrete mucus, which protects the surface of the reservoir from harmful contact with urine.
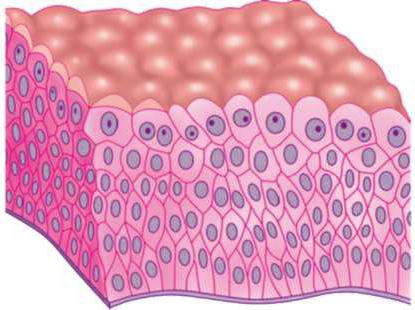
Glandular epithelium
Characterization of epithelial tissue was incomplete.without a description of the structure and functions of the so-called glandular epithelium. This type of tissue is widely distributed in the body, its cells are able to produce and secrete special substances - secrets. The size, shape, structure of glandular cells is very diverse, as is the composition and specialization of secrets.
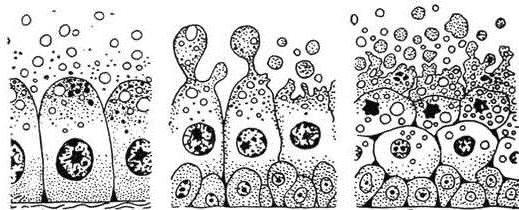
Особенности строения эпителиальной ткани, consisting of glandular cells, primarily due to its purpose. From this type of tissue, the formation of organs takes place, the main function of which is to produce a secret. These organs are called glands.