According to biology, fabric is a specialstructure that ensures the functioning of any organism as a whole. What features of the structure you need to have to perform such an important function?
What is tissue: biology will answer
According to the definition of the concept, the fabric representsa group of cells similar in structure and function. Not all living organisms are formed by similar structures. So, viruses are non-cellular life forms, and all bacteria are unicellular.
Groups of specialized cells allowcarry out all physiological processes more efficiently. That is why highly organized living objects consist of organs. This fact proves biology. Tissue is just a structure consisting of cells and forming organs.
Fabrics of plants
What is fabric made of? Plant biology shows that not only from cells. Between them there is an intercellular substance that acts as a link. Plant tissue is practically devoid of it.

They are represented by the following species:
1. Cover coat:
- peel - living tissue with special structures - stomata, which serve for gas exchange;
- cork is a dead tissue in which the metabolism is performed by lentils.
2. The main one - stores nutrients, carries out the process of photosynthesis, forms the basis of organs.
3. Mechanical - performs a support function.
4. Conductive - provides upward (water from the root) and descending (organic matter from the leaves) current of substances.
5. Educational - during division, it restores the cells of any affected tissue, carrying out regeneration.
Animal Fabrics
A distinctive feature of this group of cells is the presence of a large number of intercellular substance.
The following tissues are classified in animals:
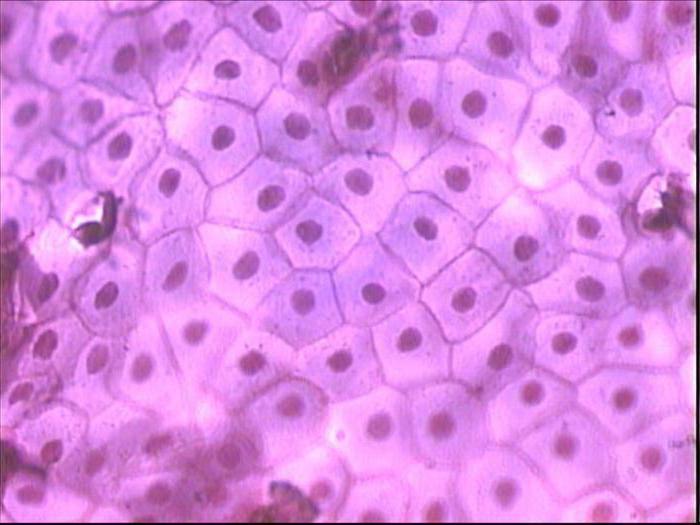
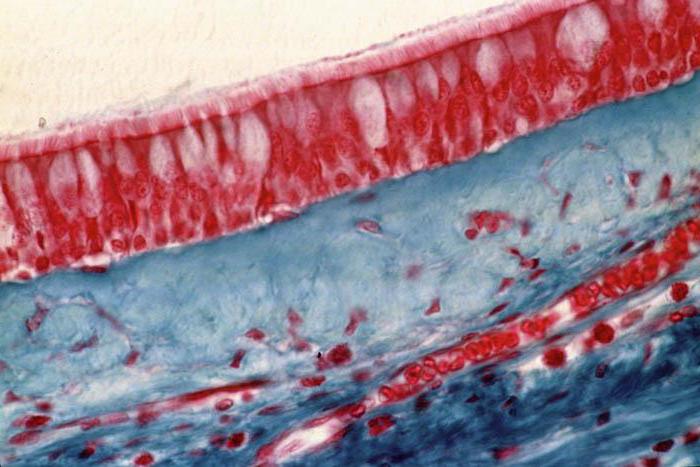
1. Epithelial - performs a protective function.It also forms glands and metabolizes. What is the formation of epithelial tissue? Its biology is simple: small, tight-fitting cells of various shapes.
2. Connecting - consists of large cells and a large number of intercellular substance. It is the basis of the whole organism. Its varieties are blood, bone, cartilage and adipose tissue.
3. Muscular - represented by individual fibers capable of contraction - myofibrils. Thanks to them, it is possible to move the body in space and the movement of individual organs.
four.Nervous - connects the body with the environment, determines the presence of conditioned and congenital reflexes. It consists of cells called neurons, and their processes - axons and dendrites. It is through them that information is transmitted from the receptors of sensory systems to the brain, and from there to the working organs.
The relationship of structure and function
But most importantly, according to the science of biology, tissue is a group of cells whose functions are due to their structure.

For example, small, closely spaced cellsepithelium, almost devoid of intercellular substance, like a shield. With such structural features, the function is obvious - protection. The connective tissue is completely different. Because it creates the foundation of all organs, there must be a lot of it. This explains the presence of large cells and a large amount of extracellular substance. Especially a lot of it in the blood. This substance is known to all under the name of plasma. It contains shaped elements. Red blood cells - red blood cells - transport oxygen from the lungs to the organs and carbon dioxide in the opposite direction. Platelets - blood plates, provide blood clotting. Leukocytes are colorless cells. They form an immunity by helping the body resist infectious diseases.
Fabrics and evolution
Biology did not immediately recognize what tissue is. After all, only with the invention of the light microscope a man discovered an amazing microscopic image of cells, and with it, tissues.
Lower plants, which include algae,tissues do not have. And even their multicellular representatives consisted of separate unspecialized cells, functionally unrelated to each other. Further, with the change of climatic conditions, the first vegetable migrants to the land appeared on the Earth. According to biology, fabric is a necessary condition for their survival in new conditions. Moss and moss appeared first with mechanical tissues necessary for their spatial arrangement. And after - and conducting. This development led to the formation of these organs: the root and the shoot.
In the most primitive multicellular animals alsono real fabrics. This is a representative of the intestinal type of the freshwater hydra. Her body is formed by specialized cells: epithelial, muscular, sex, skin-muscular, glandular, etc. But they do not form clusters, but are scattered throughout the body.
Thus, the appearance of tissues was the beginning of the complication of the structure of living organisms, allowing better adaptation to any conditions.











