Even in anatomy school course children are taught simplebiological patterns in the structure of living multicellular beings: the basis of everything is the cell. A group of them gives rise to tissues, which, in turn, form organs. The latter are combined into systems that carry out livelihoods, metabolic processes, and so on.
Therefore, what are tissues, their structure and functions,studied from the middle level of the school curriculum. Consider what types of tissues are found in the composition of the human body, what is the epithelial variety of these structures and what is its meaning.
Animal tissues: classification
Fabrics, their structure and functions, featuresdevelopment and functioning are of great importance in the life of all living beings who are capable of their formation. They perform a protective function, secretory, organ formation, nutritional, thermal insulation, and many others.
In total, there are 4 types of tissues characteristic of the structure of the human body and highly organized animals.
- Different types of epithelial tissue or integumentary (skin).
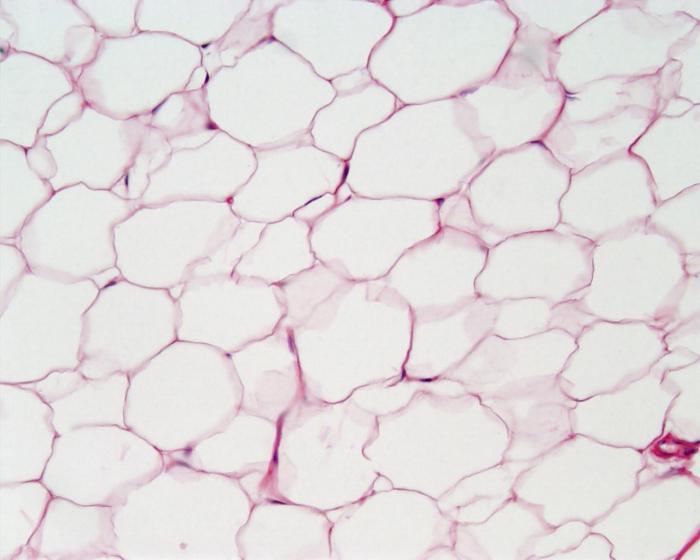
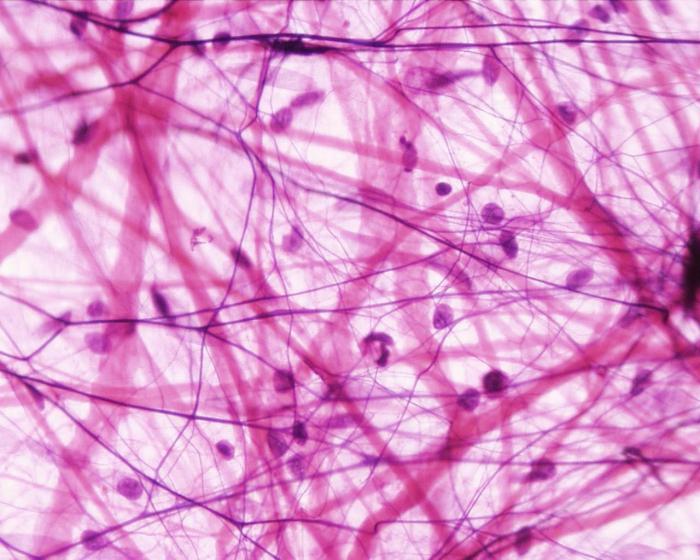
- The connective tissue is represented by several main varieties: bone, blood, fat and others.
- Nervous, formed by peculiar branched cells.
- Muscle tissue that forms with the skeleton the musculoskeletal system of the whole organism.
Each of the listed tissues has its own place of localization, method of formation and performs certain functions.
General characteristics of epithelial tissue
If you characterize the types of epithelial tissues in general terms, then you should select a few basic features that they all possess, each to a greater or lesser extent. For example:
- the absence of a substance between cells, which makes the structures tightly adjacent to each other;
- a unique way of feeding, which consists not in the absorption of oxygen from blood vessels, but in diffusion through the basement membrane from connective tissue;
- unique ability to restore, that is, regenerate the structure;
- cells of this tissue are called epithelial cells;
- each epithelial cell has polar ends, so all tissue ultimately possesses polarity;
- under any type of epithelium is the basal membrane, which is important;
- localization of this tissue is carried out in the body by layers or strands in certain places.
Thus, it turns out that varieties of epithelial tissue are combined by common patterns in location and structural organization.
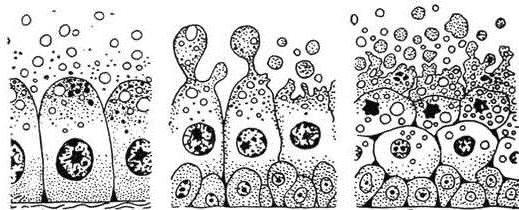
Types of epithelial tissue
They can be divided into three main ones.
- Superficial epithelial tissue.The epithelium of its structure is particularly dense, because it performs primarily a protective function. It forms a barrier between the outside world and the inside of the body (skin, external integument of organs). In turn, this type includes several other components, which will be considered further.
- Ferrous epithelial tissue. Glands, ducts of which open outwards, that is, exogenous. These include tears, sweats, milky, greasy genital.
- Secretory varieties of epithelial tissue.Some scientists believe that some of the nerve cells eventually pass into epithelial cells and form this type of structure. The main function of such epithelium is to perceive irritations, both mechanical and chemical, transmitting a signal about this to the appropriate authorities of the body.
These are the main types of epithelial tissue that are released in the human body. Now consider a detailed classification of each of them.
Classification of epithelial tissues
It is quite capacious and complex, as the structureEach epithelium is multifaceted, and the functions performed are very different and specific. In general, all existing types of epithelium can be combined into the following system. The entire epithelium is divided as follows.
1. Single Layer. Cells are located in a single layer and are in direct contact with the basement membrane, in contact with it. His hierarchy is as follows.
A) Single row, divided into:
- cylindrical;
- flat;
- cubic.
Each of these types can be borderless and beskemchatym.
B) Multi-row, including:
- prismatic ciliated (atrial);
- prismatic bezresnitchaty.
2. Multilayer. The cells are located in several rows, so contact with the basement membrane is carried out only at the deepest layer.
A) Transient.
B) Hornous flat.
B) Non-keen, subdivided into:
- cubic;
- cylindrical;
- flat.
The glandular epithelium also has its own classification. It is subdivided into:
- unicellular;
- multicellular epithelium.
At the same time, the glands themselves may be endocrine, excreting a secret into the blood, and exocrine, having ducts in the epithelium under consideration.
The sensory fabric of the structural unit division does not have. It consists of nerve cells transformed into epithelial cells that form it.
Single-layered flat epithelium
Got its name for the structure of cells.Its epithelial cells are thin and flattened structures that are tightly interconnected. The main task of such epithelium is to provide good permeability for molecules. Therefore, the main places of localization:
- alveoli of the lungs;
- walls of blood vessels and capillaries;
- lines the inside cavity of the peritoneum;
- covers serous membranes;
- forms some ducts of the kidneys and renal bodies.
The epithelial cells themselves are of mesothelial or endothelial origin and are characterized by the presence of a large oval nucleus in the center of the cell.
Cubic epithelium
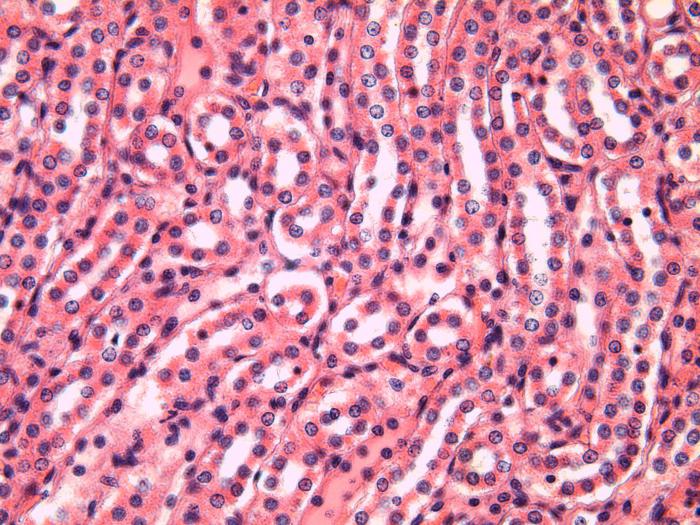
Such types of epithelial tissue as single-layer andmultilayer cubic epithelium, have a somewhat special structure of the cell in shape. For what, in fact, got their name. They are cubes of slightly irregular shape.
Single-layer cubic localized in the tubules of the kidneys and serves there as a permeable membrane. The nuclei in such cells are rounded, shifted to the cell wall.
Multiple cubic epithelium is located inas a series of deep layer in contact with the basement membrane. All other external structures cover it from above in the form of flat scales of epithelial cells. This type of tissue forms many organs:
- cornea;
- esophagus;
- oral cavity and others.
Prismatic epithelium single layer
This is one type of tissue, also called epithelial. Features of the structure, function due to the shape of the cells: cylindrical, elongated. The main places of localization:
- intestines;
- small and rectal;
- stomach;
- some tubules of the kidneys.
The main function is to increase the suction surface of the working body. In addition, the channels of specialized goblet cells that produce mucus open here.

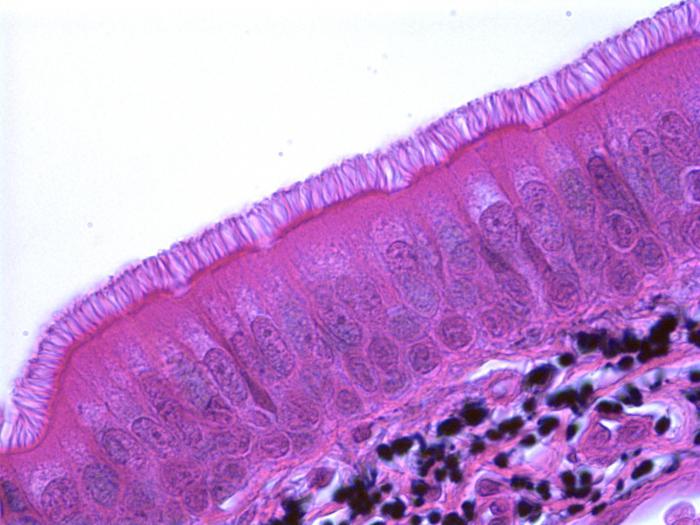
Types of epithelial tissue: single-layer multi-row
This is a type of surface epithelium.Its main task is to provide the external covers of the respiratory tract, which are lined with it. All cells are in close contact with the basement membrane, the nuclei in them are rounded, are located at unequal level.
The ciliated epithelium is named for the fact that the edges of the epithelial cells are framed by cilia. In total, there are 4 types of cells that are part of this structure:
- basal;
- ciliated;
- long inserted;
- goblet mucus-forming.
In addition, single-layer multi-row epithelium is found in the genital ducts and the corresponding system (in the oviducts, testes, and so on).
Multilayer transitional epithelium
The main distinguishing feature of any multi-layered epithelium is that its cells can be stem, that is, those that are capable of differentiation into any other tissue species.
Specifically, transitional epithelial cells are part ofbladder and associated ducts. Divided into three large groups, united by a common ability - to form fabrics with high elongation.
- Basal - small cells with round-shaped nuclei.
- Intermediate.
- Superficial - cells of very large size, most often in the form of a dome.
There is no contact with the membrane in these tissues; therefore, the food is diffuse from the connective tissue located under them of a loose structure. Another name for this type of epithelium is urotelium.

Multilayer nonthreshold epithelium
This type includes the epithelial tissues of the body that line the inner surface of the cornea of the eye, the structure of the oral cavity and esophagus. All epithelial cells can be divided into three types:
- basal;
- prickly;
- flat cells.
In organs they form strands of a flat structure. They are called non-threshold for the ability to exfoliate over time, that is, to be removed from the surface of the organ, being replaced by younger analogues.
Stratified squamous epithelium
Its definition can be as follows:this is the epithelium, the upper layers of which are capable of redistributing and forming hard flakes - corneas. Among all the surface epithelium, this one is the only one characterized by such a feature. Everyone can see it with the naked eye, because the main organ of this layer is the skin. The structure includes epithelial cells of different structures, which can be combined into several main layers:
- basal;
- prickly;
- grainy;
- brilliant;
- horny.
The last - the most dense and thick, is presentedhorny scales. It is their desquamation that we observe when the skin of the hands begins to peel off under the influence of adverse environmental conditions or old age. The main protein molecules of this tissue are keratin and filagrin.

Glandular epithelium
In addition to the coverslip,glandular epithelium. It is another form that epithelial tissue has. The considered tissues and their classification are very important for a correct understanding of the place of their localization and the functions performed in the body.
So, the glandular epithelium is very different fromcoverslip and all its varieties. Its cells are called glandulocytes, they are part of various glands. In total, there are two main types:
- exogenous glands;
- endogenous.
Those who throw their secrets directly into the glandular epithelium, not the blood, belong to the second group. These include: salivary, milk, greasy, sweat, tears, sex.
There are also several options for secretion, i.e. excretion of substances.
- Ekkrinovy - cells secrete compounds, but do not lose their integrity in the structure.
- Apocrine - after removing the secret partially destroyed.
- Holocrine - the cells are destroyed completely after performing the functions.
The work of the glands is very important and meaningful. For example, their function is protective, secretory, signaling, and so on.
Basement membrane: functions
All types of epithelial tissue are in close contact.at least one of its layers with such a structure as the basement membrane. Its structure consists of two bands - light, consisting of calcium ions, and dark - including different fibrillar compounds.
It is formed from the joint production of connective tissue and epithelium. The functions of the basement membrane are as follows:
- mechanical (keep epithelial cells together, while maintaining the integrity of the structure);
- barrier - selective permeability for substances;
- trophic - nutrition;
- morphogenetic - providing a high ability to regenerate.
Thus, the joint interaction of epithelial tissue and the basement membrane leads to a harmonious and orderly work of the organism, the integrity of its structures.
In general, not only epithelial tissue is very important. Tissues and their classification is considered at all levels of education related to medicine and anatomy, which proves the importance of these topics.