Tissue is a collection of cells unitedsimilar structure and functions, and intercellular substance. Organs are formed from tissues, which, in turn, form organ systems. Most multicellular organisms are composed of many types of tissue.

Diversity
The science that studies tissues (histology) distinguishes many of their types.
Types of animal tissue:
- connecting;
- muscular;
- nervous;
- integumentary tissue (epithelial);
Types of plant tissue:
- educational (meristem);
- parenchyma;
- cover fabric;
- mechanical;
- excretory;
- conducting
Each type of fabric combines several types.
Types of connective tissue:
- dense;
- loose;
- reticular;
- cartilaginous;
- bone;
- fatty;
- lymph;
- blood.
Types of muscle tissue:
- smooth;
- cross-striped;
- hearty
Types of educational fabric:
- apical;
- lateral;
- intercalary.
Varieties of conductive tissue:
- xylem;
- phloem.
Types of mechanical fabric:
- colechyme;
- sclerenchyma.
The varieties, structure and functions of integumentary tissue of animals and plants will be discussed in more detail below.

Features of the structure of the coating fabric. general information
The structural features of the covering tissue are due to its purpose. Although there are many varieties of this type of fabric, they are all similar.
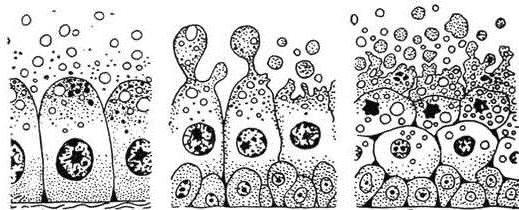
There is always a large number of cells and fewintercellular substance. Structural particles are located close to each other. The structure of the integumentary tissue also always provides for a clear orientation of cells in space. The latter have an upper and lower part and are always located the upper part closer to the surface of the body. Another feature, which is characterized by the structure of the covering fabric, is that it is well regenerated. Her cells do not live long. They are able to quickly share, due to which the fabric is constantly updated.
Functions of integumentary tissues
First of all, they play a protective role, separating the internal environment of the body from the outside world.
They also perform exchange and excretory functions. Often the coverslip has pores to ensure this. The last main function is receptor.
One type of integumentary tissue in animals, the glandular epithelium, performs a secretory function.
Plant cover tissues
There are three types of them:
- primary;
- secondary;
- additional.
The epidermis and the exoderm can be attributed to the primary integumentary tissues of plants. The first is on the surface of the leaves and young stems, and the second - at the root.

Secondary integumentary tissue - periderm. She covered more mature stems.
Additional surface tissue - peel, or ritidom.
Epidermis: structure and function
The main task of this type of fabric is to providePlant protection from drying out. It appeared in organisms as soon as they reached the land. Algae still have no epidermis, but it is already present in spore-bearing plants.
The cage of integumentary tissue of this type has a thickened outer wall. All cells fit snugly together.
In higher plants, the entire surface of the fabric is covered with a cuticle - a layer of wax cutin.
The structure of the covering tissue of plants providesthe presence of special pores - stomata. They are necessary for water, gas exchange and temperature control. The stomatal apparatus is formed by special cells: two closing and several side. Trailing cells are distinguished from others by an increased amount of chloroplasts. In addition, their walls are unevenly thickened. Another feature of the structure of the locking cells is a greater number of mitochondria and leukoplasts with spare nutrients.
The stomata of higher plants are located on the leaves, most often on their lower side, but if the plant is aquatic, on the top.
Another feature of the epidermis is the presence of hairs, or trichomes. They can consist of one cell or several. The hairs may be glandular, as, for example, in nettle.

Periderm
This type of integumentary tissue is characteristic of higher plants that have a stiff stalk.
Periderm consists of three layers. The middle one - phellogen - is the main one. When dividing its cells, the outer layer is gradually formed - fellema (cork), and the inner layer - felloderm.
The main functions of the periderm are plant protection.from mechanical damage, from the penetration of pathogens, as well as ensuring a normal temperature. The latter function is provided by the outer layer - felema, since its cells are filled with air.
Functions and structure of the crust
It consists of dead cells fellogen. Additional surface tissue is outside, around the periderm.
The main function of the peel is to protect the plant from mechanical damage and from sudden changes in temperature.
Cells of this tissue are not able to divide.The cells of other tissues inside are divided. Gradually, the crust stretches, thereby increasing the diameter of the trunk of the tree. However, this fabric has a rather low elasticity, since its cells have very hard keratinized shells. In this regard, the crust soon begins to crack.
Cover tissue from fauna
Types of integumentary tissues of animals are much more diverse than those of plants. Consider them in more detail.
Depending on the structure, such species are distinguished.integumentary tissues in animals: single-layer epithelium and multilayered. According to the shape of the cells, the first is subdivided into cubic, flat and cylindrical. Depending on the functions of the tissue and some features of its structure, there is a glandular, sensitive, ciliated epithelium.
There is another classification of the epidermis - independing on the tissue from which it is formed during the development of the embryo. According to this principle, epidermal, enterodermal, whole-nephrodermal, ependymo-glial and angiodermal epithelium can be distinguished. The first is formed from the ectoderm. Most often it is multi-layered, but it can also be multi-row (pseudo-multi-layered).
Enterodermal is formed from endoderm, itsingle layer Celonephrodermal formed from mesoderm. This type of epithelium is single-layered; it can be cubic or flat. Ependymaglial - a special epithelium that lines the brain cavity. It is formed from the neural tube of the embryo, is single-layer, flat. Angiodermal is formed from the mesenchyme, it is located on the inner side of the vessels. Some researchers attribute this tissue not to epithelial, but to connective.

Structure and functions
Features of the integumentary tissue of animals lies in the fact that the cells are located very close to each other, the intercellular substance is almost absent.
Еще одна черта – наличие базальной мембраны.It is formed by the activity of the cells of the integumentary and connective tissues. The thickness of the basement membrane is about 1 micron. It consists of two plates: light and dark. The first is an amorphous substance with a low content of proteins, rich in calcium ions, which provide communication between cells. The dark lamina has a large amount of collagen and other fibrillar structures that provide the strength of the membrane. In addition, the dark plate contains fibronectin and laminin, which are necessary for the regeneration of the epithelium.
Multilayer epithelium has a more complexstructure than single-layer. For example, the epithelium of thick areas of skin consists of five layers: basal, prickly, granular, shiny and horny. Cells of each layer have a different structure. The cells of the basal layer are cylindrical in shape, the spiny layer is in the shape of a polygon, the granular is rhomboid, brilliant is flat, the horny layer is dead scaly cells filled with keratin.
The function of epithelial tissue is protection.organism from mechanical and thermal damage, from the penetration of pathogens. Some types of epithelium have specific functions. For example, glandular is responsible for the release of hormones and other substances, such as earwax, sweat, milk and others.

Location of different types of epithelium in the body
For the disclosure of this topic, we present the table.
| Epithelium type | Location |
| Flat | Oral cavity, nasopharynx, esophagus |
| Cylindrical | The inner side of the stomach, intestines |
| Cubic | Kidney tubules |
| Sensitive | Nasal cavity |
| Ciliated | Airways |
| Glandular | Glands |
| Layered | Top layer of skin (skin, epidermis) |
Some of these species have specific functions. For example, the sensory epidermis, located in the nose, is responsible for one of the five senses - the sense of smell.

conclusions
Cover tissues are characteristic of both plants and animals. Secondly, they are much more diverse, have a more complex structure and perform more functions.
Cover tissues of plants are of three types:primary, secondary and additional. Primary are characteristic of all plants, except algae, secondary - for those, the stem of which is partially woody, additional - for plants with completely stiffening stem.
The integumentary tissues of animals are calledepithelial. There are several classifications of them: by the number of layers, by the shape of the cells, by functions, by the source of formation. According to the first classification, there is a single-layer and multi-layered epithelium. The second highlights flat, cubic, cylindrical, ciliated. The third is sensitive, glandular. According to the fourth, there is an epidermal, enterodermal, whole-nephrodermal, ependymo-glial and angiodermal epithelium.
The main purpose of most types of surface tissue in both animals and plants is to protect the body from any environmental influences and to regulate temperature.