The word "interval" is used in severalvalues. In music, intervals are consonances consisting of two sounds. The distance between them may be different. There are simple and compound intervals, enlarged and reduced (characteristic, tritons), harmonizing and dissonant, as well as melodic and harmonic. This will be discussed further.
Meaning of the word
Many researchers point out that the intervals areThese are some gaps, distances between something or breaks. For example, it may be a certain distance between military units or rows of troops. Also, this word characterizes the time interval.
In music, spacing is the ratio of heighttwo sounds. They can be taken alternately. Such intervals are called melodic. If the sounds are taken simultaneously, their names are harmonic.

Musical intervals
As mentioned above, the intervals - aconsonance, which consist of two sounds (two steps of the mode). The distance between them may be different. From one step to fifteen. The upper sound of the interval is called the peak, and the lower sound is called the bottom. There are melodic and harmonic, consonant and dissonant, simple and complex, enlarged and diminished (characteristic tritons).

The interval consists of two values:the first is the tone, the second is the step. The tone value determines how many tones in a particular interval. So, for example, in the example - zero tones, in the big second - one tone, in the minor third - one and a half tones and so on. The step value makes it clear how many steps a particular interval covers. So, for example, in a quart - four steps, regardless of whether it is clean, increased or decreased. That is, here the tone value already affects. If the quart is clean, then it should have four steps and 2.5 tones. If the quart is reduced, then there are four steps, but there will already be two tones. Accordingly, in the increased quarte the same number of steps, but three tones. We repeatedly speak of tone and semitone. Let us dwell in more detail on these concepts.
Tone and semitone
Tone - the distance between two adjacent sounds,consists of two semitones. Consider them exclusively on the white keys. These are sounds: do - re, la - si, re - mi, salt - la, fa - salt. Many teachers, explaining this topic to children, indicate that if there is black between two white keys, then this is the tone, and if there is no black key, then it is a semitone.
In music, a semitone is the smallest distance between two adjacent sounds. These are the remaining sounds: si-do and mi-fa.

Tones and semitones are built not only on whitekeys, but also in interaction with black. So, for example, b - c sharp and mi - sharp - this is already a tone. And here: re - e-flat, do - re-flat, la - b-flat, salt in a sharp - la, fa sharp - in a salt (and so on) are semitones.
Simple intervals
Not more than one octave. There are only eight of them. It:
- Prima Covers one step and contains zero tones.
- Second - the interval, which consists of two steps. It happens big and small. In a big second one tone, in a small one - half a tone.
- Third. Covers three steps. Just like a second, it is small and big. Small contains one and a half tones, and large - two.
- Quart. In this range, two and a half tones and four steps. It only happens clean.
- Quint.It covers five stages and contains three and a half tones. Just like a quart, it is clean. However, if there are three tones and four steps in a quart, then this is an increased quart. If there are as many tones and five steps in a quint, then this is a reduced fifth. Such intervals are also called tritons.
- Sexta consists of six steps. The big sixth contains four and a half tones. Small - four tones.
- Septima covers seven steps. Small Septim consists of five tones. Big - out of five and a half.
- Octave consists of eight steps. It only happens clean. Contains six tones.
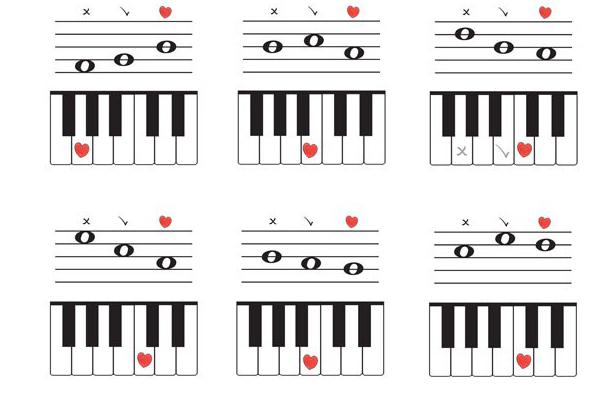
Compound intervals
The musical diploma for beginners contains information not only about simple intervals, but also about components. These are intervals that are more than one octave.
- Nona - consists of nine steps. Simply put, this is a second through the octave.
- Decima - contains ten steps. Accordingly, this is the third after the octave.
- Undetsim - consists of eleven steps. To build it, you need to rise from this sound to a quart through an octave.
- Duodetsim - covers twelve steps. This is the fifth after the octave.
- Tertsdetsim - contains thirteen steps. Accordingly, this is sixth sect one octave.
- Quartdetima - consists of fourteen steps. To build it, you need to go up a septim through an octave from a certain sound.
- Quintdecym - covers fifteen steps. This is a double octave.
After quintdetsimy intervals have no names.
Reversal intervals
Each musical diploma for beginnerscontains information not only about the intervals, but also about their treatment. And this, in fact, transferring the base (bottom sound) one octave up or the top (top sound) one octave down. In this case, the lower and upper sounds are interchanged.
Pure prima turns into a clean octave. A small second turns into a large septim. The big second becomes a small septim.
The small third turns into a great sixth. The big third goes into a small sixth. A clean quart is drawn into a clean fifth (and vice versa).
That is, pure ones go into pure ones, small ones - to large ones (and vice versa), increased ones - to smaller ones (and vice versa).
Consonance and dissonance
According to its sound, all harmonic intervals are of two types: consonant and dissonant.
Consonance is a consonant sound. It is associated with a calm state, it is characterized by a lack of aspirations. Consoning intervals are divided into:
- A very perfect consonance is pure octave and pure prima.
- Perfect consonance - fifth and fourth.
- Imperfect consonance - minor third and sixth, large third and sixth.
Dissonance is antagonism of consonance.To the ear, this is a sharper sound, inconsistent. The sound of dissonance in music is widely used to convey various human feelings: anxiety, tension, anxiety. Dissonances, like these agitated feelings, require compulsory resolution. That is, they all strive for consonance. Among the discordant intervals worth noting: a small and large second and septim, newts, characteristic intervals.
Monotone intervals
Music has an amazing ability -own our psychological state. Everything is abstract in it. The human mind in the whole stream of sounds recognizes the emotions and feelings, the inherent idea. Musical fabric is woven from tonal distances between sounds and chords. Many have heard of such concepts as gamma, the quint circle, modulation, and so on. However, not everyone knows what monotony intervals are.
Marina Korsakova-Krein (a neuropsychologist) conducted a series of experiments to identify the reaction of listeners to this or that music.
The essence of the first experiment was tostudy of the human response to different distances in various keys and frets. For another experiment, a major key was chosen and short and monotonic sequences were written. Monotony was necessary in order that listeners concentrated on the intuitive feeling of distances in tonal space. For the second experiment, the simplest chains of chords were used, as well as episodes of classical and romantic music.
Therefore, this topic is carefullyconsidered in the solfeggio class. Intervals have several meanings. These are: time interval, any distance, and also a break. In music, the interval is the distance between two sounds, which can be completely different. There are simple and compound intervals, enlarged and reduced (characteristic, tritons), consonant and dissonant, as well as melodic and harmonic. Simple intervals are within one octave. The compound intervals go beyond the octave. Consoning intervals have a pleasant sound. Dissociatives sound harsh and require permission.












