The management decision is the choice of one ofpossible alternatives. The choice is made on the basis of an analysis of the causes of the situation to be resolved. Responsibility for them is the most important management function. Methods of developing and making management decisions are diverse and not similar to each other. The task of the manager is to choose the appropriate method and apply it correctly.
Stages of management decision making
The manager before whom this or that arisesthe problem, should not rush headlong to solve it and should not grab one after another. The process and methods of making management decisions are interconnected, but when choosing any method of management theory recommends several steps of preparing and making choices. They can be divided into preparatory and final.
Preparatory stages
Algorithm of decision making:
- Identify the problem. At this stage, out of the total number of tasks facingorganization, select one specific, which is required to solve. At the same time, a deadline is set for solving the problem. You can not solve everything at once and you can not solve one problem forever.
- Record the facts. Here documented the conditions of the problem being solved, as well asThe reasons for this situation are determined. So that the problem does not recur again and again, the solution must be final and eliminate these causes.
- Search for solutions to the problem. Here менеджерами применяется все многообразие методов choice of alternatives. The main thing is to choose a particular method and not follow all the methods at once. The list of alternatives should be clear and final.
- Optimize the list of alternatives of action. Constriction списка до двух-трех альтернатив, удовлетворяющих conditions of sufficiency of material, human, financial and time resources. The stage is especially important in the case of collective selection. Beginning to discuss a variety of options will easily and permanently turn the meeting into an empty talker. Complicated and organization of the voting procedure.
Final stages
Sequence:
- Decision-making.
At this point, one of thealternatives, and the manager or collective body accepts responsibility for this choice. It must be documented, with deadlines, responsible and allocated resources. Sometimes, as a fallback option (the so-called “Plan B”), one of the shortlisted options is recorded. This is done in complex and emergency situations so that in case of failure of the main option, not to repeat the entire selection procedure, but immediately go to the solution.
- The implementation of the solution.
At this stage, the general plan of action formulated in the document is specified and detailed. The plan is executed, the results are reported to the manager or a collegial body.

Methods of developing and making management decisions
It also requires a systematic approach. Methods of theory of management decision making can be systematized:
- According to the composition of the group of persons making a choice - group and individual.
- By the approach used - intuitive and rational.
- According to the branch of science on which the method is based - social, probabilistic, economic, etc.
Any classification is conditional, the same byEssentially, a method can belong to several classes. The task of the manager is not to delve into the classification, but to select the appropriate methods of making management decisions. And in the end to choose the best.
Group methods
Group management decision making methodsimply the use of the synergy of several intelligences on the one hand and the distribution of responsibility on the other. Used in the work of collegial governing bodies. Can also be used in the sole exercise of the choice of the manager and used in this case as additional information.

The main expert management decision-making methods are as follows:
- Consensus. It consists in conducting discussions, negotiations and reciprocal concessions until all the members of the group (or their predetermined number) agree with this or that option.
- Voting. The variant that will be qualified by the majority of participants according to a pre-approved procedure is accepted.
- Delphi A series of closed anonymous expert polls is being conducted. The interaction of experts against each other is excluded as much as possible. It is applied subject to availability of sufficient time.
It should be remembered that the distribution of responsibility should be specified in advance.
Individual methods
They are as follows:
- Franklin method. It consists in comparing for each option pros and cons. Choose the option that gives the greatest benefits at the lowest cost of resources.
- Simple prioritization. Selection alternatives with maximum utility.
- Method first acceptable. Moved options until you find the first minimum acceptable.
- Concession to authority or "expert."
- Flipism, or at random. A coin is thrown, they consult with astrologers, etc.
- Decision support systems. Using software support solutions.

There are other, less common approaches.
Decision-making methods in terms of approach
Another classification of methods is based on the approach used:
- Intuitive. The manager acts on the basis of personal feelings and premonitions. In real life, a well-working intuition is a reflection of the unconscious experience of making past decisions.
- Common sense. The choice is made by analogy on the basis of available historical knowledge or personal experience.
- Rational methods. Based on a quantitative and / or qualitative analysis of the situation. It may be contrary to the experience accumulated by the individual or organization.
Mathematical methods for making management decisions
They belong to rational quantitative methods.Based on a mathematical model of a situation in which an organization exists and in which it is necessary to make a choice. Mathematical models and methods of making management decisions are many and varied:
- Game theory. Synthesis of military science and gambling.The method of strategic modeling of reciprocal actions of the adversary in the conditions of the external environment, which are sellers, buyers, competitors, etc.
- Queuing theory. Operational situational modelingresource allocation for the best customer service according to specified criteria. Examples: minimizing customer expectations in the queue of bank customers or machines at a gas station, equipment repair plan to minimize downtime
- Inventory Management. MRP II and ERP theory of operational planning of the order, supply and consumption of resources, optimization of inventory and the accumulation of finished products.
- Simulation. The behavior of a real system is predicted on the basis of studying behaviors under one or another influence of a model created with a certain degree of similarity.
- Linear programming models. Finding the best balance between resources and needs, also to optimize equipment utilization.
- Economic analysis. Основан на макро- и микроэкономике, описывающих market and individual enterprise behavior, respectively. It is used most often because it offers models and calculation algorithms that are simple and easily scalable under the conditions of a particular enterprise and market situation. The essence of this method is to determine the conditions for the economic profitability of certain actions in a particular situation.
- Balance method. It is based on the construction of material, financial and other balances and the study of the shift of their equilibrium point under certain managerial influences.
- Payment matrix Based on risk analysis and probabilistic methods. By assessing the likelihood of risks affecting the achievement of a goal, a solution is selected with a minimum amount of risks.
- Decision tree A schematic is built (in the form ofbranching tree) options with an indication of their financial (or other quantitative) indicators. By predetermined criteria, the optimal solution is selected, characterized by the maximum probability and the best indicators.
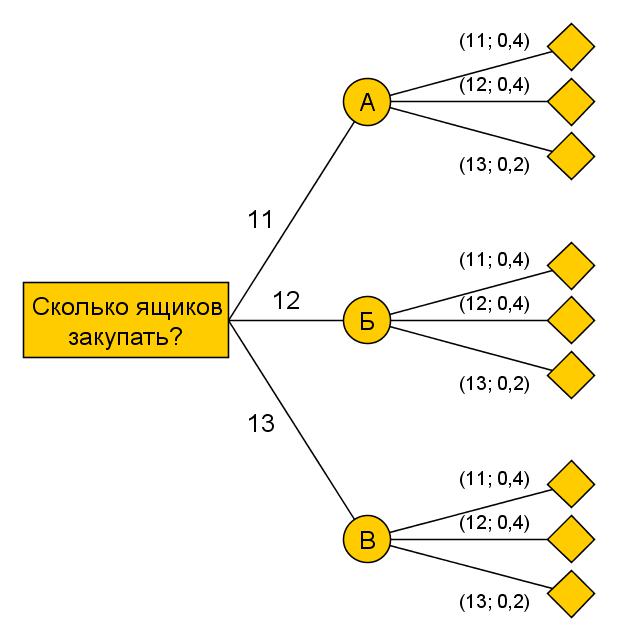
- Forecasting. It consists in predicting the direction of change of an object or situation on the basis of accumulated experience and current values of indicators, and in extrapolating these directions for the future.

The manager, as a rule, does not carry out calculations and analytical calculations personally. His role is to correctly set the task for analysts subordinate to him and to accept the result of the analysis from them.
Mistakes when making decisions
Many managerial errors stem fromwrong choice. If an error is detected in the early stages of implementation, then the chances of correcting it are high, and the costs of corrective actions are small. If the error is detected after the deadline, the opportunity to correct it is significantly reduced, and the costs, respectively, increase many times.

An erroneous choice of alternative is influenced by two groups of factors - internal and external to the manager who makes the choice.
Internal error factors
Determined by the properties of the individual who made the choice:
- Skills of understanding and processing data.
- Nuances of personal development.
- Individual or group value system.
- Motivation.
An example is:
- making a trivial decision;
- unintended fit of information to the expected;
- reliance on irrelevant past experience;
- unreasonable and excessive risk;
- procrastination (delaying the decision);
- incorrect assessment of the significance of this or that information, underestimation of resources, etc.
To minimize this negative impact,the head must develop the appropriate personal qualities, and above all the ability to make independent decisions. To do this, we need to develop critical thinking, focus only on those basic data that are crucial in a particular situation.
External error factors
Determined by the negative influence of the external environment:
- Falsely understood sense of duty.
- Audience influence.
- Lack of time.
- The impact of advertising.
- The influence of authorities.
A good manager is able to abstract from the negative effects of the external environment, focusing entirely on the situation and the upcoming choice.
Errors due to insufficient execution control
Sometimes the decision itself may be correct, but it is not possible to execute it and achieve the required results. Performance control is an essential management function.
The error may be hidden:
- in incorrect setting goals for performers;
- in the incorrect definition of criteria for achieving the goal;
- in the error in setting the deadlines.
The most dangerous mistake is wrong setting.goals performers. The correct goal must be measurable, achievable, time-bound and relevant situation (the so-called goal setting criterion S.M.A.R.T.).
How to avoid implementation errors

To minimize the risk of errors in the process of making and executing a decision, the manager should:
- Goal setting is carried out in accordance with the criteria of S.M.A.R.T.
- Clearly set selection criteria.
- Consider only relevant information.
- Observe the terms of the decision. To do this, choose the appropriate methods of decision-making.
- To exercise clear and unrelenting control of execution.
- It is thoughtful to appoint responsible, areas of responsibility and implementation dates.
Избежать ошибок также поможет обязательный этап analysis after the execution of the decision. Methods for analyzing management decisions are simple. It is necessary to determine how fully it is implemented, what was possible, and what could have been done better. Such an analysis will definitely come in handy in the future.
Manager's Role in Decision Making
При всем многообразии методов анализа ситуации и making a choice is his responsibility. The area of responsibility of the manager includes the choice of management decisions, management methods. Making management decisions - this is the very unique product produced by the manager. That is why he is paid a salary higher than that of his subordinates.
What methods of management decision makingchoose how to select information relevant to the situation, how to determine the criteria for achieving the result? For this, the manager will need both theoretical knowledge and the practical experience of many choices made. It is impossible to disregard and it is difficult to formalize, but an important factor that distinguishes all successful managers is luck. Historians of entrepreneurship call this a long chain of consistently taken right decisions that lead an enterprise or organization to success.


