Organisms whose body includes only one cell,relate to the simplest. They can have a different shape and all sorts of ways of movement. Everyone knows at least one name, which is the simplest living organism, but not everyone guesses that it is just such a creature. So, what are they, and what types are most common? And what are these creatures? Like the most complex and intestinal cavities, single-celled organisms deserve detailed study.

Unicellular kingdom
The simplest are the smallest creatures.Their bodies consist of a single cell, which has all the functions necessary for vital activity. So, the simplest single-celled organisms have a metabolism, can be irritable, move and multiply. Some have a constant body shape, while others constantly change it. The main component of the body is the nucleus, surrounded by cytoplasm. It contains several types of organoids. The first - all-cell. These include ribosomes, mitochondria, Galdzhi apparatus, and the like. The second is special. These include the digestive and contractile vacuoles. Almost all the simplest single-celled organisms can move without much difficulty. In this they help pseudopods, flagella, or cilia. A distinctive feature of organisms is phagocytosis - the ability to capture solid particles and digest them. Some may also perform photosynthesis.

How is unicellular spread?
The simplest can be found everywhere - in fresh airpond, soil or sea. A high degree of survival is provided by the ability to encystize them. This means that under adverse conditions, the body falls into a stage of rest, covered with a dense protective shell. Creating a cysts contributes not only to survival, but also to proliferation - so the body can be in a more comfortable environment, where it will receive food and the opportunity for reproduction. The simplest organisms carry out the latter by dividing into two new cells. Some also have the ability to sexual reproduction, there are species that combine both options.

Amoeba
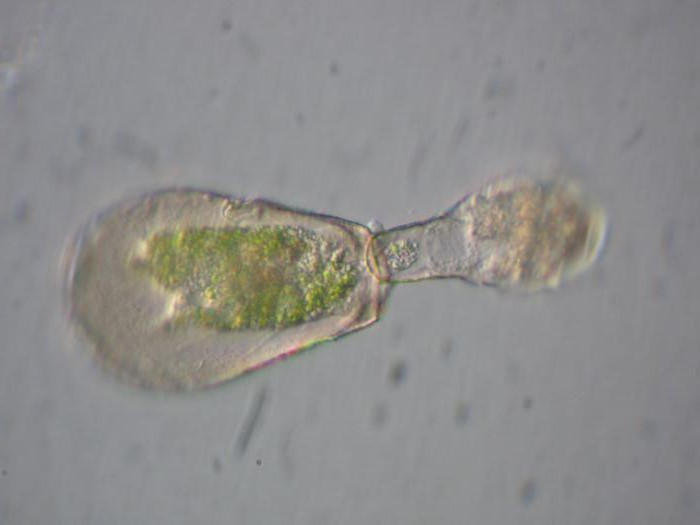
It is worth listing the most commonorganisms. The simplest are often associated with this species - with amoebas. They have no permanent body shape, and paws are used for movement. They amoeba captures food - algae, bacteria or other protozoa. Surrounding it with pseudopods, the body forms a digestive vacuole. From it all the substances obtained fall into the cytoplasm, and the undigested is thrown out. Breathing of the amoeba is performed by the whole body through diffusion. Excess water from the body is derived from the contractile vacuole. The process of reproduction occurs through the division of the nucleus, after which two are obtained from a single cell. Amoebas are freshwater. There are protozoa in humans and animals, in which case they can lead to a variety of diseases or worsen the general condition.

Euglena Green
Another organism found in freshwaterreservoirs, also belongs to the simplest. The euglena has a green spindle-shaped body with a dense outer layer of cytoplasm. The front end of the body ends with a long flagellum, through which the body moves. In the cytoplasm there are several oval chromatophores, in which chlorophyll is located. This means that in the light of the world, euglena feeds on autotrophic - not all organisms can do this. The simplest oriented with the eye. If euglena stays in the dark for a long time, chlorophyll will disappear and the body will switch to a heterotrophic diet with absorption of organic matter from the water. Like amoebas, these protozoa multiply by division and breathe with the whole body.
Volvox
Among the unicellular found and colonialorganisms. The simplest called Volvox live that way. They have a spherical shape and gelatinous bodies, formed by individual members of the colony. Each volvox has two flagella. The coordinated movement of all cells provides movement in space. Some of them are capable of reproduction. This is how Volvox daughter colonies arise. The same structure is different and the simplest algae, known as chlamydomonad.

Infusoria slipper
This is another common denizenreservoir. The name of the ciliate is obliged to form its own cage, resembling a shoe. The organelles used for movement are called cilia. The body has a constant form with a dense shell and two cores, small and large. The first is necessary for reproduction, and the second controls all life processes. The ciliate uses bacteria, algae and other single-celled organisms as food. The simplest ones often create a digestive vacuole; for shoes, it is located at a certain place at the mouth opening. Powder powder is present to remove undigested residues, and the selection is carried out using a contractile vacuole. Infusoria is characterized by asexual reproduction, but it can be accompanied by the combination of two individuals for the exchange of nuclear material. This process is called conjugation. Among all the freshwater protozoa, the infusorium is the most complex in its structure.
Single-celled in soil and seawater
In addition to the inhabitants of the fresh water, it is worthlist other types of protozoa. So, in the sea, organisms of radiolarians and foraminifera are most often found. The dead bodies of the former form the mineral deposits of opals and jasper. Foraminifera are distinguished by the presence of a shell of sand grains or calcium, and after death they form lime or chalk. Both are part of plankton. A variety of protozoa also inhabit the soil. They play a significant role in the formation of a new land. In addition, organisms can be parasites. They lead to the most dangerous diseases of people and animals. The most famous is malarial plasmodium, which is settled in human blood. Dysenteric amoebas can disrupt the colon. Trypanosomes carry sleeping sickness.