The subject of systematics science isclassification of living organisms. Bringing creatures into groups based on certain traits is of practical importance for their study. The main systematic categories of animals and the principles laid down in their classification will be discussed in our article.
Basics of animal classification
What is the sign of the variety of livingorganisms can i distinguish animals? On the only - way of nutrition. All animals, from the microscopic amoeba to the giant whale, are heterotrophs. This means that they feed only on ready-made organic substances and are not capable of producing them on their own.

The smallest taxon of animals is the species.This is a group of individuals that are united according to the principle of similarity of structure, physiology and ecology. This systematic category of animals has a double name. It was first introduced to science by the famous scientist Karl Linney. May beetle, migratory locust, polar owl - the first name is species. The second word defines the genus to which the animal belongs.
Systematic animal categories: table
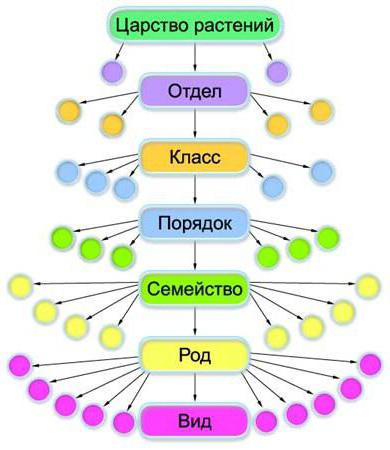
Systematic units are also called taxa.Species and genus are the smallest of them. The largest taxon is the kingdom. At the present stage, taxonomists distinguish them by five. These are plants, fungi, bacteria, viruses and animals. Their main difference is the way of nutrition and the particular structure of the cell. The sequence of systematic categories of animals is given in our table.
Taxon name | Example |
View | European cat |
Rod | Cats |
Family | Feline |
Order | Predatory |
Class | Mammals |
A type | Chord |
Kingdom | Animals |
Unicellular
Systematic category of animals thatare the simplest, combines single-celled organisms. All of them are eukaryotes. Their cell is a complete organism capable of carrying out all the processes of vital activity: nutrition, respiration, growth, reproduction, movement.

Typical examples of animals that belong to the single kingdom kingdom are the ameba proteus, euglena green, the infusorium of the shoe.
Multicellular
The body of the representatives of this systematicunits are not just formed by a multitude of cells. These smallest structures are similar in structure and function, which are consistently combined into tissues, organs and their systems. This systematic category of animals includes several types, the structure of which is consistently complicated. There are seven of them. The most primitive in structure are sponges. These organisms lead an attached lifestyle, feeding on filtering. Freshwater hydra, jellyfish and polyps are representatives of the intestinal type. They have specialized cells that do not yet form real tissue.

For the first time these structures appear in worms,which form several types of animals: flat, round and ringed. Moreover, the latter are characterized by the appearance of the circulatory system. The next type of multicellular animal is called mollusks. They have a soft body that is not segmented and often protected by a sink. The largest species diversity is the type of arthropods, which combines insects, crustaceans and arachnids.
Chord
This systematic category of animalsmost complex and has a general structure plan. This is the presence of an axial cord, or chord, of the neural tube and gill slits in the throat. Depending on the habitat, they are modified. Representatives of classes of chordates are known to all and are widely used by man in economic activity. These include typical aquatic inhabitants - fish, which are characterized by gill breathing. Amphibious animals live on land, and breed in water bodies. These are frogs, toads and frogs. Reptiles completely come to the land - crocodiles, lizards, snakes, turtles. And the birds conquered the air habitat. The most highly organized animals of chord type are mammals, of which man is a representative.

So, to the animal kingdom are living organisms, which are characterized by a heterotrophic type of food. Representatives of this systematic unit are combined into the following taxa:
- single-cell kingdom;
- subaccum multicellular.
The latter include sponges, intestinal cavities, flat, round and annelids, mollusks, arthropods, mammals.