Клетка — элементарная единица всех организмов.The degree of activity, ability to adapt to environmental conditions depends on its condition. The processes of cell activity are subject to certain laws. The degree of activity of each of them depends on the phase of the life cycle. In total, they are distinguished by two: interphase and division (phase M). The first takes time between the formation of a cell and its death or division. During the interphase period, virtually all the main processes of cell activity are active: nutrition, respiration, growth, irritability, movement. Cell reproduction is carried out only in phase M.
Interphase periods
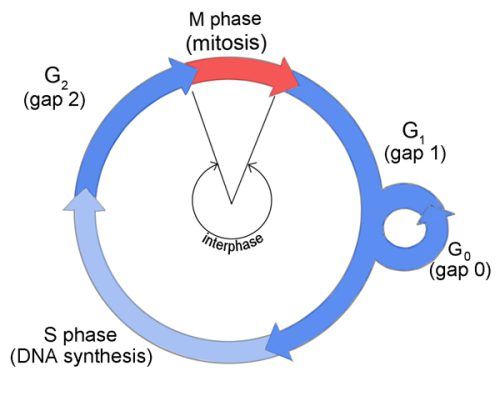
The time of cell growth between the divisions is divided into several stages:
- Presynthetic, or phase G-1, - the initial period: the synthesis of messenger RNA, proteins and some other cellular elements;
- synthetic or phase S: DNA doubling;
- postsynthetic, or phase G-2: preparation for mitosis.
In addition, after differentiation, some cells cease to divide. There is no G-1 period in their interphase. They are in the so-called resting phase (G-0).
Metabolism
As already mentioned, the processes of vital activityliving cells for the most part flow during interphase. The main of them is the metabolism. Thanks to him, not only various internal reactions take place, but also intercellular processes linking individual structures into the whole organism.
Metabolism has a specific pattern.The processes of cell activity are largely dependent on its observance, the absence of any violations in it. Substances, before affecting the intracellular environment, must penetrate the membrane. Then they undergo a certain processing in the process of feeding or breathing. At the next stage, the resulting processed products are used to synthesize new elements or transform existing structures. Remaining after all transformations, metabolic products that are harmful to the cell or simply do not need it, are removed to the external environment.
Assimilation and dissimilation
Regulation of sequential change of transformationssome substances involved in other enzymes. They contribute to the more rapid flow of certain processes, that is, act as catalysts. Each such “accelerator” affects only a specific transformation, directing the process in one direction. The newly formed substances are further exposed to other enzymes that promote their further transformation.
At the same time all the processes of cell activityone way or another associated with two opposing trends: assimilation and dissimilation. For metabolism, their interaction, balance or some opposition are the basis. A variety of substances from outside, are transformed under the action of enzymes in the usual and necessary for the cell. These synthetic transformations are called assimilation. At the same time for such reactions requires energy. Its source is the processes of dissimilation, or destruction. The disintegration of a substance is accompanied by the release of energy necessary for the main vital processes of the cell to proceed. Dissimilation also contributes to the formation of simpler substances, which are then used for new synthesis. Part of the decay products is displayed.
Cell life processes are often associated withbalance of synthesis and decay. Thus, growth is possible only with the predominance of assimilation over dissimilation. It is interesting that a cell cannot grow endlessly: it has certain boundaries, after which growth stops.
Penetration

Transport of substances from the environment tothe cell is passively and actively. In the first case, the transfer becomes possible due to diffusion and osmosis. Active transportation is accompanied by energy expenditure and often occurs contrary to the specified processes. Thus, for example, penetrate potassium ions. They are injected into the cell, even if their concentration in the cytoplasm exceeds its level in the external environment.
Characteristics of substances affect the degreepermeability to them of the cell membrane. So, organic substances get into cytoplasm easier, than inorganic. For permeability, the size of the molecules also matters. Also, the properties of the membrane depend on the physiological state of the cell and such environmental features as temperature and light.
Food
Intake of substances from the environmentfairly well studied processes of vital activity take part: cell respiration and its nourishment. The latter is carried out using pinocytosis and phagocytosis.
Breath

Nutrition is not the only process contributingthe appearance in the cell of the necessary elements. Breathing is inherently very similar to him. It is a series of successive transformations of carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids, as a result of which new substances arise: carbon dioxide and water. The most important part of the process is the formation of energy, which is stored in the cell in the form of ATP and some other compounds.
With the participation of oxygen
Human cell vital processes, likemany other organisms are unthinkable without aerobic respiration. The main substance required for it is oxygen. The release of much-needed energy, as well as the formation of new substances, occurs as a result of oxidation.
The breathing process is divided into two stages:
glycolysis;
oxygen stage.
Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose in the cytoplasm.cells under the action of enzymes without oxygen. It represents eleven successively successive reactions. As a result, two ATP molecules are formed from a single glucose molecule. The decay products then enter the mitochondria, where the oxygen phase begins. As a result of several more reactions, carbon dioxide, additional ATP molecules and hydrogen atoms are formed. In general, the cell receives 38 ATP molecules from a single glucose molecule. It is because of the large amount of stored energy that aerobic respiration is considered more efficient.
Anaerobic respiration
Для бактерий свойственен другой тип дыхания.They use sulfates, nitrates and so on instead of oxygen. This type of breathing is less effective, but it plays a huge role in the circulation of substances in nature. Thanks to anaerobic organisms, the biogeochemical cycle of sulfur, nitrogen and sodium is carried out. In general, the processes are similar to oxygen respiration. After the end of glycolysis, the formed substances enter into a fermentation reaction, which can result in ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.
Irritability

The cell constantly interacts with the surroundingby the medium. The response to the influence of various external factors is called irritability. It is expressed in the transition of the cell to the excitable state and the occurrence of the reaction. The type of response to external influence differs depending on the functional features. Muscle cells respond with contraction, gland cells respond with secretion, and neurons respond with generation of nerve impulses. It is irritability that underlies many physiological processes. Thanks to it, for example, nervous regulation is carried out: neurons are capable of transmitting excitation not only to similar cells, but also elements of other tissues.
Division

So there is a certaincyclic scheme. The life processes of the cell in it are repeated during the entire period of the interphase and are completed either by cell death or cell division. Self-reproduction is the key to the preservation of life in general after the disappearance of a particular organism. During cell growth, assimilation exceeds dissimilation, the volume grows faster than the surface. As a result, the vital processes of the cell are inhibited, deep transformations begin, after which the existence of the cell becomes impossible, it proceeds to division. At the end of the process, new cells are formed with increased potential and metabolism.
You can not say what processes of lifecells play the most important role. All of them are interrelated and meaningless in isolation from each other. A subtle and well-functioning mechanism of work that exists in a cell, once again reminds of the wisdom and grandeur of nature.