We face it daily and more than once.We can take an active part in it, and keep neutrality. She lies in wait for us at home, on the street, at work, in the store, in the transport ... Have you still not guessed what you are talking about? Not? Then let me imagine: her majesty is a speech situation! And we begin our acquaintance, of course, with vivid examples.

Speech situation: examples
Remember the Soviet lyrical comedy EldarRyazanov "Office Romance"? In one of the initial scenes, the unlucky, insecure senior statistician, comrade Novoseltsev, during a party from a friend, tries to “beat him up” after his boss, “heartless” and “callous” Kaluginoy-mymroy, but all his attempts fail. Why? There are many reasons for this, but one of them is trivially simple: the participants in this dialogue simply had a different vision of the question “what is the speech situation”. And now about everything in order.
Participants of the speech situation in practice
So, all sorts of speech communication situations beforetotal guess participants. They are major and minor. In our case, Anatoly Yefremovich Novoseltsev and Kalugina are the main participants, who are called the speaker and the listener, or the addressee and the addressee. During communication, their roles are constantly changing. This is typical for a dialogue, conditionally for a dispute, and it is impossible for an oratorical speech. The secondary participants in this speech situation are Samokhvalov and Ryzhova - close friends and colleagues of Novoseltsev, who mainly play the role of observers and advisers. It is considered that the observer is a passive position. However, this is not quite true. Even without participating directly in the dialogue, he can influence his course, which we see in the example described.

Relations
Now about the relationship between the parties.This is another important point on the topic "Speech situation and its components." Speaking about them, they first of all mean not the relations in the literal sense of the word, but the social roles of the speaker and the addressee. In the described case, the relationship between Kalugina and Novoseltsev is defined as “chief-subordinate”. However, there is no stability. It all depends on the conditions and circumstances. In a formal setting, at work, in the office, during business meetings, the business style should be emphasized. But if the “place of action” is transferred from the government cabinet to the usual home environment - to Samokhvalov’s apartment, there is a change of scenery: music, a festive table, guests ... In short, the situation becomes informal, respectively, social roles and communication style change.

Incorrect vision of the situation
But the "old woman" stubbornly ignores this, ignoresawkward attempts at courtship on the part of Comrade Novoseltsev, and in the midst of general merriment continue to maintain the official tone of business. It is not clear to her and the purpose of their forced communication. Urgency and perspective, as the main defining goals of business communication, are absent, which means there is nothing more to talk about. However, the timid, shy "senior statistician" - either from experienced fear, or from an accepted cocktail - also goes over the edges of what is permitted. After several challenging attempts to charm her interlocutor with her singing, reading poetry and dancing, without having received due recognition, he openly, in the presence of guests, calls Lyudmila Prokofievna “heartless” and “callousness”. Comic situation there. But this is, so to speak, a speech situation, examples. And what does the theory say?

The concept of "speech situation"
One of the sections of linguistics islingopragmatics. It is a science that studies the practical use of language, that is, how a person uses the word to influence the addressee, and what determines the characteristics of a person’s speech and behavior in the process of communication. And the speech situation in this case is precisely that basic concept of linguistic pragmatics, on the basis of which basic research is conducted. It consists of several components: the participants of communication, their relationship, the subject of communication, external and internal conditions of communication. The speech situation and its components were presented in detail by the example of a scene from the movie, so to speak, in practice. For a better understanding of the theory, you can use the scheme proposed by N. I. Formanovskaya and supplemented by T. A. Ladyzhenskaya. What is the speech situation and its components, clearly seen in the figure below.
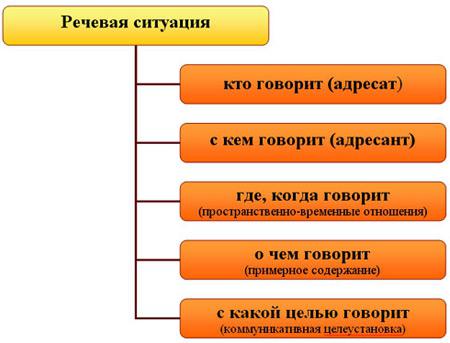
Addresser
As for the participants of communication, we think with thisThere can be no questions: the addresser and the addressee are the one who speaks and the one who listens. In other words, the addresser is the initiator of the speech situation, he is its active participant. It can be either speaking or writing, depending on how and in what form the communication takes place - written or oral (the sixth item in the “Speech situation” table). The scheme, as you can see, is quite simple. It is believed that the role of the addressee is often tactically advantageous, as it sets the theme, tone and pace of communication. He is the “director” of this action, which means that he has special rights: he directs the conversation in the right direction and, accordingly, can regulate its time frame.

Addresser
Однако, как говорится, всё в этом мире абсолютно and relatively simultaneously. Therefore, the role of the addressee in the dialogue is not always a passive position. During the conversation, the listener performs a number of such verbal and cogitative operations, such as:
- control of what is reported to him
- control of understanding
- generalization
- definition of concepts
- position adjustment.
All of the above points are realized withusing the obligatory reactive replicas: “Thank you for the information”, “Of course”, “In other words, you think that ...”, “If I understand you correctly ...”. By the way, every speech situation, be it acquaintance, greeting, congratulations, has its own specific set of stable phrases and expressions - this is the so-called “formula of the speech situation”. With these clichés, the addressee can seize the initiative and then act as a speaker.
The social nature of the relationship
Невозможно отрицать или преуменьшать значимость social roles of communicants. Imagine that a mother, having just had a warm conversation with her daughter at breakfast, an hour later, appears at school as a teacher of her child. Relationships are changing. In one case, they act as “parent-child”, in the other - “teacher-student”. Accordingly, both speech situations and their speech roles will be completely different. The one who does not understand or does not see the difference, does not control the situation, is doomed to inevitable problems.

Social roles can be permanent andvariables. The first are those that are determined by the sex of the participant, his age, kinship, and so on. The second, variable roles are those that determine the social status and social status of one communicator at the time of communication with respect to another: “teacher - student”, “leader-subordinate”, “parent-child”, etc. status are official and social position, merit, wealth.
External conditions of communication
The external conditions of communication include time and place.communication On the question of whether they are important and what role they play in the process of communication, we can use the remarks of the playwrights in the play as an example. The scene, time, lighting, description of the interior, the surrounding nature - everything that is “outside” will necessarily be reflected “inside” - in every word, sigh, phrase.
Depending on participationspace-time factor, canonical and non-canonical speech situations are distinguished (according to the “Russian language”, children write even abstracts on this topic). Canonical - when the addresser and the addressee are in the same place or, at least, they see each other, have a common field of view, and the time of pronouncing the utterance of one coincides with the time of perception of the listener. In other words, all participants in the speech situation are in direct interaction. As for the second option, here we see an absolute non-fulfillment of all the above conditions: the coordinates "I-you-here-now" are missing.

Internal circumstances
Motives and goals are also importantelements of the concept of "speech situation". Why do we speak? What is pronounced aloud that or another phrase? What are the intentions of all participants of communication? A goal is an invisible link between the speaker and the listener. No it - the connection is broken, and the speech situation ceases to exist. What can be the goals so that the thin thread does not disappear as long as possible? The first is the desire to inform, tell, describe, give an idea about something. The second is the inclination, the conviction of the listener to something with the help of evidence and arguments. Third - suggestion, change in the emotional state of the partner. Here in the course goes appeal not only to the mind, but also to the feelings of the interlocutor. Emotional leverage is used. Fourth - the impulse to action. In this case, the desired response is direct action. And the last - the maintenance of mutual positive emotions, the desire to please yourself and your partner by the process of communication.
Take, for example, the phrase:"I have an important business meeting." It can be used for the purpose of failure. You are planning an important event, and you cannot accept the invitation of friends to go to the cinema: “I have an important business meeting” (so I cannot go with you). Another verbal situation is a late commemoration of a close friend, another goal is an apology: “I have an important business meeting” (which I cannot miss in any way). This statement can also inspire colleagues at work, help them move things off the ground, hence the new goal - to instill confidence: “I have an important business meeting” (partners promise us new projects, new perspectives). As you can see from the examples, the same sentence may sound and be perceived differently. It all depends on the speech situation and the intentions of the speaker, conscious or unconscious.








