Cancer is a scourge of the XXI century, the farther it movesprogress, the greater the incidence of cancer. One of the new methods for the detection of cancer tumors - tumor markers. What is it and can you trust such an analysis?
What are tumor markers
The word marker comes from the English verbmark, which translates as "mark, mark something." A tumor marker is a generic name for a blood or urine test for traces, that is, "tags" that leave cancerous tumors in the body during nucleation, formation and growth.

Such tracks are specific proteins orenzymes and their breakdown products. Such proteins are produced either by the cancer itself or by the immune system as a reaction to oncological processes in the body.
Depending on the location of the tumor canto form different proteins. Accordingly, this means that tumor markers show where, possibly, a cancer tumor is located without an X-ray. That is why the analysis is used as a diagnostic method along with visual, such as ultrasound and x-rays.
Types of tumor markers and what they show
According to the standard, the varieties of tumor markers are more than 200. The most popular of them are the following:
- PSA (prostate gland);
- UBC (bladder);
- SA125 (ovaries);
- SA 15–3 (mammary gland);
- SA 19–9 (stomach, intestines, pancreas);
- SA 242 (intestine and pancreas);
- HCG (ovaries, testicles, uterus);
- AFP (cancer of the liver, gallbladder, ovaries, etc.);
- B-2-MG (cancer of the blood and lymph nodes);
- CEA (cancer embryonic antigen).
The brackets indicate the localization of the cancer,which indicates a specific tumor marker. As you can see, some point to a specific location, while others have a variability of diagnosis. Therefore, a combination of markers is often used. For example, if pancreatic cancer is suspected, SA 242 and SA 19–9 are immediately prescribed, and ovarian cancer - AFP, SA125, and hCG. But in any case, in case of deviation from the norm, complex diagnostics will be required.
When used to test for tumor markers
Assign them in the following cases:
- if a tumor that is not visible on visual examination is suspected;
- to control relapses;
- at risk of malignancy;
- with suspected metastases;
- in the preventive purposes, at hereditary and other risks;
- as part of a comprehensive diagnosis;
- control of treatment success, with a positive outcome, the concentration will begin to decrease.
It is important to understand that a single test for thyroid tumor markers, even cross-cutting, is not enough to exclude or, conversely, confirm the presence of a tumor.
Thyroid cancer
This type of cancer is quite rare,mainly in women and the elderly. The thyroid gland is an organ that produces many vital hormones. Lack or excess of which affects growth, mental development, metabolism and general well-being. The organ is located on the front of the neck and looks like a butterfly: the two lobes are connected by a thin isthmus. Because of its location close to the surface, it is quite often found at an early stage during palpation by the patient himself, for example, when washing.
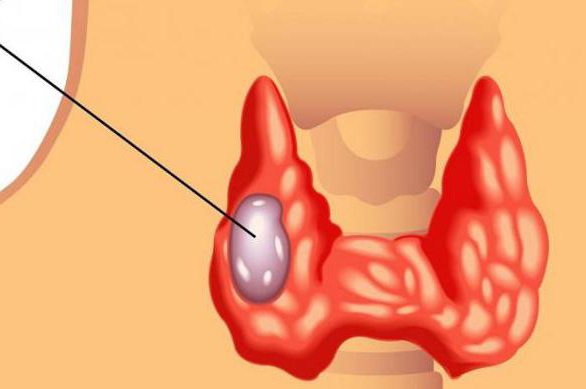
Thyroid cancer has 4 types:
- Papillary is about 75% among all malignant tumors in the thyroid gland. Prone to invasive invasions of neighboring organs and lymph nodes.
- Follicular - the second in particular type of thyroid cancer. The main reason is iodine deficiency. With this type of cancer, the tumor usually does not leave the limits of the thyroid gland.
- Medullary. It is very dangerous, the tumor with it practically does not accumulate radioactive iodine, which makes treatment with it ineffective.
- AnaplasticThis type is characterized by rapid growth and brightly flowing symptoms: hoarseness, coughing up blood, wheezing when breathing, weight loss and difficulty breathing. It is less common, but most dangerous.
Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
The following symptoms are considered signs of a tumor:
- hoarse voice;
- sharp fluctuation in weight;
- feeling of depression and loss of physical strength;
- pain when swallowing;
- unexplained fever;
- enlarged goiter

If there is at least one symptom, then it is alreadyto worry, and when there are two of them from this list, then you should definitely pass the diagnosis. As well as the diagnosis is regularly passed to those who have a history of the next of kin have tumors of the thyroid gland.
Diagnostic Methods
The most informative diagnostic methods will be the following:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- morphological examination (biopsy of a tumor fragment for cytological examination);
- blood test for tumor markers of the thyroid gland.
But separately, none of them for stagingdiagnosis does not apply. If a tumor is suspected when analyzing tumor markers, an ultrasound examination is necessary to detect the tumor itself and its exact location. If detected, a morphological study will be required to determine the degree of malignancy. And only then the diagnosis is made.

Равномерное увеличение размера указывает на pathological processes in the gland. Normally, the thyroid gland in women is no more than 19 cm³ and 25 cm³ in men. A cancer is characterized by an uneven growth, as seen on an ultrasound.
Ранняя диагностика заболевания может спасти the patient lives, because at the 1st and 2nd stages, the cancer is successfully treated, and the cases of healing at the 3rd stage are rare. At the 4th stage, doctors can do little, only prolong life and alleviate suffering.
Oncomarkers informative about thyroid cancer
Так какой онкомаркер показывает рак щитовидной glands? These tumor markers are hormones that are produced by the gland itself, if there is a tumor or other degenerative changes in it. These are hormones such as calcitonin and thyroglobulin. Additionally indicates tumor growth levels of cancer-embryonic antigen or abbreviated CEA.

Thyroid tumor marker calcitonin is produced by C-cells of the thyroid gland. It is indicative of diagnosing medullary type of cancer.
Thyroglobulin is produced by epithelialby cells. A blood test for thyroglobulin is indicative only for papillary and follicular cancers. In the event of a deviation from the norm, tests for the level of triiodothyronine and thyroxine (T3 and T4) will be indicative.
Each has its own specificity:
- The level of cancer and embryonic antigen increases at various locations of the cancer, including in the thyroid gland.
- The level of thyroglobulin usually increases with the recurrence of thyroid cancer.
- The hormone calcitonin rises in medullary thyroid cancer.
Preparation for analysis
For the most reliable results, it is recommended to fulfill the following requirements before taking the test for tumor markers of the thyroid gland:
- The analysis is done in the morning on an empty stomach. It is recommended to stop eating at least 8 hours before serving, but you can drink some water.
- 48 hours stop taking any medication and dietary supplements, alcohol.
- For 24 hours it is better not to eat spicy, salted and smoked.
- Do not overwork and do not be nervous if possible, during stress hormonal disruptions occur.
- For a week, stop taking hormonal drugs.
If any requirements cannot be met, then the laboratory technician should be informed about this, he will make a note. For example, refusal from regular intake of any medication is fraught with risk to life.

5 minutes before donating blood to the level of calcitonin, pentagastrin is administered to the patient for stimulation.
Rules for women and men
The amount of thyroglobulin in the blood of a healthya person usually does not exceed 10 ng / ml, but a slight increase is not terrible, since the rates are slightly higher. The norms of certain hormones, for example, calcitonin in men and women may vary.
Tumor marker | Norm in the thyroid gland in men | Norm in the thyroid gland in women |
Thyroglobulin | From 2 mg / ml, but not more than 20 mg / ml, according to other data the rate is up to 60 mg / ml | |
Calcitonin | 0.68–33 mg / ml, preferably closer to 8 mg / ml | 0.07–12.97 mg / ml |
Cancer embryonic antigen (CEA) | Not more than 5 ng / ml | |
Norms are not the same, they differ in different laboratories. But, even if you get a hands on analysis with deviations from the norm, you should not panic.
Statistics show that people often turn to laboratories bypassing the doctor, orienting themselves to the norms, but this is wrong. After all, as an isolated diagnostic method, it is useless.
But if this happened, the analysis should beevaluated by an oncologist, who will diagnose or disprove it by referring to an additional examination. It is worth remembering that in the presence of a tumor, the indicators are likely to be overestimated significantly, 10 or even 20 times. A small increase indicates more likely to malfunction of the thyroid gland.

About 10% of healthy people have elevatedindicators. During pregnancy, rates can increase significantly and this is normal, as various hormonal changes occur. After the end of breastfeeding, hormones should return to normal. With age and with inflammatory processes in the body, the indicators also increase.
Advantages of tumor markers before other diagnostic methods
Is it possible to trust the analysis for tumor markers, if so many factors can affect their accuracy? As with any method of diagnosis has its drawbacks and pluses, as well as a narrow focus.
Disadvantages of visual diagnosis:
- There is a risk that the tumor will not be detected, especially at an early stage.
- A small dose of radiation or electromagnetic radiation.
The only negative test for tumor markers, but serious, is unreliability.
If the method is perceived not as the only, butauxiliary, then all claims to him will disappear, analysis copes quite well in its area of responsibility. As a control for the resumption of growth of a remote tumor, analysis is indispensable. It also helps to control the effectiveness of treatment and the appearance of relapses after the removal of the tumor. But for prophylactic diagnosis is more indicative of ultrasound. There is a risk that the tumor has already begun to develop, and tumor markers will be negative.







