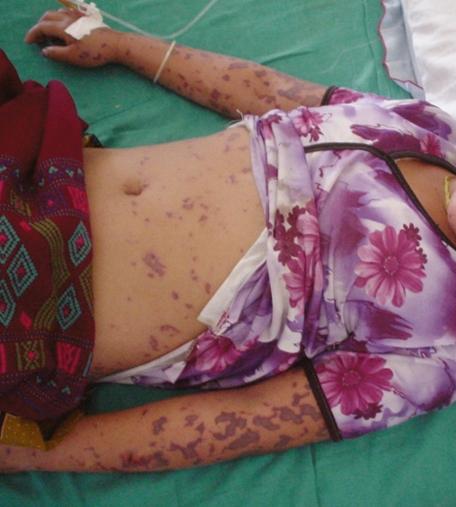
Meningitis is an inflammatory process,which is almost always triggered by an infectious agent in a membrane that covers the brain. Not all germs can cause this disease, but only those viruses, bacteria, fungi or protozoa that are particularly aggressive with respect to the structures of the central nervous system.
Bacterial meningitis: how can you get infected?
This inflammatory process is more common,than viral, proceeds harder and more likely to leave behind a variety of consequences. Depending on the route of infection, bacterial meningitis is of two types:

- a bacterium carrier, that is, a completely healthy person, in whom the bacterium “lives” in the nasopharynx;
- patient with meningococcal nasopharyngitis:in this case, a person may feel mild malaise, a slight fever, accompanied by sore throat and discharge of purulent snot;
- A patient with meningococcal meningitis or meningococcemia.
Please note: meningitis from a patient who suffers from the same disease can only be infected if it is caused by meningococcus.
2) If secondary meningitis is meant - ascan you get infected? By this term is meant a disease that has arisen as a complication of another purulent process. In this case, the infection penetrates the brain:
- from the ears - with purulent otitis;
- from the nasal cavity - with bacterial rhinitis;
- from the paranasal sinuses - with frontal sinusitis, sinusitis, ethmoiditis;
- with an open wound of the cranial cavity;
- With pneumonia, sepsis - spreads by blood.
Such meningitis is not contagious, it is impossible to “transfer” it to another.
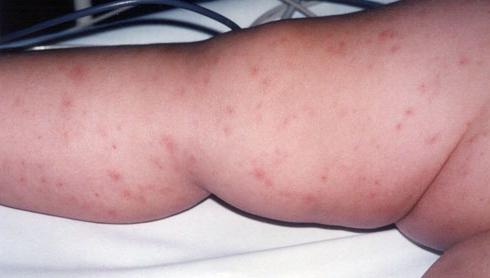
Viral meningitis: how can you get infected?
1) Airborne droplets: this is how the varicella-zoster viruses, herpes simplex viruses, and mumps enteroviruses “fly in”.
2) Through dirty hands and drinking insufficiently heat-treated foods. This is how enteroviral, adenoviral, some other meningitis arises.
3) The virus can be sexually transmitted: it mainly refers to the herpes simplex virus.
4) If a healthy person injures an element of the patient's rash and inflicts its contents on the skin (with an infection caused by the herpes simplex virus).
5) Some viruses can cross the placenta or pass through the birth canal, causing illness in newborn babies.
6) Other viruses are transmitted to humans by the bite of insects and arthropods.
Fungal meningitis: how can you get infected?
This type of disease rarely occurs in people withhealthy immune system. If it is found out that it was the fungus that caused the disease, you need to donate blood for the determination of antibodies to HIV, and if this test is negative (the person has not undergone chemotherapy and does not treat systemic hormone disease), it is necessary to examine the immunogram.
The incubation period of meningitis in children and adultsdifferent: it all depends on which microbe caused the disease. It usually takes from two to ten days from infection to the onset of the first symptoms (on average, 5-7 days).

How to protect yourself from meningitis?
- Observance of basic hygienic rules.
- Do not use common dishes and toothbrushes.
- Do not swallow water from the reservoir when bathing.
- Teach a child not to communicate with coughing, sneezing people and those who complain of fever. If necessary, wear a mask.
- Do not drink unboiled water and milk, look at the shelf life of products.
Since there are many different types of diseases, meningitis vaccination includes:
1. Vaccinations against measles, mumps, rubella, hemophilic infection - these are vaccines that are mandatory to be offered to all children.
2Vaccinations against meningococcus and pneumococcus are additional protection. If a child is often sick, is in a dispensary with a neurologist, then it is advisable before you take him to kindergarten, to consult with an infectious disease specialist about the need to make such a vaccination.
From other types of microbes that can cause meningitis, vaccines are not invented, so it is very important to learn to follow all the above rules for the prevention of this disease.