Inflammation of the membranes of the brain or spinal cordcalled meningitis. There are several types of meningitis. Given the nature of the inflammation, they can be purulent, serous-fibrinous, serous, and hemorrhagic. Adrift - acute, subacute, chronic. According to the localization of the inflammatory process, meningitis is generalized and local, according to etiology - viral, bacterial, fungal, protozoal. In the process of irritation of the meninges, intracranial pressure increases, hypesthesia appears, rigidity of the neck muscles, paresis and paralysis of the limbs, pupil dilation, impaired vision and hearing, ataxia, possibly strabismus.
Meningitis: symptoms, methods of treatment
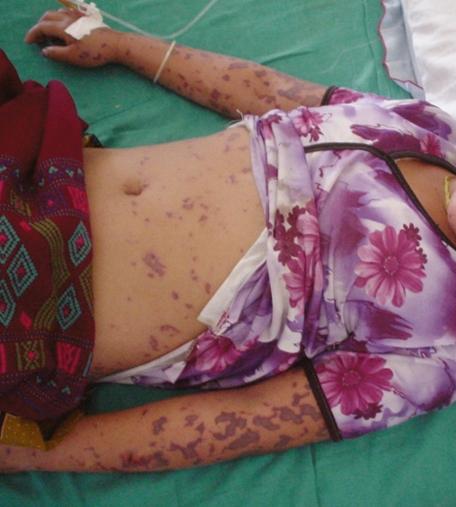
Generally, the disease has meningitis symptomsaccompanied by general depression, hyperthermia, headache, drowsiness, nausea and vomiting. Often, pain occurs in the neck and lower back, sometimes hemorrhages of various sizes appear on the skin. It should be noted that the disease meningitis symptoms depends on the type of the disease. For example, viral meningitis has symptoms similar to those of an infectious disease that provoked it. This type of meningitis is considered the most dangerous, the signs of the disease, which manifest themselves after a few days, are not very pronounced. As a rule, in patients with a diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis, symptoms occur against the background of general weakness and fever. For several days, headache, nausea and vomiting occurs. In patients with a diagnosis of meningitis, symptoms usually appear on day 3–4.
The therapy is symptomatic andIt aims to eliminate the main signs of the disease that are dangerous to human life and health. Diuretic drugs are used to reduce the amount of fluid in the cells and tissues of the body. The mechanism of their action is associated with increased urination, while they inhibit the reabsorption of sodium ions in the tubules of the kidneys, resulting in reduced water reabsorption. When edema of the brain are effective dehydration drugs (mannitol, urogluk, lasix). Urogluk is a lyophilized solution of urea, which is prepared before use. Contraindications to the use of the drug are kidney disease. The most effective anti-edematous drug is lasix, its action is manifested within a few minutes. It is proved that corticosteroid drugs (dexamethasone) have a decongestant effect. Approximately 12 hours after their use, a decrease in intracranial pressure occurs. For normalization of blood microcirculation use reopigluquine, mannitol, furosemide. In the presence of symptoms of toxic shock, hormonal preparations (hydrocortisone, prednisone, cortin, etc.) are used in combination with ascorbic acid, heart drugs (cordiamine, strophanthin), adrenergic mimetics (ephedrine, mezaton). Vaccines and serums are used as specific therapy. Young children are vaccinated against meningitis at 3, 4, 5 and 6 months with re-vaccination at 12 months. Vaccination against pneumococcal infection also protects against the development of meningitis. For patients older than sixty-five years, the use of pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine is recommended. Of particular popularity are complex vaccines against rubella, mumps and measles, their use protects the child from those meningitis that develops against the background of these diseases.
Prevention of meningitis
Кроме проведения вакцинаций, следует follow the rules of personal hygiene, avoid contact with the source of infection, as well as carriers of meningococcal infection. Some types of meningitis can be transmitted by droplets when sneezing, coughing or kissing. Personal hygiene items must be individualized (towel, toothbrush).