Meningitis refers to those diseases thatUnlike viral hepatitis or HIV infection, it is extremely difficult to get infected directly to a person from a person. In the role of a source of infection can act as a person, and an animal, and an insect, which is the carrier of some of the viruses that can potentially cause inflammation of the meninges. Meningitis with direct contact can develop only in one case: when it is caused by a bacterium, namely meningococcus. Let's see how meningitis is transmitted in each case

What causes the disease?
It can occur when it enters the brain:
1) a virus;
2) bacteria;
3) fungus;
4) unicellular pathogen;
5) mixed infection.
In order to hit the brain sheath, thisthe microorganism must have a specific structure, strong aggressiveness or get to the person in such quantity that will allow him to pass through all the protective barriers surrounding the brain. In addition, in order for the disease to develop, the human body must be either weakened, or its immune system is not sufficiently developed (which is why babies get sick more often than adults). Meningitis is more likely to develop for someone who has abnormal blood supply to the brain, suffered hypoxia during childbirth, or had a stroke at any age.
How do these pathogens penetrate the lining of the brain?
Virus can get:
- airborne;
- through the use of common toys;
- at the use of boiled water, dairy or other products;
- with kisses - when a person is ill with ARVI (provoked by a virus that can cause meningitis); he had acute herpes exacerbation; he suffers from mononucleosis or chickenpox;
- through insect or tick bites.

It would seem that the question:“Serous meningitis - how is it transmitted?” Is exhausted. But there is one "but": in fact, it is very difficult to get sick with viral inflammation of the lining of the brain when in contact with a patient who has such a diagnosis. That is, if someone from your family had contact with a child, a man or a woman who (who) was hospitalized with a diagnosis of “Serous meningitis of viral origin” a few days later, then you have a great chance that a similar viral disease will develop, but NOT meningitis. A child communicating with another child in the kindergarten who has developed measles meningitis has a great chance of getting measles and a very small one with the same measles meningitis.
Outbreaks of viral meningitis are often not related tocontacts of people in a close team or family, and with the use of food products (most often it is boiled water or milk) in which the active virus lives.
How is meningitis caused by bacteria transmitted?
Гнойный менингит можно «подхватить», если not enough, incorrectly or not to treat at all such diseases caused by bacteria, such as otitis, sinusitis, rhinitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, pneumonia, sepsis. This disease also occurs with a penetrating injury of the cranial cavity or spinal canal. These are secondary meningitis, which developed as a complication that occurs in adults in almost 90% of all purulent meningitis cases.

The only meningitis that reallytransmitted by airborne droplets - this is meningococcal. This disease can be transmitted exactly as meningitis from a patient with meningitis (not like for a viral reason: one suffers from viral diarrhea - the second gets meningitis from him). This disease is primary, children are more likely to get sick because they have a less mature immune system. Infection with a meningococcal infection of one of the children in the children's team may cause an outbreak of infection; there are frequent cases when all children in the family become infected with this disease.
How is meningococcus disease transmitted?
Meningitis is transmitted by airborne droplets. The source of infection can be a child or an adult who has:
- this bacterium is in the nasopharynx, while it does not bother him and he does not consider himself ill, generously “distributing” the bacterium over short distances (that is, through close contact);
- meningococcal nasopharyngitis (symptoms: low body temperature, pain, soreness or discomfort in the throat, mucopurulent nasal discharge);
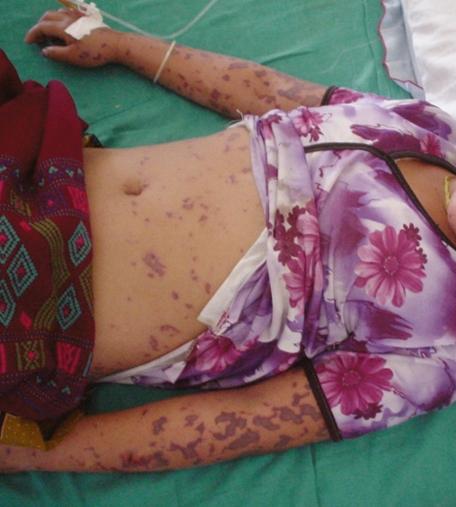
- generalized form of meningococcal infection:meningitis or meningococcemia; a rash that has a dark color and does not disappear when pressed with glass is not a mandatory symptom of this disease.
The bacterium is transmitted by airborne droplets over short distances, quickly dying in the air. It often infects children in a closed group (kindergarten or school) or children in the family.
How is fungal meningitis transmitted?
This type of meningitis is not contagious.It occurs mainly in those who have major problems with the immune system (congenital, acquired, HIV infection) or blood diseases. Less commonly, it can be “caught” after chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
What if you are afraid of contracting meningitis?
- Inoculate meningococcus and pneumococcus before the child goes to kindergarten. In addition, routine vaccinations protect against viral meningitis.
- Follow the basic rules of hygiene, as well as conduct sufficient heat treatment of products.
- Do not communicate with feverish, coughing and sneezing people (no matter what family they are) without a gauze or disposable mask; to teach this child.
- If you are worried about discomfort in the throat or a “mild” runny nose, while the discharge is yellow, contact the ENT and infectious diseases to exclude the meningococcal nature of the disease.
- Strengthen immunity by hardening, healthy lifestyle.
- Regularly drink multivitamins during the off-season, try to eat more vegetables and fruits grown in our area.
- To carry out appointments of doctors regarding this or that disease.
Now you know how meningitis is transmitted. Be attentive to your health.