The root, being the most important organ, performs a number ofirreplaceable functions and is rather various on features of a structure. Without it, the life of plant organisms would practically be impossible. In our article, the friable root system will be discussed in detail: which plants it develops, what characteristics it has and how it helps the organism adapt to the constantly changing environmental conditions.
What is the root
The root is an underground organplants. It is obvious that in plants it is not in the singular. Indeed, all the roots of one organism differ in appearance and developmental features. There are three types of underground part of plants: main, lateral and accessory. Distinguish them will not be difficult. The main root of the plant is always one. It stands out against the background of the others in size and length. On it grow lateral roots. They are quite numerous. And if the roots grow directly from the escape, then they are subordinate.

Functions of the root
Без корня растение погибнет, поскольку его functions are really vital. First of all, it is the fixation of organisms in the soil, the provision of mineral nutrition and the ascending current of water. If necessary, many plants form a modification of the root. For example, beets, carrots and radishes form root crops. This is the thickening of the main root. They accumulate water and a stock of necessary substances for experiencing unfavorable conditions.

Types of Root Systems
A root of one type is not enough for a plant.After all, the life of the whole organism depends on the functioning of this organ. Therefore, the root system is formed in the plant, consisting of several types of subterranean organs. They are more effective. The main types of root systems are pivot and fibrous. Their main difference is in the features of the structure. For example, the friable root system is distinguished by a small depth of penetration, and the pivot root, on the contrary, allows plants to receive water from considerable depths.

Core root system
The name of this structure is characterized byfeatures of its structure. It has a pronounced main root. This rod root system differs from the fibrous root system. Thanks to this, plants with this structure are able to extract water from a depth of several tens of meters. From the main root, lateral ones depart, which increases the suction surface.
The structure of the fibrous root system
The fibrous root system consists only ofroots of one type - the subordinate. They grow directly from the aerial part of the plant, so they form a bundle. Usually they are all the same length. And the main root at the beginning of development all the same grows. However, later it dies. As a result, only those roots that grow from the escape itself remain. Such a beam is, in most cases, quite powerful. Try to wrest the plant of wheat from the moist soil - and you will see that it is necessary to exert considerable strength for this. Sometimes on the additional roots can develop and lateral, which further increases the diameter occupied by this system.
Which plants have a fibrous root system
In the process of evolution, this structure for the first timeappears in representatives of higher spore plants - ferns, plaunids and horsetails. Since most of them have a body represented by an underground modification of the shoot, namely the rhizome, the accessory roots grow from it. This is a big step forward in the phylogeny of plant organisms, since algae and other spore representatives had only rhizoids. These formations had no tissues and performed only the function of attachment to the substrate.
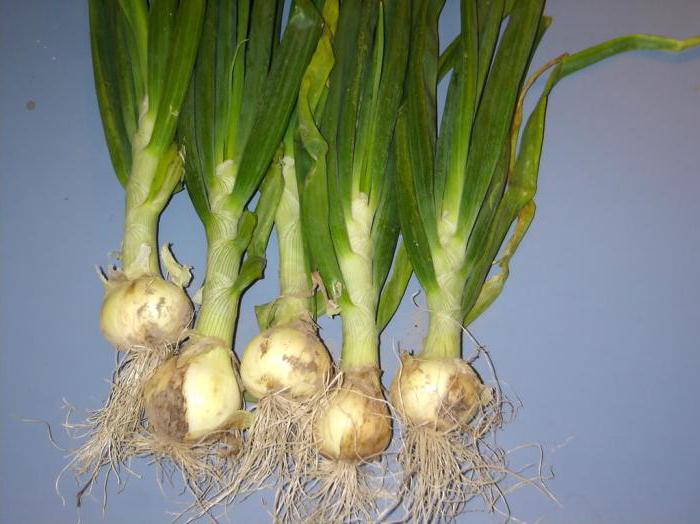

The friable root system is also found in all plants,which belong to the Monocotyledon class. Along with the absence of cambium, arc or parallel venation and other signs, this is their systematic feature. This class is represented by several families. For example, the Lily and the Onions are characterized by a characteristic modification of the shoot. It is a thickened underground stalk, in which water and all the necessary mineral substances are stored. It is called a bulb. From it and grow bunches of additional roots. Rice, wheat, corn, rye, barley are representatives of the family Cereals. For them, the urine root system is also characteristic. Examples of this structure are also dahlia, asparagus, sweet potato, chistyak. Their subordinate roots are largely thickened and become tuberiform. They also accumulate nutrients. Such changes are called root tubers. Support, respiratory, suckers and hooks also grow from escape. Therefore, they can also be considered a modification of the urine root system. For example, vines with the help of root-trailers can grow even on a vertical surface. And orchids absorb moisture directly from the air. This is done by subordinate respiratory roots. A special modification is formed in maize. These are the supporting roots. They surround the lower part of the stem and support a powerful shoot with heavy fruits-cobs.

Advantages and disadvantages of the fibrous root system
The fibrous root system has plants,which do not have to extract moisture from a considerable depth. This largely distinguishes it from another similar structure-the core structure. It has a well developed main root, capable of penetrating tens of meters deep into the soil. This characteristic feature for all plants of the Dicotyledon class. But the urine root system has advantages. For example, it can occupy a considerable area, which increases the suction surface. In wheat, the furry root system in diameter occupies up to 126 cm with a length up to the 120 mark. The degree of development of this structure completely depends on the environmental conditions. In loose soil in corn, the accessory roots can grow in a radius of 2 m, in apple trees up to 15 or more. At the same time, the depth of penetration is quite significant. At some weeds it reaches 6 m. Therefore from them so it is difficult to get rid. If the soil is dense, and the oxygen content in it is not enough, then practically all the additional roots are located in its surface layer.
So, the fibrous root system has a numbercharacteristic features. It is characteristic of plants of the monocots class: the cereal, onion, and liliaceae families. This structure consists of adventitious roots, which grow from the shoot beam, occupying a large area.












