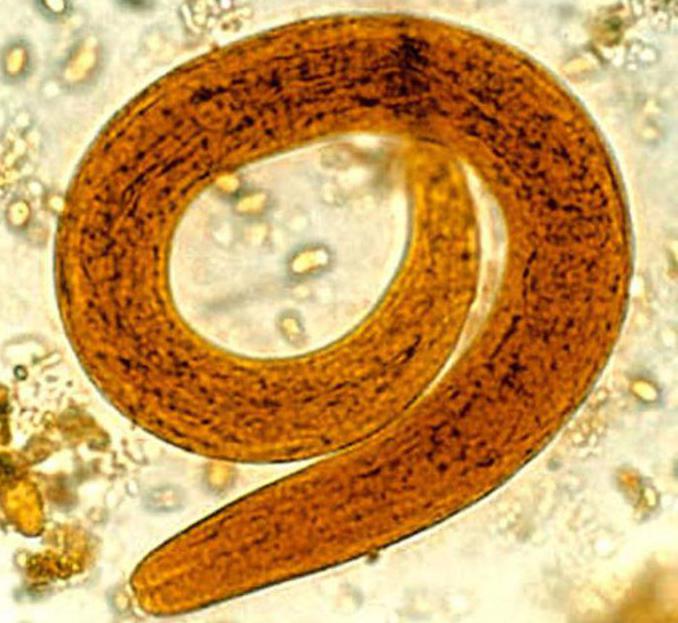
Flatworms are traditionally considered dangerous.helminths that cause significant damage to many animals and humans. However, these organisms have many progressive features of the structure, compared with the previous systematic units, and occupy their niche in the system of the organic world. From our article you will learn what bilateral symmetry is in flatworms, why some of them do not have the digestive system, and why they are an important link in the food chain.
Features of the structure of flatworms
A characteristic feature of flatworms is theirbody shape. It has the form of a sheet or ribbon. In this regard, these animals do not have a cavity, and the gaps between the organs are filled with a special type of connective tissue - the parenchyma. The concept of "bilateral symmetry" in flatworms is encountered for the first time, because another type of radiation is characteristic of the intestinal cavities.
A progressive feature is also the presence offormed organ systems. So, the musculoskeletal consists of a set of surface epithelium and the layer of muscles located under it. The digestive system is closed. The excretory system is represented by a system of tubules, which are expelled to the outside by pores. Due to the presence of the nervous system, flatworms have sense organs: sight, touch, balance and chemical perception. Most of these animals are hermaphrodites. This means that both male and female germ cells are formed in their bodies. But the respiratory organs flat worms are deprived. They carry out gas exchange with the entire surface of the body. Within the type, classes are distinguished: ciliated, tapeworms and flukes.

What is bilateral symmetry in flatworms?
In the process of evolution for the first time this featureit appears in worms of this type. And what does the concept of symmetry mean? This is the location of the individual parts of the body about the axis or center. The first multicellular animals, which include sponges, do not have symmetry at all. Growing on the substrate, they can form any shape.
Remember what a jellyfish looks like.In the middle of her body, you can put an imaginary point from which to draw lines in all directions. This is the radial, or radial, symmetry. It is characteristic of animals that live in the thick of the seas and oceans.
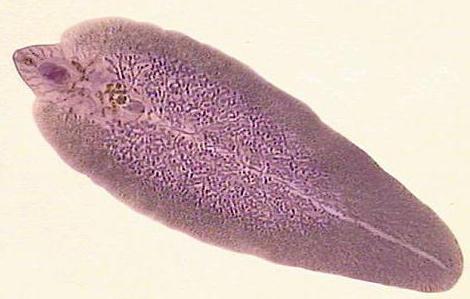
What is bilateral symmetry in flatworms?Pay attention to the photo. An imaginary line can be drawn along the body of the worm, which seems to divide it into two equal parts. This is bilateral, or bilateral, symmetry.
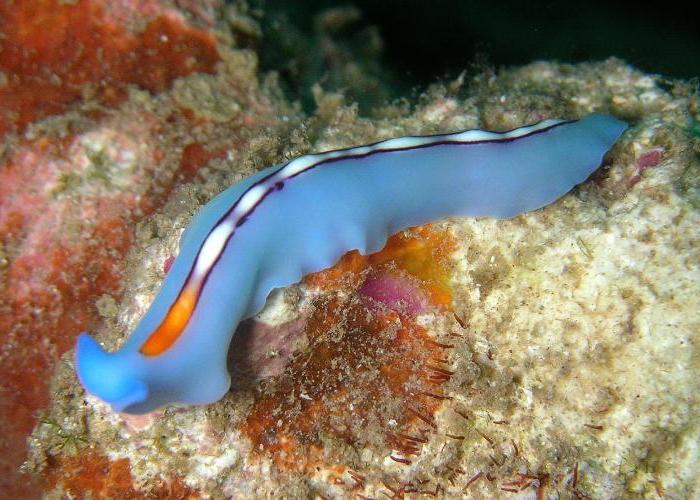

Features of bilateral symmetry
What is the reason for the emergence of a new type of symmetry?First of all - with a change in the lifestyle of organisms and the complexity of their structure. Bilateral symmetry is characteristic of animals that actively move in space. This allows them to move in a single line and rotate. Such organisms clearly distinguish the anterior specialized section of the body. It contains receptors for attachment and seizure of prey. Flatworms have formed organ systems. This is another progressive feature of their structure. The bodies of flatworms, like other animals with bilateral symmetry, are located on the sides of an imaginary line.
Ciliated worms
All worms of this class are free-living.by organisms whose size does not exceed 6 cm. The ciliated worms owe their name to the ciliary epithelium covering their body. They live in fresh, salty waters, forest litter. What is bilateral symmetry in flatworms is best considered just by their example, since their body has the shape of a fairly wide sheet, flattened in the dorsal-ventral direction. Ciliated worms are predators. They crawl all over the victim, holding it. Then a small proboscis appears from the mouth opening. With it, the worm sucks the contents of the victim. These organisms feed on smaller animals: crustaceans, hydras, insect larvae. Representatives of this class are dairy and freshwater planarians.

Flukes
But flukes are typical parasites.Their most common species is feline and liver. This name they received by the form of the final owner. Their body can reach 8 cm. With the help of the oral and abdominal suckers, they are attached to the internal organs of the host and feed on its tissues. Their development cycle includes a series of stages in which they change several hosts. So, the cat fluke develops in the body of freshwater mollusk and fish. Only after that the worm forms a mature individual, which is parasitic in the liver of dogs, wolves or cats.

Tape worms
Самыми гигантскими представителями этого типа animals are tapeworms. Their body consists of a small head with attachment organs, necks and segments. The number of the latter can reach several thousand pieces or tens of meters. Bovine and pork tapeworm, tapeworm wide, echinococcus parasitize in the lumen of the small intestine of many animals and humans. Therefore, tapeworms do not have organs of the digestive system. They absorb already split organic matter.
So, representatives of the type of flat have a number of progressive features of the structure. These include the appearance of bilateral symmetry of the body, which is associated with the formation of these organ systems.