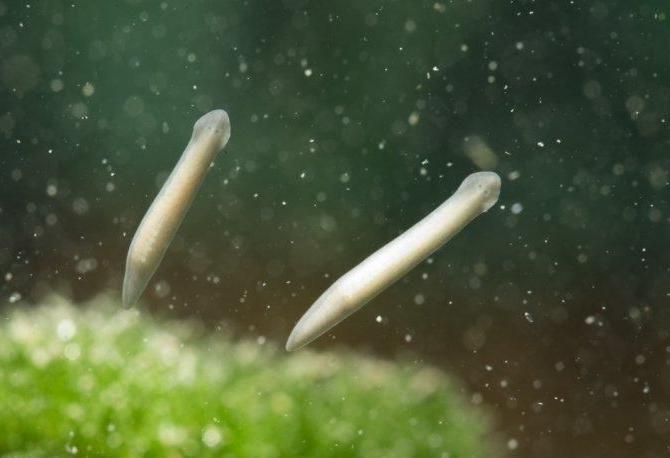
The White Planaria is a primitive creature thatable to dwell not only in fresh water, but also in salt water. The presented kind of flatworm does not harm either animals or humans. However, this creature also does not belong to the category of beneficial organisms. What is a planaria? The structural features of such a flatworm will be considered further.
What is planaria?

In freshwaters, at the very bottom, under pebbles andBy snags, you can find a miniature creature in the form of a flat white worm with a translucent body structure. Scientists classify such organisms as harmless parasites.
Visually, the planarian has both body surfacesare symmetrical and reflect each other. Despite the negative reputation of parasitic flatworms, such an animal does not pose any danger to other living organisms. Experts attribute planaria to predators that feed on simple organic compounds, small crustaceans, fish fry.
External structure planaria

Planaria has a bipolar body.The right side of the creature is mirrored in relation to the left. The conditional boundary line runs along the whole body. Such external structure of the white planaria allows it to live in conditions not only of water bodies, but also of land.
The length of the body of a flatworm is not more thantwo centimeters. Thickness can reach 5 mm. In front of the body, the planarium has a special extension, where the tactile tentacles are located. The back of the worm is narrowed and somewhat tapering at the end. Over the entire surface of the body are the so-called cilia, the movement of which contributes to the movement of the creature in space.
Internal structure of planaria

Planaria has the following internal structure:
- The muscle bag is specific fibers that run across the entire body. When shortened, the flatworm lengthens. The back and abdominal cavity of the animal are connected by longitudinal muscle fibers.
- Sense organs - tactile cells, paired tentacles, balance organ, primitive eyes, capable of reacting to light.
- Nervous system - nodes in the form of clusters of receptors, nerve branches.
- Excretory system - branched tubules that permeate the entire body of a creature.
- Digestive System - Special Cellsepithelium, which enable the flatworm to capture prey. Retractable pharynx is responsible for the absorption of food. Food is digested in a single-layer intestine. Waste is discharged outside, passing back through the mouth.
How does a planarium move?

So we reviewed the structure of the planaria. Now let's find out how this primitive animal moves.
Planaria crawls under water, moving alonghard objects. The flatworm moves extremely smoothly, evenly and slowly. Looking at the planaria in the aquarium, you might think that the animal swims in the water column without much effort. In fact, on the body of the worm there are a lot of mobile cilia that are invisible to the human eye.
Among other things, planarians emit specificmucus, with the help of which tracks are laid on objects for repeated movement. Small planarians are able to swim, performing paddle-like movements with cilia.
Lifestyle
Planaria are active in the dark. The flatworm hides under stones, snags, underwater foliage.
The creature carries a danger to shellfish. Planaria enter their respiratory system, which leads to the gradual death of the mollusk.
In the process of life planarii produce mucus, which swells in the water, forming a kind of webs. Due to this, the creature envelops its potential prey.
Development
Primitive creature despite its attitudethe category of parasitic flatworms is completely independent of other organisms. For the development of planarians are not required intermediate or final owners. On the contrary, close relatives of this creature, such as tsepny and flukes, parasitize in the body of animals and humans, without without it the possibility for development and reproduction.
Reproduction

Planaria is hermaphroditic. The creature is characterized by several methods of reproduction at the same time:
- Division - at the onset of the period of sexualThe activity of the flatworm's body is exfoliated. An adult individual is gradually divided into several parts. After some time, the mechanisms necessary for normal life are formed in both halves. As a result of such simple manipulations, one parasite transforms into several full-fledged individuals.
- Sexual - Mature Planaria lays eggson a fruitful substrate. For the fertilization of the clutch, flatworms touch their bodies for several moments. Thus, as a result of the connection of female and male germ cells, a zygote is formed. From it forms a cocoon, where the eggs remain until its full maturity. Usually the appearance of numerous young planarians takes from two to three weeks.
Interesting Facts
The simple structure of the planarian contributes to itsthe highest survivability. The body of a flatworm has regenerative abilities. Even after the head is separated from the body, a new one gradually grows in its place. If you divide an adult into separate pieces, over time, the original organism can recover from them. This feature contributes to the survival of planaria in the most adverse conditions.
The specific structure of the planarian gives herable to withstand aggressive environmental factors. For example, when there is a lack of oxygen for breathing and a rise in temperature, the creature changes to a low-active form. In the future, planarians are able to independently break up into separate pieces. The latter are regenerated upon the occurrence of favorable conditions.
Planaria are extremely sensitive topotential mining. With a lack of food in the habitat, flatworms sense nutrients at a considerable distance. Having tasted the food, the colonies of the planarians crawl out of their own shelters and move by the hundreds to the places where the prey is located.
Planarium content in aquariums

Despite the gentle structure of the planarian, softnessexternal covers, such a creature can be kept in an aquarium. And the flatworm is not able to harm the other inhabitants of an artificial reservoir. As noted above, planaria in the process of vital activity produces an abundance of rather unpleasant mucus. Therefore, even large fish such creatures do not like. Smaller predators who have decided to attack planarians are enveloped in a sticky substance and lose their movement, while remaining in a paralyzed state.
Planaria in the aquarium does not need a special feed. It feeds on the creature waste products of other animals, decaying debris, particles of dead plants.
Finally
Here we consider the internal as well as externalstructure of flatworms. Planaria due to its lifestyle is a harmless parasite. Throughout life, such a flatworm does not require a host. Unlike its parasitic counterparts, the represented creature is capable of independently obtaining food in natural habitats.