There are millions of different kinds of organisms.Of these, only non-cellular forms of life are viruses. All the others have their own smallest, but the main structural unit. Therefore, it is an important indicator of the individuality of the being, belonging to this or that kingdom of living nature. The parts and organoids of a cell can explain how the organism lives and grows, what processes inside it occur. Knowledge of the structure of a given structural unit is important for understanding the entire wildlife as a whole.

General plan of cell structure
Cell under a microscope - sight is enoughInteresting. It's amazing how much everything is hidden from the human eye and exists at the level of the microcosm! With the invention of this unique optical instrument, it became possible to become part of this level, to study and understand its life mechanisms, to learn how to interfere with them and use it for the benefit of people.
Thus, it was found that not all organisms haveidentical units of structure. Almost every representative of the kingdom has differences. For example, the main parts of the plant cells are different from those in animals. The features of the structure of bacteria and fungi. However, it is still possible to single out general principles of cell structure.
- Genetic material in the form of DNA molecules (for eukaryotic organisms - plants, fungi, animals - is concentrated in the nucleus, prokaryotes (bacteria) have no nucleus).
- A cytoplasmic membrane that delimits internal contents from external space and effects.
- Cytoplasm with organoids and inclusions.
Many organelles are also the same forall cells, which once again confirms the unity of the origin of all life on our planet. There are a lot of structural parts in each living unit. We are talking, for example, about:
- mitochondria;
- lysosomes;
- the Golgi apparatus;
- EPS (endoplasmic reticulum or reticulum);
- ribosomes;
- inclusions of protein and carbohydrate nature and others.

There are also narrowly specific organoids, characteristiconly for representatives of a particular kingdom of living nature. For example, the main part of plant cells is not only the nucleus, but also the cell wall, and also the vacuole. Plastids are important, however, these structures do not exist in animal units.
Which parts of the cell are the most important?
The answer to this question is quite complicated.After all, without any of its structural parts, the cell can not normally live and develop. But nevertheless it is possible to single out some of the most important organoids and parts that are important for the functions performed.
- A nucleus with nucleoli and genetic material concentrated in chromosomes.
- Cell wall (for plants), cytoplasmic membrane (all cells), mucous membrane (for bacteria).
- Cytoplasm with structural components.
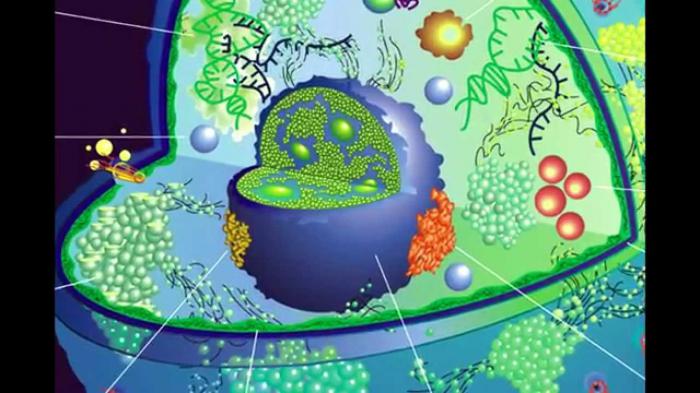
The components listed are the backbone of any cell, regardless of whether the organism belongs to this or that species. Among the cytoplasmic organoids, it is also possible to identify which parts of the cell are the most important.
- Mitochondria.
- Ribosomes.
- EPS.
- Lysosomes.
- Apparatus (complex) Golgi.
It is obvious that the main part is the majority of all structural units of the unit of the structure of organisms.
The core and its structure
Historically, it was believed that the main part of the cell is the nucleus. However, not all of them have it. So, there are no cores in:
- mature red blood cells;
- cells of the conducting tissues of plants;
- bacteria.
There are some species in which, conversely, several nuclei. For example:
- peppered muscle;
- mushrooms;
- seaweed;
- milky plant vessels.
In general, the general plan of the structure of the structure under consideration is one. There are several main parts that make up any core.
- Karyolemma (nuclear envelope) - representsis a double membrane structure that acts as a barrier between the cytoplasm and the inner part of the nucleus. To it from the outside are attached ribosomes, EPS, Golgi complex.
- Carioplasma is an internal gel-like matrix that fills the core. Another name is nucleoplasm. Contains various proteins, ribosomal RNA.
- Chromatin, capable of spiraling during division into tightly packed chromosomes. Its composition is mostly provided by DNA strands. Also present are calcium and magnesium ions, proteins, RNA, lipids.
- The nucleoli localized around chromosome regions. Consist of RNA, DNA, proteins. Serve to assemble ribosome subunits, synthesize r-RNA (ribosomal RNA).

This is a general plan for the structure of the nucleus, from whichIt is obvious that the value of this structure in each cell is crucial for the reproduction, storage and transmission of hereditary information, the combination of genetic traits.
Cytoplasm and its meaning
Важное значение данной структуры было открыто only with the invention of particularly powerful equipment to increase. Prior to this, it was assumed that it is simply a nutrient medium for organoids. However, it has now become clear that the cytoplasm has the following structure.
- Cytoskeleton - a complex of microfilaments and protein tubes that form the supporting network. Inside it, and move the organelles of the cell.
- Cytosol or hyaloplasma - коллоидное внутреннее содержимое цитоскелета, в which dissolved minerals, water, are lipids, proteins, carbohydrates. It is here that the processes of cell metabolism are carried out, the structures communicate with each other.
- Ectoplasm - part of the cytoplasm adjacent directly to the membrane. Endoplasm - the entire space located between the karyolemma and ectoplasm.

В цитоплазме происходят процессы внутриклеточного transport, which allows you to be in close contact with all parts. It is thanks to the constant dynamic movement of the structure under consideration that organoids inside the cell move.
Cytoplasmic membrane
It is a bilipid elastic layer,riddled with protein molecules. The most common theory of the structure of this organoid is a liquid-mosaic model. It serves to separate the external and internal environment of the cell. It has selective permeability, therefore, it protects and protects against foreign particles. In many ways, it is she who maintains the shape of the cell.
If you answer the question:“Which parts of the cell are the most important?”, Then the membrane will stand first, because each of them has it. Differences in composition occur in different species of organisms. For bacteria, chitin included in the composition is characteristic, for animals - its absence.
Mitochondria
Данные структуры не зря называют энергетическими, or "power stations" cells. After all, it is in them that the processes of oxidative phosphorylation occur, as a result of which energy is released from ATP molecules (adenosine triphosphoric acid). In the future, this energy is the source of all life processes, both internal and external.
The names of the cell parts were not always taken immediately. In the case of mitochondria, initially in 1894, these structures were described under the name of bioblasts.

The structure of this organelle itselfquite interesting. The outer membrane is double-layered. The inner layer has a folded structure, forms cristae, on which are located numerous ribosomes.
Mitochondria have their own DNA and two types of RNA(transport and matrix). Also present is a complex of proteins. The number of structures under consideration in the cell may vary, that is, it depends on the activity of the organ. The greatest number of mitochondria contain muscle cells.
Ribosomes
Мелкие округлые темные структуры, которые видны when viewing cells under an electron microscope, they are called ribosomes. These are also the main parts of the cell, because they are directly involved in the assembly of protein molecules.
By themselves, they are represented by ribonucleoproteinand make up a quarter of the entire cell mass. They consist of two unequal subunits combined into one rounded shape. Attached to the Golgi complex, EPS, mitochondria, nucleus. They are located inside some parts.
It is in the ribosomes that protein molecules are synthesized, which are necessary for all processes of plastic and energy metabolism.
Endoplasmic reticulum
The cell under the microscope resembles stronglystriated maze. This is due to such a structure as EPS or endoplasmic reticulum, reticulum. It represents a whole network of branched canals and tubules, bubbles, which entangle all the organelles and concentrate especially closely around the nucleus.

It is through these tubes and channels that various particles move (transport) from one part of the cell to another. Therefore, EPS is also one of its main structures.
Cell wall and vacuole - parts of plant cells
Если же отвечать на вопрос:"Which parts of the cell are the most important in plants?", Then, in addition to the above, a few more should be added. The first is the cell wall. This is a dense membrane that follows the cytoplasmic membrane. It consists of cellulose and other carbohydrates and provides special cell strength. In trees, it is impregnated with a special substance - lignin. That is why their trunks are so durable. Also, it is the cell wall that is the structure that forms the shape of the cell as a whole.
Vacuole is the largest part of vegetableunits of structure. It occupies almost the entire volume of the inner space of the cell. Filled from the inside with liquid, which is a cell sap. This is a mixture of water, vitamins, minerals, hormones, carbohydrates.
Plastids
Another component of the plant cell is plastids. Presented in three varieties:
- leucoplasts are colorless;
- chromoplasts - red, orange, yellow pigments;
- chloroplasts - contain green pigment chlorophyll.
The most important are the latter, since they are directly involved in the processes of photosynthesis.