The process of protein biosynthesis is extremely important.for the cell. Since proteins are complex substances that play a major role in tissues, they are indispensable. For this reason, a whole chain of processes of protein biosynthesis is realized in the cell, which proceeds in several organelles. This ensures cell reproduction and the possibility of existence.
The essence of the process of protein biosynthesis
The only place for protein synthesis isrough endoplasmic reticulum. Here is the bulk of the ribosomes that are responsible for the formation of the polypeptide chain. However, before the translation stage (protein synthesis process) begins, activation of the gene is required, which stores information about the protein structure. After that, copying of this DNA segment is required (or RNA, if bacterial biosynthesis is considered).
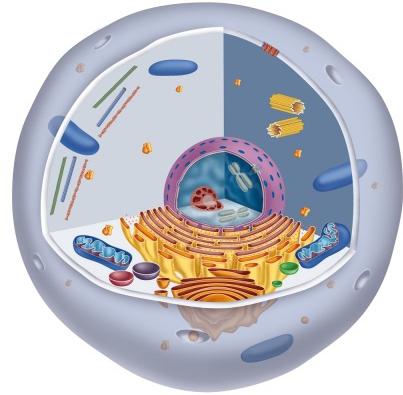
After copying the DNA, the creation process is requiredinformational RNA. Based on it, protein chain synthesis will be performed. Moreover, all stages that take place with the involvement of nucleic acids should occur in the cell nucleus. However, this is not the place where protein synthesis occurs. This is the location where preparation for biosynthesis is carried out.
Ribosomal protein biosynthesis
The main place where protein synthesis occurs is -This is a ribosome, a cellular organelle consisting of two subunits. There are a huge number of such structures in the cell, and they are mainly located on the membranes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The biosynthesis itself takes place as follows: informational RNA formed in the cell nucleus goes through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm and meets the ribosome. Then the mRNA is pushed into the gap between the subunits of the ribosome, after which the first amino acid is fixed.
To the place where protein synthesis occurs,Amino acids are served using transport RNA. One such molecule can once carry one amino acid. They are joined in turn depending on the codon sequence of the messenger RNA. Also, the synthesis may stop for a while.
When promoting mRNA, the ribosome may enteron sites (introns) which do not encode amino acids. In these places, the ribosome simply moves along the mRNA, but the attachment of amino acids to the chain does not occur. As soon as the ribosome reaches the exon, that is, the region that encodes the acid, then it joins the polypeptide again.
Postsynthetic modification of proteins
After the ribosome reaches the stop codonmessenger RNA process of direct synthesis is completed. However, the resulting molecule has a primary structure and cannot yet perform the functions reserved for it. In order to fully function, the molecule must be organized into a specific structure: secondary, tertiary, or even more complex - quaternary.

Protein structural organization
Secondary structure - the first stage of structuralorganizations. To achieve it, the primary polypeptide chain must spiral (form alpha-spirals) or bend (create beta layers). Then, in order to occupy even less space along the length, the molecule is even more tightened and wound into a ball due to hydrogen, covalent and ionic bonds, as well as interatomic interactions. Thus, the globular structure of the protein is obtained.

Quaternary protein structure
Quaternary structure is the most complex of all.It consists of several globular sites connected by fibrillar filaments of a polypeptide. In addition, the tertiary and quaternary structure may contain a carbohydrate or lipid residue, which expands the spectrum of protein functions. In particular, glycoproteins, complex compounds of protein and carbohydrate, are immunoglobulins and perform a protective function. Also, glycoproteins are located on the cell membranes and work as receptors. However, the molecule is modified not where protein synthesis occurs, but in a smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Here there is the possibility of attaching lipids, metals and carbohydrates to the protein domains.