Proteins are vital for any organism.substances. They participate in all metabolic processes of the cell, they are structural components of organs and tissues, they work as signaling molecules. In the process of protein synthesis, many enzymes are directly involved, as well as cell organelles and the nucleus.
Stages of protein synthesis: biological chemistry
The mechanism for building a protein molecule is very complex and requires a large number of factors. Peptides are composed of several amino acid molecules, and their number varies in a very large range.
Proper protein function depends on conformationmolecules, as well as the number of amino acids and their correct sequence in the peptide. Information about this sequence is stored in DNA, and its violation due to mutations and other factors can lead to the shutdown of vital proteins and cell death.
The following stages of protein synthesis in the cell are distinguished:
1. Transcription.
2. Broadcast.
Stage One: Transcription
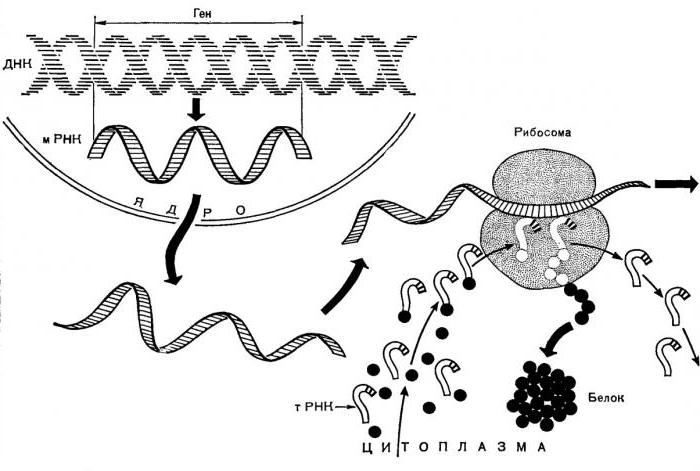
В процессе синтеза белков непосредственное nucleic acid molecules are involved. DNA, as a repository of all genetic information, encodes the sequence of a future peptide with its structural nucleotides. Starting from the start codon (triplet) and ending with the terminal one, information about a protein for another nucleic acid, RNA, is read. This single-stranded molecule is transferred through the pores in the nucleus to the cytoplasm of the cell.
If a eukaryotic transcription process is associated withthe participation of the nucleus, then its absence in prokaryotes simplifies peptide synthesis. RNA that forms on the bacterial chromosome is immediately processed and attached to the ribosomes.
Enzymes play a crucial role in the formation andRNA synthesis on the DNA template. Such molecules as transcription factors, or TF, are directly involved in the process of protein synthesis. This is a series of proteins that contribute to the process of reading information from deoxyribonucleic acid.

Stage Two: Broadcast
When RNA enters the cell's cytoplasm from the nucleus,Information on the composition of the peptide must be read by special structures. In the process of protein synthesis, ribosomes are directly involved - non-membrane, small in diameter structures consisting of two subunits: large and small. RNA is placed between these subunits, after which reading begins.
Codon for codon is building longprotein molecules like a gun. This is explained as follows: in the interribosomal space, only two codons are placed at once. When one of them has been read, the amino acid joins the peptide and drops out of the ribosome as a kind of tail through a special opening. This happens as the sleeve falls out of the gun after the shot.
In the process of protein synthesis, directIF proteins, or initiation factors, are involved. With their help, begins the synthesis of the polypeptide from the start codon, which in most cases is methionine.
It is worth mentioning that amino acids are supplied toribosomes are special carriers, called tRNA, or transport RNA. These molecules have the form of a clover leaf, at the end of which an amino acid is attached, as well as ATP and a special protein, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. All this complex together allows us to deliver the structural component of the protein to the ribosome with the expenditure of energy and attach it with the help of a peptide bond.

What are nucleotides?
Нуклеиновые кислоты – это группа органических compounds that are polymers. They consist of purine (adenine, guanine) and pyrimidine (thymine, cytosine, uracil) bases. The sequence of these nucleotides determines the information that is stored in DNA or RNA. This information is read on the ribosomes with the formation of proteins, and for the simplicity of the task, the nucleotides are broken up into triplets. Each triplet encodes its own amino acid, which is delivered by tRNA to the ribosomes.
Synthesis of mitochondrial proteins
Mitochondria and plastids have a distinctivefeature - they have their circular DNA, similar to the bacterial chromosome of bacteria. Using this nucleic acid, organelles can work autonomously, synthesizing most of their structural proteins.
However, mitochondrial DNA is not storedinformation on factor proteins that are necessary for the process of transcription and translation. These peptides are assembled on ribosomes, using RNAs, not mitochondria, but nuclei. Therefore, two-membrane structures are not completely autonomous.
How did mitochondria and plastids find theirown DNA? It is assumed that these organelles are descendants of bacteria. They lost autonomy inside the cell, however they brought circular nucleic acid with them. The similarity of mitochondrial DNA with a similar prokaryotic molecule also hints at this.

Conclusion
All stages of protein synthesis are interconnected, and theirthe challenge is to build peptide molecules using information that is stored in nucleic acids. The direct participants in the process are such structures as the nucleus and ribosomes, as well as some specialized proteins.
In prokaryotes, the process of peptide synthesis proceedsmuch faster due to the lack of a core. RNA, which is transcribed on a matrix of bacterial DNA, is immediately attached to the ribosomes, after which the translation also proceeds simultaneously.