Let's talk about how to find protons, neutrons and electrons. In an atom there are three types of elementary particles, each having its own elementary charge, mass.

The structure of the nucleus
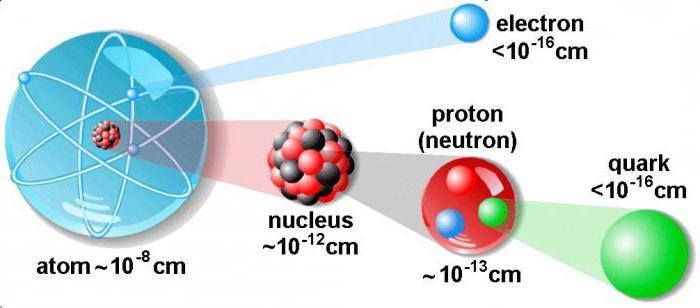
In order to understand how to find protons,neutrons and electrons, we will represent the features of the structure of the nucleus. It is the main part of the atom. Inside the nucleus are located protons and neutrons, called nucleons. Inside the core, these particles can cross into each other.
For example, to find protons, neutrons, andelectrons in the hydrogen atom, it is necessary to know its ordinal number. If we take into account that this element is the head of the periodic system, then its nucleus contains one proton.
The diameter of the atomic nucleus is ten thousandths of the entire size of the atom. In it the bulk of the entire atom is concentrated. By mass, the nucleus exceeds by a thousand times the sum of all the electrons present in the atom.
Characteristics of particles
Consider how to find protons, neutrons, andelectrons in the atom, and we learn about their features. The proton is an elementary particle, which corresponds to the nucleus of the hydrogen atom. Its mass exceeds the electron in 1836 times. An electrical charge is used to determine the unit of electricity passing through a conductor with a given cross-section.
Each atom in the nucleus has a certain number of protons. It is a constant value, characterizes the chemical and physical properties of a given element.
How to find protons, neutrons and electrons in an atomcarbon? The ordinal number of this chemical element is 6, therefore, the nucleus contains six protons. According to the planetary model of the structure of the atom, six electrons move around the nucleus along the orbits. To determine the number of neutrons from the value of the relative atomic mass of carbon (12), subtract the number of protons (6), yielding six neutrons.
For the iron atom, the number of protons corresponds to 26, that is, this element has the 26th ordinal number in the periodic table.
The neutron is electrically neutrala particle that is unstable in the free state. The neutron is capable of spontaneously transforming into a positively charged proton, emitting antineutrinos and electrons. The average half-life is 12 minutes. The mass number is the total value of the number of protons and neutrons inside the nucleus of the atom. Let's try to find out how to find protons, neutrons and electrons in the ion? If an atom acquires a positive oxidation state during a chemical interaction with another element, then the number of protons and neutrons does not change in it, only electrons become less.

Conclusion
There were several theories concerningstructure of the atom, but none of them was viable. Until the version created by Rutherford, there was no detailed explanation of the location within the nucleus of protons and neutrons, as well as the rotation in circular electron orbits. After the appearance of the theory of the planetary structure of the atom, researchers have the opportunity not only to determine the number of elementary particles in an atom, but also to predict the physical and chemical properties of a particular chemical element.











