In the periodic table with the number 1is the most common element in the universe - hydrogen. Its distribution, as a percentage, is close to 75%. Its lowest content is noted in the layers of the atmosphere - 0.0001%. The earth’s crust contains 1% gas by mass. Its greatest amount is noted in water: 12%. On our planet it is the third most common chemical element.
Item Description
A hydrogen molecule, the formula of which is HH or H2, is endowed with physical and chemical properties.

Hydrogen is a gas that is not endowed withcolor or smell. The location of hydrogen in the table at 1 place is due to the fact that in various conditions this element can manifest itself as a metal or as a gas. In its outer orbital there is 1 electron, which hydrogen can give (metallic properties) or accept one more (gas quality).
The diameter of the hydrogen molecule is 27 nm.
The diameter of the hydrogen atom is 1A, the radius is 0. 41 A.
Properties
The following are physical:
- Boiling point - 256aboutFROM.
- Melting point -259.2aboutFROM.
- The mass in the air (D) - 0,069.
- Hydrogen is poorly soluble in water.
Chemical properties are as follows:
- The non-polar bond between the particles of the molecule has an energy of 436 kJ / mol.
- The temperature of thermal dissociation is 2000aboutFROM.
- Reacts with:
- halogens;
- oxygen;
- sulfur;
- nitrogen;
- nitrogen oxide;
- active metals.
Under natural conditions, hydrogen is found both in its natural form and in the form of isotopes: protium, deuterium, and tritium.
The structure of the molecule
The element molecule has a simple structure.The composition of the hydrogen molecule is represented by two atoms, which, approaching, form a covalent non-polar bond, as well as one electron pair. The structure of a single atom is: 1 positively charged nucleus, around which 1 negatively charged electron moves. This electron is located on the 1s orbitals.
H - 1e = H + this hydrogen ion is positive.
This expression indicates that hydrogenhas similar parameters with elements of group 1 in the periodic system, which are alkali metals (lithium, sodium, potassium), donating their only electron in the outer orbitals.
H + 1e = H - the hydrogen ion is negative.
This equation shows that hydrogen isrelated with similar elements from the 7th group, which are gas and are able to accept the missing electrons to their external electronic level. Such gases include: fluorine, chlorine, bromine, etc.
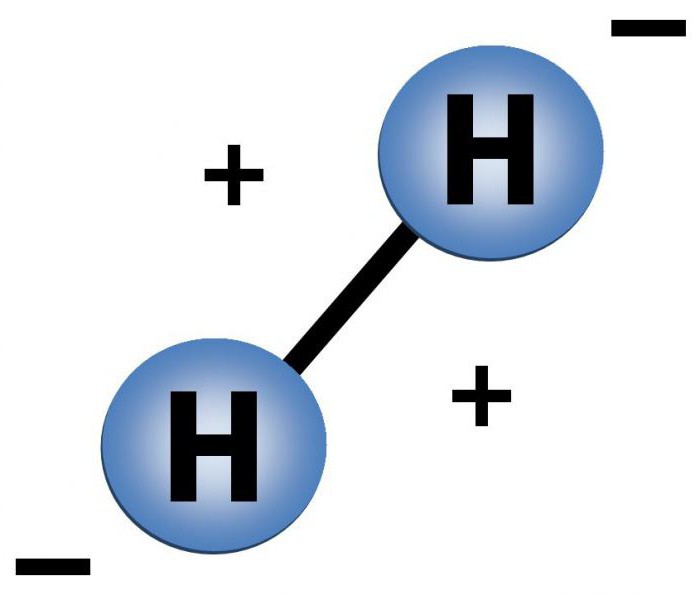
The composition of the hydrogen molecule is graphically presented below.

The distance between hydrogen atoms is r = 0.74 A,While the sum of the orbital radii is 1.06 A. This affects the depth of the overlapping electron clouds and the strong, stable hydrogen bond.
The hydrogen atom is the most elemental atom in nature. The size of the atomic proton is 10.5 A, and the diameter of a single atom is 0.1 nm.
Molecules of isotopes have a special structure. The atomic nucleus of protium consists of only one proton. Denoted isotope: 1H.
The nuclear structure looks like a complex of proton and neutron (2H).
3H - tritium - in its atomic structure is endowed with a nucleus with 1 proton and two neutrons.
Weight
In science, there are formulas that calculate what the mass of a hydrogen molecule is equal to. In relation to the element, determine the molecular and atomic mass.

The molar mass of the hydrogen molecule is calculated by the general formula:
M = m / n, where m is the mass of a substance, n is its quantity.
The mass of the atom is 1.008 amu.Consequently, the relative mass of the molecule will also be equal to 1.008. Since the hydrogen molecule consists of two atoms, the relative atomic weight is equal to 2.016 a. E. m. The mass of the hydrogen molecule is expressed in grams per mole (g / mol).
Importance in nature

The most significant substance in nature, which forms hydrogen in combination with oxygen, is water. Water is the source of life, so hydrogen is a vital element.
Of the 100% of all chemical elements thatmake up the body environment, 1/10 part, or 10%, is hydrogen. In addition to water, it is able to maintain a quaternary protein structure, which is possible due to the hydrogen bond.
The principle of complementarity of nucleic acidsalso occurs with the action of the hydrogen molecule. In the plant cell, H takes part in the process of photosynthesis, biosynthesis, and energy transfer through membrane channels.
Application
In the chemical industry, hydrogen is widely applicable. It is added in the manufacture of plastic products, in soap, as well as in ammonia and menthol production.
Food industry:when producing food, hydrogen is added as a food additive E949. Such a component can be seen on the packaging of margarine, vegetable oils. Additive E949 allowed food industry of the Russian Federation.
Hydrogen was once involved inthe aeronautics industry because matter is lighter than air. So, in the 30s of the last century balloons and dirigibles were filled with this type of gas. Despite its cheapness and ease of use, hydrogen was soon ceased to be used as a filler, as the incidence of aircraft explosions became more frequent.
Nowadays, gas is used as fuel,used in the space industry. However, it is considered methods of applying it to the operation of engines of cars and trucks, because the element does not emit harmful impurities into the atmosphere, and, therefore, is environmentally friendly.
An integral component of hydrogen isotopesact as part of many drugs. Deuterium is used in pharmacological studies to determine the behavior and effects of the drug in the body. Tritium is used in radio diagnostics, as an element that determines the biochemical reactions of enzyme metabolism. Hydrogen is part of the peroxide, which is a disinfectant.






