Cells of organisms of various systematicunits have a number of differences. They relate to the shape, size and availability of some structures. In this article we will tell you what bacteria cells differ from plant cells, and compare their structure.
What is a cell
The cell is called the smallest unit of the structureorganisms. This is the so-called "building material". The obligatory parts of each cell are the surface apparatus, cytoplasm and obligatory structures - organoids. Spare substances, the number of which is not constant, are called inclusions.

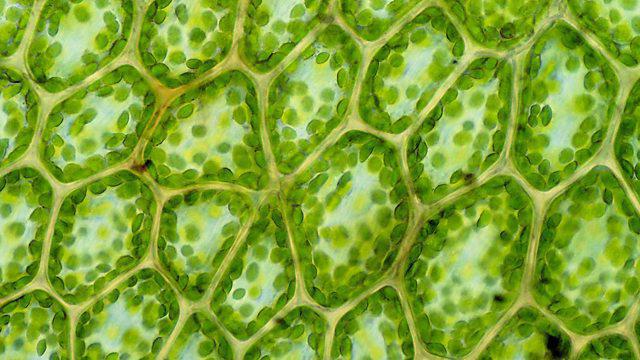
Structure of plant cells
A distinctive feature of plant cells ispresence of chloroplasts. These are plastids of green color, on the inner surface of which the process of photosynthesis is carried out. This structure determines the autotrophic way of feeding these organisms. Cells of bacteria differ from plant cells by the presence of other organoids. Thus, for the latter, vacuoles are characteristic. This cavity is filled with an aqueous solution of minerals.
Dimensions of plant cells vary in significantlimits. For example, green alga chlamydomonas can reach 1 mm, and the length of bast fiber flax - 5 mm. The average value for plants is from 15 to 60 microns. Most of them can be considered only in a light microscope.
According to the form, bacterial cells differ fromplant cells: do not have a particular variety. In parenchymal the length is almost equal to or slightly larger than the width. They form the basic, mechanical and conductive tissue. Proximal cells are extended in length, and their tips are pointed. They are part of the wood.

Bacteria: features of the organization
Cells of bacteria differ from plant cells in much smaller sizes. The smallest of them are on the border of visibility in a light microscope. Their size is only 2 μm.
But the form of bacterial cells is differentsignificant variety. Kokki have the form of a ball, bacillus - rods, staphylococci - clusters of grapes, vibrios - a comma. Most bacteria are capable of active movement. This is done with the help of flagella, mucus or gas vacuoles.
The body of bacteria is represented by a single cell.On the one hand, this structure is distinguished by a fairly simple structure and physiology. On the other hand, it fulfills the functions of the whole organism. A microscopic bacterial cell is capable of feeding, multiplying, moving, breathing, growing. Of course, all these processes occur at a primitive level. But this can not be called a disadvantage.
On the contrary, unpretentiousness of bacteria made themcreatures with the highest level of adaptation. They are found in boiling springs, in ice water, soil, inside and outside of other organisms, air and outer space.

Surface Apparatus
Similarity in the structure of the surface apparatus inbacteria and plants is the presence of a membrane formed by a complex complex of proteins and lipids. This structure performs transport, mechanical and barrier functions. Both organisms have a cell wall in the surface device. But its chemical composition is significantly different. In plants it consists of cellulose, and in animals - pectin and murein. All of them are complex carbohydrates.
Bacterial cells have one more structuresurface apparatus - mucous capsule, which contains a reserve of organic substances of the cell. It is an additional protection against mechanical damage and loss of moisture. Another function of this structure is to create a barrier for the onset of phagocytosis - intracellular digestion of solid particles.

Than bacterial cells differ from plant cells: response
There is another fundamental difference.Cells of bacteria differ from plant cells by lack of ... The answer will be unexpected: structures for storing genetic information. But this means that bacteria do not transmit hereditary traits and their subsequent generations of cells are not like them.
In fact, this is not the case at all.Cells of bacteria differ from plant cells only by the organization of genetic material. They do not contain a decorated kernel. DNA molecules have a ring structure and are localized directly in the cytoplasm. Such cells are called prokaryotic. Plants have a nucleus in which hereditary information is stored and RNA molecules are synthesized.

Cells and tissues
Cells of bacteria differ from plant cellslack of specialization. Each of them works separately, functioning as a separate organism. It also occurs in unicellular plants. For example, green algae chlorella and chlamydomonades. The higher plants form tissues. These groups of cells are similar in structure and function. Thus, in the integumentary they are small and closely adjacent to each other, creating a kind of barrier. And the main fabric, which forms the basis of the plant organism, includes large, loose loam.
So, in this article we have looked at what bacteria cells differ from plant cells. The main features are the features of the surface apparatus and the structure of the genetic material.