Cell cycle - time from one cell divisionuntil next. Passes in two successive stages - interphase and proper division. The duration of this process varies and depends on the type of cells.
In this period, the cell grows and doubles itsDNA, as well as mitochondria and plastids. In the interphase is the synthesis of protein and other organic compounds. The synthesis process is most intense in the synthetic interphase period. At this time, nuclear chromatids are doubled, energy is accumulated, which will be used during fission. The number of cellular organelles and centrioles also increases.
The interphase takes up almost 90% of the cell cycle. After it passes mitosis, which is the main way of dividing eukaryotic cells (organisms whose cells contain a formed nucleus).
In mitosis, the chromosomes are condensed, anda special apparatus is formed, which is responsible for the even distribution of the hereditary information between the cells, which are formed as a result of this process.

Phases of mitosis
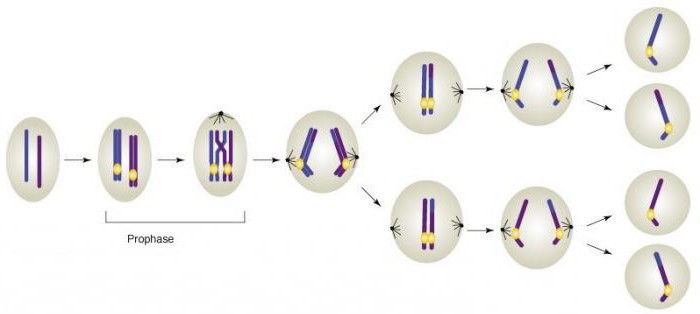
In mitotic cell division, the corresponding phases of mitosis pass: prophase, after it there is a metaphase, an anaphase, telophase is the final.
The phases of mitosis are characterized by the following features:
- prophase - the nuclear envelope disappears. In this phase, the centrioles diverge towards the poles of the cell, and the chromosomes condense (condense);
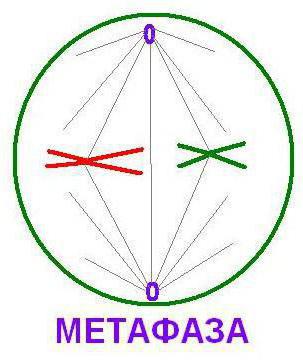
- metaphase - characterized by placementmaximally compacted chromosomes, which consist of two chromatids, at the equator (in the middle) of the cell. This phenomenon is called the metaphase plate. It is in this period that chromosomes can be viewed well under a microscope. In the metaphase of mitosis, attachment of one ends of the threads of the division spindle to the centromeres of the chromosomes also occurs, while the other ends attach to centrioles.
- anaphase - in this period is separationchromosomes on chromatids (they diverge to different poles). When this chromatids become separate chromosomes, which consist of only one chromatid filament;

- telophase - characterized by decondensationchromosomes and the formation around each chromosome of a new nuclear envelope. The threads of the division spindle disappear, nucleoli appear in the nucleus. In telophase also undergoes cytotomy, which is the division of the cytoplasm between the daughter cells. This process in animals is carried out by a special division groove (constriction, which divides the cell in half). In plant cells, the cytotomy process is provided by a cell plate with the participation of the Golgi complex.
What is the biological significance of the process of mitosis?
The phases of mitosis contribute to the accurate transmission of the child.cells of hereditary information, regardless of the number of divisions. In addition, each of them receives 1 chromatid, which helps to maintain the constancy of the number of chromosomes in all cells, which are formed as a result of division. It is mitosis that ensures the transmission of a sustainable set of genetic material.