Molecules built from amino acid residuesproteins. Such polymers are high molecular weight natural materials. They include such chemical elements as carbon, hydrogen in them, oxygen atoms, and nitrogen. Nucleic acids contain phosphorus, and many proteins contain sulfur.

Features of the structure
Since amino acid residues are builtmolecules of protein molecules, they have a high relative molecular weight. They are called macropolymers. As examples of low molecular weight compounds, alcohols, carboxylic acids, nucleotides, monosaccharides, amino acids can be given.

Macromolecules
It is from amino acid residues builtmolecules of proteins necessary for the life of living organisms. On average, their relative molecular weight is in the range of several thousand to a million. In molecules of protein compounds, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, a certain number of repeating units is assumed.
Monomers are called simple molecules thatare the basis for the formation of polymer molecules. What molecules are built from amino acid residues? The answer to this question is familiar to any high school student. Amino acids act as a monomer for them. For polysaccharides, monosaccharides are needed, and nucleotides are necessary for the construction of nucleic acids.

Value of biopolymers
So, from amino acid residues are builtprotein molecules that perform several functions at once. It is necessary to note their construction function. It allows you to build protein molecules that are specific to an individual living organism. In addition, protein molecules are a source of energy, so proteins are included in the daily diet. Cells contain different amounts of organic compounds. For example, animals are characterized by the predominance of lipids and proteins, and in plants - a sufficient amount of carbohydrates.
Molecules built from amino acid residuesanimal proteins. Such "building blocks", which are amphoteric chemical compounds, are arranged in a protein molecule in a specific sequence. Currently there is information about the existence of two hundred amino acids, but only twenty of them are used to form natural proteins. They are called protein-forming. For example, proteins can be constructed in alternations of alanine, leucine, lysine, aspartic acid, valine, methionine, glutamine, threonine. On the question of what amino acid residues are built molecules of which, students give examples of animal proteins.

Features of the chemical structure
In amino acids that are able to formmacromolecules, amino group and carboxyl group are linked to one carbon atom. It is this feature that unites the above number. Amino acid residues differ in the composition of the radical. It can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic, polar or non-polar, which gives amino acids specific properties.
The main part of the amino acids capable of formingprotein molecules, has one carboxyl group (it has hydroxyl and carbonyl) and one amino group, so they are considered neutral molecules.
There are basic amino acids that have several amino groups at once, as well as acidic amino acids, which include several carboxyl groups. For example, sulfur atoms are in the cysteine molecule.
Synthesis options
Autotrophic organisms synthesize amino acids from nitrogen-containing inorganic substances, as well as from the products of photosynthesis.
Heterotrophic organisms are used asThe main source of amino acids is food. In humans, some amino acids are synthesized from metabolic products. Such compounds are considered interchangeable. As a source of essential amino acids that are unable to synthesize in the human body, certain foods are used. What acids are called essential for humans? These are lysine, phenylalanine, leucine, valine, isoleucine, tryptophan, methionine. For the child's body, there are two more essential amino acids: histidine and arginine.
Since amino acids are amphotericcompounds, they are highly reactive. A chemical bond, called a peptide (amide) bond, forms between the amino group of one acid and the carboxyl group of the second molecule.
As a result of a similar chemical reactiona linear peptide structure is formed. One end of the compound has an amino group, and the other has a free carboxyl group. Such a structure allows the dipeptide to interact with other amino acid molecules to form polypeptide compounds.
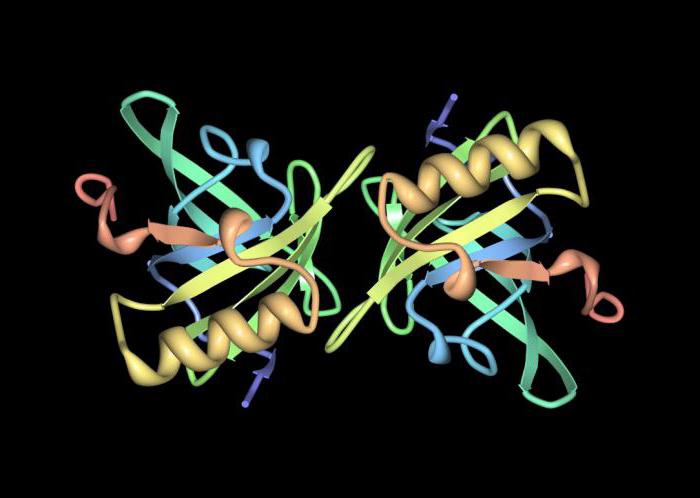
Conclusion
Peptides are particularly important forhuman life. The structure of the polypeptides are toxins, antibiotics, as well as part of the hormones. Polypeptide chains may comprise thousands of amino acid residues located in a specific sequence. If the composition of the protein macromolecules are only amino acid residues, they are called simple.
Если в структуре белковой молекулы есть не только amino acid components, but also cations of iron, manganese, zinc, sugar, nucleotides, lipids, in this case, the molecules are called complex proteins. As common simple proteins we select fibrin, blood albumin, enzymes.
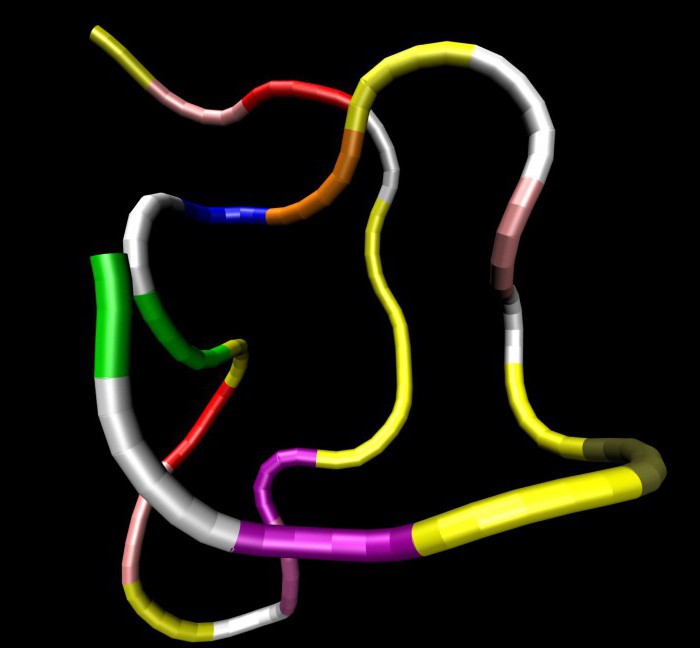
Сложными белковыми молекулами считают антитела (immunoglobulins), enzymes. There are four types of structural organization of protein molecules. The primary structure is a linear sequence of amino acid residues connected by peptide (amide) bonds.
It is this that determines the functions, properties, andform of protein. On the basis of the primary structure create other options for structures. Each organism has its own unique primary structure, which creates certain problems for synthesis. For example, there are problems in the selection of pharmaceuticals for specific people.