The origins of Mesopotamian culture
Probably, the development of art and culturecontributed to just a large number of diverse peoples in one territory. The Sumerian culture developed after the fall of the dynasty of rulers, and the Persians and Syrians also exerted their influence. It is the Sumerians who became the founders of the country's written language. Cuneiform writing exerted a strong influence on the art of ancient Mesopotamia, because not only state documents and scientific treatises were created with this style of writing, but also works of art, religious and poetic texts, some of which have survived to this day.

The Sumerians laid the foundations for the scientificdevelopment of the state, irrigation systems and city fortifications were created by them. For two thousand years before our era the art of Mesopotamia was represented by applied and pictorial works, literary and musical
compositions.
Architecture of Mesopotamia
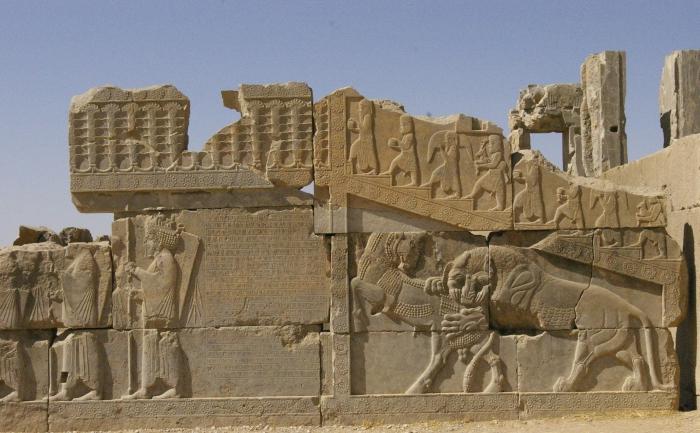
Permanent wars led to the fact that the mainThe direction of architecture was called for the creation of fortresses. Distinctive features of the Mesopotamian cities were powerful gates, fortified doors and frames, heavy columns. Bronze lions, located at the door, brought the Babylonians. In addition, there were such architectural forms as towers and domes, as well as arches. Houses were built of clay and brick, in the center of the city, as a rule, was a ziggurat.
Temples-ziggurats were intended for believers,who could come there and bring gifts to God. It is the architectural art of Mesopotamia that created one of the most famous temples in history - the Tower of Babel. It was a structure of seven towers, located one on top of another, and at the top was the sanctuary of the god Marduk. Another important construction is the gate of the goddess Ishtar. Babylon, then the largest city of the state, was filled with many palaces and temples, but powerful gates, adorned with blue plates with images of bulls and dragons, stood out among other architectural structures.

Glyptic
The art of Mesopotamia has survived to this day inglyptic. These are convex, rounded sculptural images carved, usually on a stone (seals, rings, vases, dishes, bas-reliefs), made according to the canons. The figure of a person has always been portrayed with a nose in profile, legs on the side, and eyes from the front. Art reflected not reality, but the accepted canon, a certain tradition of art. The mountains and trees were also depicted conditionally and symmetrically. The works do not reflect the individuality of the creator, but his ability to create sculptures according to the general canon. Therefore, according to the surviving examples of glyptics, it is possible to judge the original Sumerian culture as a whole, and not about its individual masters.