The lower limbs (legs) carry enough.big load. Their task is to provide movement and support. The muscles of the lower extremities, the anatomy of which will be described in detail in the article, are considered the most powerful of all. Next, consider the muscles of the legs in more detail.

General information
The muscles of the human lower limbs are very well developed.OK. They correct flexion, extension, adduction, leg abduction in the knee and hip joint, movement of the fingers and feet. The lower limbs include two muscular groups. The first is the fibers of the pelvis. The second group consists of the muscles of the free lower limb. The musculature of the pelvic region begins from the pelvis, lumbar vertebrae and the sacral area. The fibers are also fixed to the femur. The tasks of the muscles of this part of the leg include keeping the body in a vertical position, extending / flexing the hip joint and coordinating the movements of the thigh. The muscles of the free lower limb include the segments of the thigh, foot, and tibia.
Thigh musculature
Мышцы нижних конечностей человека в этой области divided into three groups. So, allocate front, back and medial departments. The first is the flexors, the second is the extensors. The third group includes the muscles leading the femoral part of the leg. With considerable weight and length, these muscles of a person’s lower limbs can develop great strength. Their activity extends to the knee and hip joints. The thigh muscles perform dynamic and static tasks while walking and standing. As well as the pelvis segments, these fibers reach their maximum development due to the ability to erect.
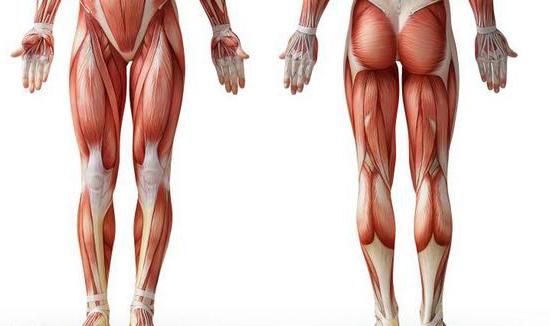
Muscles of the lower extremities: anatomy. Anterior group of the femoral muscles
В нее входит портняжная мышца.The fibers start from the anterior superior ilium. The segment intersects the femoral surface medially, top to bottom obliquely. The site of attachment is the tibial tuberosity and the fascia of the tibia. In this place the fibers form tendon strain. At the site of attachment, it grows together with similar elements of the semitendinosus and thin muscles, forming a fibrous triangular plate - the "goose foot". Under it is her bag. This muscle of the lower limbs functions consist in turning the outside of the thigh, flexing it and bringing the tibia.
Quadruple fibers
They form a strong and large muscle.It has a large mass. The quadriceps muscle consists of four segments: intermediate, medial, lateral and straight. Almost all sides of the fiber adjacent to the femur. In the distal third, 4 heads form one tendon. It is attached to the tibial tubercle, lateral edges and the top of the patella.
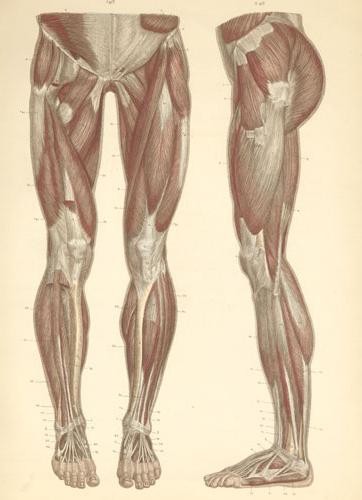
Straight fibers
Ими образована мышца, начинающаяся от передней lower ilium. Between the fibers and the bone is located synovial bag. The muscle runs down in front of the hip joint. Then it comes to the surface between the tailoring segment and the fibers of the wide fascia. As a result, it occupies a position in front of the wide intermediate muscle. The segment ends with a tendon. It is fixed to the base of the patella. The rectus muscle has a feathery structure.
Lateral segment
Эта широкая мышца бедра считается самой крупной out of four. It starts from the intertrochanteric line, gluteal tuberosity, the greater trochanter, the upper part of the femoral rough line, and the lateral septum. Fibers are fixed on the tendon of the rectus muscle of the lower extremity, the tibial tubercle, the upper lateral patella. Part of the tendon bundles continues into the supporting lateral ligament.
Medial segment
This broad muscle is quite extensive.Start. It departs from the lower half of the intertrochanter, medial lip of the rough line, as well as from the medial femoral septum. Fibers are fixed to the upper end of the patella base and the anterior side of the medial condyle on the tibia. Formed by this muscle tendon is involved in the formation of the supporting medial ligament of the patella.

Intermediate Fibers
They form a wide muscle, starting fromthe upper two-thirds of the lateral and anterior sides of the body of the bone of the thigh, from the lower part of the lateral lip of the rough line of the thigh and from the lateral intermuscular septum. It is attached to the base of the patella and, together with the tendons of the direct, lateral and medial broad muscles of the thigh, is involved in the formation of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris.
Musculature of the leg
Она, как и прочие мышцы пояса нижней конечности, developed quite well. This is due to the tasks that it performs. These muscles of the lower limbs are associated with dynamics, statics and upright walking. Fibers extensively begin on fascia, septum and bone. Their reduction coordinates the movement of the ankle and knee joints. The muscles of the lower limb in this part are divided into the lateral, anterior and posterior groups. The latter includes long flexor fingers: large and the rest, popliteal, soleus and gastrocnemius segments. Also in this group is the tibial posterior muscle. In the anterior section, there are long extensor fingers: large and others. Also present here is the tibialis anterior muscle. In the lateral division, there are long and short fibular segments.

Back group
The muscles of this department form a deep andsurface layers. The greatest development is noted in the triceps muscle. It runs superficially and forms the characteristic roundness of the tibia. The deep layer is formed by a small popliteal and three long muscles: the flexors of the fingers: the thumb and others, as well as the posterior tibialis. They are separated by a fascia plate of the tibia from the soleus segment.
Lateral group
It is formed by the fibular muscles of the lower limb:short and long. They run along the lateral side of the leg. These muscles are located between the intermuscular septa (posterior and anterior) under the fascia.
Musculature of the foot
Together with bone fixing tendonssegments of the lower leg, which belong to the lateral, anterior and posterior groups, have their own (short) fibers in the lowest part of the leg. Their beginning and site of attachment is on the skeleton of the foot. Short muscles have complex functional and anatomical-topographical relationships with those tendons of the shin muscles, the fixation points of which are also located on the bones of this part of the leg.

Musculature of the sole of the foot
In this area allocate medial (in the area ofthumb), lateral (in the little finger) and the middle (intermediate) muscle groups. On the sole, the first and second sections, unlike those on the brush, are represented by a smaller number of fibers. At the same time, the average muscles in the foot are strengthened. In general, 14 short fibers are present on the sole. Three segments belong to the medial group, 2 form the lateral. There are 13 muscles in the middle section: 7 inter-bone and 4 worm-like, as well as a square and short flexor. In maintaining the arches a significant role is played by the muscles not only of the foot, but also of the leg. Due to this, the voltage of the ligament apparatus is significantly reduced.
Furrows and channels
In them are the nerves and large vessels of the legs.In the femoral part, they are between the medial and anterior groups, in the region of the knee joint - in the popliteal fossa, on the sole - between the middle and lateral, as well as between the middle medial sections, on the lower leg - between the muscles of the back surface.

Pelvic muscles of the lower extremities: table
This area has a practically fixed joint.with the sacral region of the spine. In this regard, the musculature that sets it in motion is absent. However, the activity of the hip joint and the spine is controlled by these muscles of the human limbs. The table below summarizes all of this information.
Name of the muscle | Tasks |
Ilio-lumbar | Hip flexion, hip rotation outwards |
Small lumbar | Tension ileal fascia |
Big buttock | Leg extension in the hip joint |
Average gluteus | Hip abduction. With the reduction of the internal fibers - rotation inward, rear - outward |
Small gluteus maximus | Hip abduction. With the reduction of the internal fibers rotates the thigh inward, the rear - outward |
Strain of wide femoral fascia | Hip flexion and pronation, wide fascia tension |
Pear-shaped | Rotation of the thigh outward |
Internal locking | |
Lower and upper twin | |
External locking |
Pain in the legs
Muscle soreness may develop due to various pathologies. These, in particular, include:
- Spinal diseases (sciatica and radiculitis, neuritis and neuralgia).
- Pathologies of bones, ligaments and joints (arthrosis, arthritis, bursitis, fascia, tendonitis, flat feet, fractures, tumors).
- Direct muscle damage (rupture of ligaments, myositis, fibromyalgia, seizures, overwork and overstrain).
- Disturbances in metabolic processes and cellulose pathology (cellulite, obesity, etc.).
When paratenonitis and mioentezita pain occurspulling character in the muscles. They are caused by inflammation of the fibers and ligaments of the legs. The cause of the pathologies is an overstrain of the muscles against the background of intense loads. Accompanying the disease is the formation of microtraumas of the muscles and ligaments. As an additional risk factor are hypothermia, chronic pathology, general fatigue.
Finally
As you know, muscles take an active part inoutflow of blood through the veins. In the process of training the muscles simultaneously, an increase in myocardial mass occurs. This allows you to carry significant loads. In the process of muscle activity in the body, biologically active compounds are released - endorphins. They contribute to the adaptation of tissues and organs to a variety of negative influences and provoke a surge of energy and strength. Against the background of physical activity, the organs of the body's defense system are stimulated. In this regard, experts recommend regularly engage in sports, physical education, perform gymnastic exercises, take walks. These activities are particularly important for older people. When playing sports at children's age, correct posture is formed, the skeleton and muscles develop proportionately.





