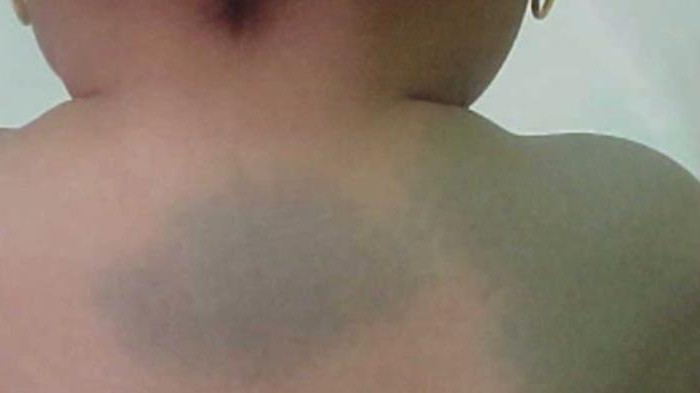
Some babies immediately after birthMongolian spot is diagnosed. What is it? Mongolian spot is a pigmentation of the skin, which has an irregular or rounded shape and a gray-blue tint. Most often, this phenomenon is localized in the lumbosacral region. In fact, pigmentation is a congenital nevus. In the diagnosis of tumors, special importance is given to its differentiation with melanohazymi. As practice shows, the Mongolian spot disappears on its own after 4–5 years.
Why is it called
Why is this pigmentation called otherwise?as the "Mongolian spot"? Indeed, what is the secret? The fact is that 90% of children of the Mongoloid race are born with a similar mark. At risk are Ainu, Eskimo, Indians, Indonesians, Japanese, Koreans, Chinese and Vietnamese. Also, the Mongolian stain often occurs in kids of the Negroid race. As for Caucasians, such neoplasms are present on the body in only 1% of newborns.
Mongolian spot is usually located in the region of the sacrum. There are a lot of names for such pigmentation. Often it has a "sacred spot."
Features of the disease
Why does the Mongolian stain appear?newborn? The skin has several interrelated layers: the dermis and epidermis. Pigmentation depends on how many specific cells are present in human skin, as well as on their activity. Melanocytes are located in the epidermis and produce pigment. It is he who affects the shade of the skin.
Studies show that 1 mm2 The epidermis has no more than 2,000 melanocytes.Their number is only 10% of the total number of cells. However, the functional activity of melanocytes affects the hue of the skin. Various kinds of disturbances in the activity of such cells can cause the development of diseases such as halonevus, vitiligo, and so on.
As for people with white skin, then melanin intheir body produces significantly less. Often this happens only under the influence of sunlight. As a result, the skin is covered with a tan. In humans, black or yellow race, melanin is produced continuously. That is why the skin and get such a shade.
Causes of pigmentation
Монгольское пятно у новорожденного появляется не at birth. While the embryo in the mother's womb is developing, the melanocytes migrate into the epidermis from the ectoderm. According to scientists, the Mongolian stain is formed as a result of the incomplete process of moving cells with pigment. In other words, after the baby is born, the melanocytes remain in the dermis. The pigment that is produced by these cells causes skin discoloration. On the skin of the baby as a result of this phenomenon appears a stain that has a gray-blue tint.
The scientists came to the conclusion that the Mongolian blot occurs due to the presence of a slight pathology of embryonic development, which is caused by the presence of a particular gene in the fetus.

Clinical picture of pigmentation
Mongolian spot, the photo of which is presented inarticle formed in the area of the sacrum and looks like a bruise. Such pigmentation is attributed to the category of congenital nevi. Most often the stain has a gray-blue tint, but in some cases it may turn blue-brown or blue-black.
Symptoms include a uniform color,distributed over the entire area of pigmentation. As for the configuration of the spot, it can be completely different. Nevus can be round or oval. However, most often the Mongolian spot has an irregular shape. Sizes of pigmentation are also different. This may be one large spot or several small ones.
Localization of the Mongolian spot
A child has a Mongolian stain at birthlocated not only in the area of the sacrum. Often, pigmentation is manifested on the back and buttocks, occupying a fairly large area of the skin. Of course, many newborns have blue spots localized in the coccyx and lower back. However, there are cases when skin areas of the forearm, back, legs and other parts of the body have been pigmented.
For some children, the Mongolian spot is able to change its location. In certain situations, pigmentation is shifted to the buttocks or the back.

Does the stain disappear?
In newborns, the Mongolian spot hasbright color. However, after some time it becomes dimmer and gradually begins to fade. At the same time, pigmentation begins to decrease in size. It is worth noting that in most cases the Mongolian spot disappears on its own. This happens 5 years after the appearance of pigmentation on the skin of the newborn.
In some cases, the Mongolian spot remains anddoes not fade until adolescence. It should be noted that in children whose pigmentation is localized in atypical places, a defect for life may persist. This also applies to those cases where the Mongolian spot consists of many spots.
Diagnostic methods
Если на коже ребенка было обнаружено пигментное spot, then first of all it is necessary to seek advice from a specialized specialist - a dermatologist. The doctor must conduct a differential diagnosis. This will make it possible to determine what pigmentation is: Mongolian blot or other types of pigmented nevi. After all, other neoplasms are not excluded. Mongolian spot can be mistaken for Ota nevus, blue nevus, hair pigment nevus and so on. All these neoplasms are melanohazardous and at any time can be reborn into malignant ones. If such nevi is present on the baby’s skin, then it should be registered not only with the dermatologist, but also with the oncologist.
To make an accurate diagnosis, appoint a series of studies. This list includes:
- Dermatoscopy. In this case, the neoplasm is carefully studied under multiple magnification.
- Siopia This is a spectrophotometric scan of the pigmented area of the skin.
- For a more accurate diagnosis can be carried out.biopsy of the spot. This method is often used to detect diseases of a slightly different nature, for example, with warts, syringome, nodular pruritus, and so on.

Treatment and prevention
After completing a full examination anddiagnosis by a dermatologist must prescribe an adequate treatment. If the pigmentation on the skin is a Mongolian spot, then therapy is not carried out. A child with such changes must be registered with a specialist. Children with pigmentation should undergo various tests at least once a year.
It should be noted that the Mongolian spot is not a disease. As a rule, pigmentation passes independently and does not cause discomfort. Prevention in this case is also not carried out.

Forecast
If at birth the child appeared Mongolianspot on the tailbone or on the buttocks, then you should not be afraid. The prognosis is in most cases favorable. Studies show that the incarnation of such pigmentation in melanoma has not yet been fixed. For the same reason, the Mongolian spot does not need therapy. Five years after the appearance, the pigmentation may disappear. Only in some cases it persists until adolescence or remains for life. Mongolian spot does not cause discomfort and does not bother the child.












