The spinal cord system is considered the most ancientbody area. The mass of this part in an adult is about 34-38 g. In the course of the progression of the central part of the nervous system in the process of evolution, the ratio between the size of the brain and the spinal cord changed in favor of the first. Next, we consider in more detail what the structure is, what tasks it performs.
General Biology
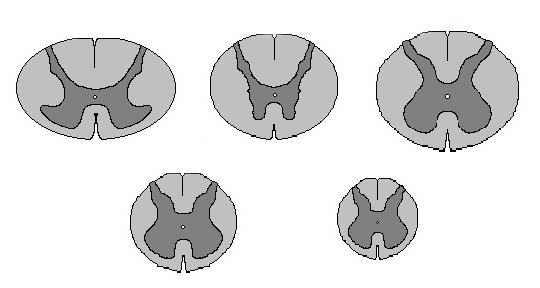
The spinal cord is an abnormal body.cylindrical shape. Its length in men is about 45, in women it is 41-42 cm. There are different sections of the spinal cord. At each site the body has a different size. Thus, the thoracic region has a sagittal size (in the plane from the back to the stomach) - about 8 mm. The diameter of this area is 10 mm. The thickening begins where the II-III segments (neck) are located. In this area, the diameter reaches 13-14 mm. In this case, the sagittal size is 9 mm. In the department, which is from the first lumbar to the second sacral fragment, a diameter of about 12 mm. Its sagittal size is 9 mm. The whole body is divided into specific areas (the number of segments of the spinal cord will be presented below). Next, we consider the constituent elements of the structure.
Spinal cord segments: picture, description
The body consists of similar (homomorphic)parts. The segments of the spinal cord are connected through nerve conductors to a specific area in the body. The length of a particular area of the body is different. The total number of spinal cord segments is 31. The lowest number of elements is in the coccygeal zone. In the structure there are:
- Lumbar segments (5).
- Sacral (5).
- Thoracic (12).
- The coccyx (1).
- Segments of the cervical spine (8).

The latter account for about 23.2% of the length of the entire structure. Most (56.4%) occupy the thoracic segments. 7.3% of the length falls on the sacral area. Spinal cord segments externally represent the posterior and anterior correctly alternating outgoing roots - the nerve processes. It should be noted that the structure does not fill the entire channel. In this regard, the spinal segments are located higher than the vertebrae of the same name. In this case, the difference between one and the second increases in the direction from top to bottom.

Location:
Skeletopy of sites is individually changeable.For example, in adults, the lower region of the lumbar region may be located from the lower third of the body of the XI thoracic vertebra to the disc between the first and second lumbar vertebrae. In this regard, a certain feature is visible. If the upper roots move in the transverse direction, the farther down the channel, the higher the exit section will be relative to the intervertebral opening. The last elements vertically tend to areas located below the level at which the spinal cord ends. All this bundle is surrounded by the end thread. It is called "horsetail".

End thread
From the second lumbar element down the spinal cordgoes into a special rudimentary education. It is called the "end thread". It is formed mainly by the pia mater. There are nerve cells in its uppermost zone. The end thread is of two kinds. It can be internal. In this case, it passes in the meninges to the second vertebra in the sacrum. The end thread may be outer. In this case, it extends beyond the second vertebra of the tailbone. The outer thread mainly consists of the continuation of connective tissue fibers. The inner end of the thread has a length of about 16, and the outer - 8 cm.
Dissymmetry
The segments of the spinal cord are not completely symmetrical.The unequal length and different level of root discharge are noted already at the stage of embryonic development. After birth, dissymmetry increases with time. It is more distinct in the chest area. In the posterior roots, dissymmetry is more pronounced than in the anterior. Apparently, this phenomenon is associated with differences in the skin and muscle innervation of the left and right sides of the human body.

Internal features of the elements
Рассмотрим коротко строение сегмента спинного the brain. In each element there is a disc - a plate located horizontally. At the level of this site are neural connections. Their position is also horizontal. There are vertical neural connections between the disks. Thus, the elements can be represented in the form of a stack of records. They, in turn, are connected by interneuron connections. The axons of the cells of the corresponding lateral horns of the spinal cord are involved in the formation of the anterior roots. They contain preganglionic sympathetic and efferent motor fibers; rear roots contain afferent structures. They are processes of neuronal ganglia. The total number of fibers present in the posterior roots is about 1 million on each side; in the front elements about 200,000 are detected in the complex. This is the ratio of 5: 1. Representatives
fauna prevailing fiber amountrear roots over those that are present in the front are not so pronounced. For example, a mouse, rat and dog ratio is 2.5: 1. In this way, one of the evolutionary patterns of the development of the nervous system of all vertebrates manifests itself. It lies in the fact that the formation of input channels is carried out more actively than the output. The latter are more stable. The number of nerve fibers in the posterior and anterior roots in one spinal segment is usually different. The difference can be up to 59% of the number of structures on the side where there are fewer.

Gray matter
In cross section, it representsa butterfly-like figure that opens its wings, or the letter N. Distinguish the rear, front and side horns. Their shape changes along the spinal cord. In the area bounded by the lateral and posterior horns, there is a reticular formation of a mesh type. Gray matter takes about 5 cm3 (about 17.8%) of the total volume of the spinal cord.The number of neurons present in it is approximately 13.5 million. They are combined into three groups: intercalated, beam, radicular. Gray matter constitutes a special apparatus of the structure. Here are some of the functions of the spinal cord. Irritations that flow through afferent fibers due to the presence of bonds can occur in both the descending and the ascending direction. In turn, they provoke a widespread motor response.
White matter
It contains projection, commissural andassociative neural pathways. The latter are bundles that pass along the periphery of the gray structure and along all the spinal cord cords. Commissural paths form a white commissure. It is located between the median front gap and the gray matter (connecting its halves). The projection paths (descending (efferent) and ascending (afferent)) provide communication with the brain.

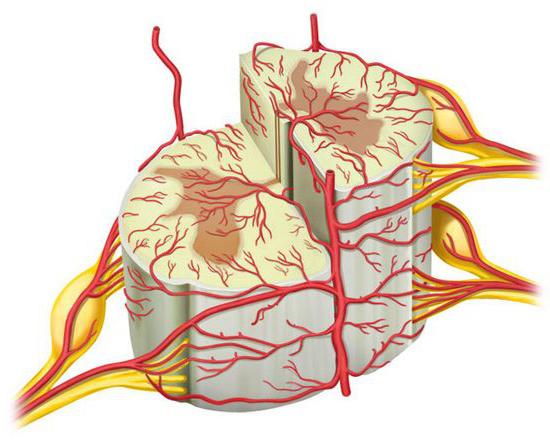
Blood supply
The flow of blood through the networknumerous vessels. They depart in the upper part of the subclavian, thyroid and vertebral arteries. The vessels also spread from the area where the second and third sections of the spinal cord are located. In this area, the blood supply comes from the branches of the aorta. More than sixty paired radicular arteries, which are formed near the intervertebral foramina, are distinguished by a small diameter (150-200 µm). They only supply blood to the roots and shells adjacent to them. In the diet, in fact, the spinal cord itself is involved about 5-9 arteries of large (400-800 microns) caliber. All of these vessels are unpaired type. They enter the channel at different levels: now through the right, then through the left hole. These arteries are called trunk or radicular-medullary. The number of the largest of them is not constant. Three vascular pools are distinguished:
- Upper or cervical-dorsal. It feeds the area where the segments of the spinal cord C1 - Th3 are located.
- Intermediate or medium. It includes areas of Th4-Th8.
- Lower. It feeds the region below the level of the Th9 segment.
Spinal anterior artery spreadsonly a few fragments of the structure. Further, it is not represented as a single vessel. It is a chain of anastomoses of several radicular-medullary large arteries. The blood flow in the spinal anterior artery goes in different directions. In the upper sections - from the top down, in the middle - from the bottom up, and in the lower - up and down.

Main goals
There are two main functions of the spinal cord.The first is reflex, the second is conductive. Each segment is associated with certain organs and ensures their activity and functionality. For example, sacral elements relate to the legs and organs of the pelvis and are responsible for the activities of these zones of the body. One or other pectoral segment interacts with the corresponding organs and muscles. The upper elements are connected with the head and hands. The reflex functions of the spinal cord are simple reflexes set by nature. These include, in particular, the reaction to pain - a person pulls his arm, for example. Also in this category include the famous knee jerk. The brain may not participate in the manifestation of these reactions. This theory is proved by ordinary experiments with animals. In the absence of the head, the frog reacted to both strong and weak pain stimuli. The conductive functions of the spinal cord are enclosed in impulse transmission. First he goes up. On the ascending path, the impulse enters the brain, and from there it is sent as a reverse command to an organ. Due to this conductor connection, any mental activity is manifested: take, go, stand, pick up, cut off, run, throw, draw. Also, the conductive functions of the spinal cord provide the implementation of actions that people, without noticing, perform daily at work or at home.
Side horns
These elements have their own functions.In the lateral horns (intermediate zone in the gray matter) are sympathetic cells of the vegetative nervous structure. It is through them that interaction with internal organs is carried out. These cells have processes that are connected to the anterior roots. A path is formed in this zone: in the region of the segments of the upper two regions of the spinal cord there is a reticular region - a bundle of a large number of nerves that are associated with regions of the activation of the cortex in the brain and reflex activity. The activity of gray and white matter beams, front and back roots is called reflex reaction. The reflexes themselves are called, by definition, Pavlov, unconditional.
Ascending paths
The anterior cords of white matter have several paths, each of which performs certain tasks:
- The cortical-spinal cord (anterior pyramidal) is responsible for the transmission of motor impulses from the cortex in the brain to the anterior horns in the spinal cord.
- Spinothalamic front provides tactile sensitivity.
- The bundle of Levental and Held - the fibers of the white substance are connected by the vestibular nuclei of 8 pairs of cranial nerve endings with motor neurons in the anterior horns.
- Покрышечно-спинномозговой путь формирует защитный reflex that is associated with visual or sound stimuli. This is due to the connection of the visual centers under the cortex in the brain with the nuclei in the front horns.
- The longitudinal beam provides coordination of the eye and other muscles, due to the binding of the upper segments with the stem of the spinal cord.
- In the ascending path passes the impulse deepsensitivity. As a result, there is a feeling of his body in a person. The impulses travel through the back to the spinal cord, spinal cord and cortical-spinal canals.
Descending paths
Impulse transmission from the cortex in the brain togray matter in the front horns is carried out along the lateral cortical-spinal canal. The red core-spinal path provides automatic adjustment of muscle tone and movements at a subconscious level. This channel is located in front of the lateral pyramidal. The spinotalamic lateral and posterior spinal cord are adjacent to the red-spinal tract.
Age features
Временные изменения касаются как строения spinal cord and its topography. In the second half of the period of prenatal development, its slow growth is noted. In particular, it lags behind the development of the spinal column. And this continues for quite a long period. In infants, the cerebral cone is located in the region of the third lumbar vertebra, and in an adult it ends at the level of the first or second. Over the entire growth period, the length of the structure increases by 2.7 r. This is mainly due to the thoracic segments. The mass of the structure increases by about 6-7 times. The growth of the white and gray matter of the spinal cord is quite uneven. The volume of the first is increased by 14, and the second - by 5 times. This is due to the fact that development in its own segmental apparatus is completed earlier than in projection nerve paths.

Finally
Между спинным и головным мозгом, ЦНС, всеми human organs and limbs have a unique connection. It is considered a "robotics dream". To date, no one, even the most modern robot, can perform all those possible actions and movements that are subject to a biological organism. Such modern machines are programmed to perform highly specialized tasks. Most often, these robots are used in automatic conveyor production. The mass of the spinal cord as a percentage is different in different representatives of the animal world. For example, in a frog - 45, turtles - 120, rats - 36, macaques - 12, dogs - 18, and in humans - 2. The general structural features and patterns of the central zone of the nervous system are quite clearly manifested in the structure of the spinal cord.





