Переломы черепа относятся к самым тяжелым травмам.Such violations of the integrity of the cranial bones occur after severe strokes on the head and are often accompanied by brain damage. Therefore, these injuries are life-threatening. And even with a favorable outcome, they have serious consequences for the patient's health. It is very important that the first aid in case of head injury is provided in time. This will help prevent a fatal outcome. But in any case, the treatment of such injuries is very long and requires a complex rehabilitation.
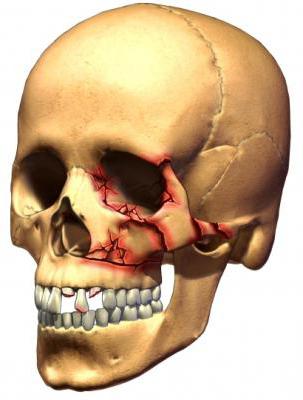
Features of skull fractures
Craniocerebral injuries are very common,especially in young and middle age. They cause about half the deaths among all injuries. This is due to the fact that a violation of the integrity of the cranial bones often leads to compression or damage to the brain and blood vessels. In addition, the skull has a very complex structure. A lot of bones are connected by seams, they have different structure and thickness. Some bones are permeated with blood vessels or have air-bearing cavities. Distinguish facial and brain departments of the skull. It is in the brain that injuries occur most often.
Features of fractures of cranial bones are thatwhen impact external damage may not be noticeable. In fact the arch of a skull consists of internal and external plates, between which the spongy substance is located. The inner plate is very fragile, so when it strikes it is damaged most often, even without disturbing the integrity of the outer plate.
The causes of such injuries
Cranial fractures occur as a result of the applicationgreat strength. They are often exposed to people of young and middle age, leading an active life or doing sports. And also alcoholics, drug addicts and representatives of criminal structures. It is possible to single out such reasons, according to which there are fractures of the skull:
- Strong strokes on the head with a solid object;
- falling from a height;
- car crashes;
- gunshot wound.
There are two mechanisms for obtaining such an injury:direct and indirect. When a bone breaks in the place of application of force - this is a direct fracture. This usually results in injuries to the cranial vault. Damaged bones are often pressed inside and damage the meninges. With an indirect fracture, the effect is transmitted from other bones. For example, when falling from a height to the pelvis or legs through the spine, a strong impact is transmitted to the base of the skull, often leading to its fracture.
Symptoms of skull fractures
On how to properly receive first aidat a craniocerebral trauma, the further condition of the patient depends. At any strong impact in the head area, one must suspect the possibility of fracture of the skull bones. Sometimes such a trauma is not accompanied by well-visible symptoms. But there are also special signs on which it is possible to determine not only the presence of a fracture, but sometimes the site of its localization and damage to the meninges.
- The main symptom of a skull fracture is impaired consciousness. This may be fainting or coma, memory loss, confusion, hallucinations.
- In addition, skull fractures are always accompanied by severe headaches, dizziness, and nausea.
- With damage to the brain and nerve fibers, there is a violation of sensitivity, paresis and paralysis.
- If the brain stem is affected by a fracture, breathing may be difficult, and blood circulation may be impaired.
- At a fracture of the base of the skull, hematomas around the eyes or in the region of the mastoid process are often characteristic symptoms. There may be bleeding with admixtures of cerebrospinal fluid from the nose, ears.
- A very serious injury is considered a fracture of the temporal bone. It causes severe dizziness, incoordination, nausea, hearing loss, paralysis of the facial nerve.
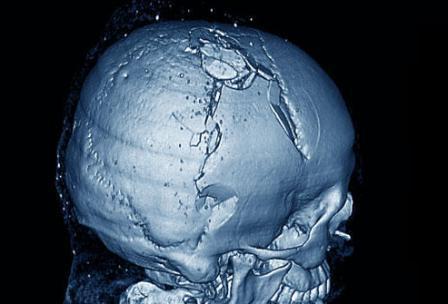
Skull fracture classification
Injuries to the cranial bones can be different.They are classified by the nature of the fracture, the site of localization, the severity of the lesion. Different parts of the skull may be affected. According to the nature of the injury, there are three types:
- the most severe is a comminuted fracture, as a result of which the meninges and blood vessels may be damaged;
- a depressed fracture also has serious consequences, because with it the bones of the skull are pressed inwards, which causes crush of the brain;
- linear fractures are considered non-hazardous, since no displacement of bone fragments occurs, but they can cause vascular damage and the appearance of hematomas;
- a perforated fracture resulting from a gunshot wound is also very rare, as a rule, such an injury is incompatible with life.
At the site of injury there is a temporal fracture.bone, occipital or frontal. They belong to the injuries of the cranial vault. If the base of the skull is damaged, it causes cracks in the facial bones, they extend to the orbit, nose bridge, and even the ear canal. In addition, the fracture of the skull bones can be open or closed, single or multiple. The patient's condition depends on the severity of the injury, the degree of damage to the meninges and blood vessels, as well as the time of medical assistance provided.

Fracture of the cranial vault
Occurs from a blow to the scalp.Therefore, the main symptom of such an injury is a wound or hematoma in this place. But the difficulty of diagnosing this trauma is that often the internal plate of the cranial bone is damaged during an impact, which outwardly is almost invisible. The patient may even regain consciousness, but gradually the symptoms of brain damage will increase. Fracture of the cranial vault can occur for various reasons, most often - upon impact. Particularly susceptible to such injuries are people in alcoholic and drug intoxication. Indirect exposure, for example, when falling on the pelvis, may be accompanied by a fracture of the skull base. In this case, the patient's condition is especially severe, and the injury can be fatal.
Skull base fracture
The survival rate for such injuries depends ontimely medical care. The fracture in this place can be independent or accompany the injury of the cranial vault. In addition, there is a fracture of the anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossa. Such injuries, depending on the location and severity, are accompanied by bleeding from the nose and ears, the expiration of the cerebrospinal fluid. A characteristic symptom of anterior cranial fossa fracture is bruising around the eyes. When such injuries affect all the senses of the patient: impaired vision, hearing, smell, coordination of movements. A very serious injury is considered a fracture of the base of the skull. The survival rate is about 50%.

Diagnosis of injuries
When any traumatic brain injury is carried outexamination to rule out a fracture. In addition to interviewing the victim or his accompanying circumstances of the injury, the doctor examines the patient. Sensitivity, reflexes, pulse rate and pupil response to light are evaluated. A radiograph of the skull in two projections is also made. To confirm the diagnosis, the results of magnetic resonance and computed tomography, brain puncture and echoencephalography are used. Such a study should be carried out even in the absence of visible consequences of injury, since after the impact only the inner lamina of the skull bones can be damaged.

Features of skull fractures in children
Despite the confidence of many that the cranialbones in a child are stronger, such injuries occur frequently in babies. Moreover, their diagnosis is difficult, and the consequences are usually more serious. Fracture of the skull of a child is dangerous because immediately after the injury the victim can feel good. This is due to the lack of development of the frontal lobes and other parts of the brain. The consequences appear later: a strong increase in pressure, loss of consciousness, vomiting, anxiety, tearfulness. A feature of the cranial injuries in children are multiple linear cracks, seam divergence and bone indentation. Fragile fractures, hematomas and hemorrhages are less common than in adults. But complications can be just as serious: often developing epilepsy, hydrocephalus, developmental delays, visual and hearing impairment.

First Aid
When getting a brain injury is veryit is important how quickly the affected person will receive medical care. Often his life depends on it. Until the victim is taken to the hospital, he should be laid on a hard surface without a pillow, fixing his head with soft objects. If he is conscious, he can lie on his back. When the victim faints, you need to turn on its side, fixing the head with pillows so that it does not choke on vomiting. It is advisable to remove all jewelry, glasses, dentures, undo clothes. The victim should be provided with free access of air.
If the injury on the head is bleeding, on ita sterile dressing is applied, ice can be applied, but you should not touch or press on the injury site. It is not recommended to give the patient any drugs before the arrival of the doctor, as, for example, narcotic analgesics can cause respiratory failure. As soon as possible, the victim must be taken to a doctor, even if he is conscious and feels normal. After all, the injuries of the skull never pass without a trace. And without timely treatment can cause serious consequences.
Features of the treatment of skull fractures
A victim with a head injury shouldbe in the hospital. Depending on the severity and location of the injury, it may be prescribed conservative or surgical treatment. Be sure to comply with bed rest. The head should be slightly raised to reduce the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid. In case of injury to the base of the skull, a lumbar puncture or drainage is necessary. In case of moderate and mild fractures, medical therapy is carried out. The following drugs are prescribed to the patient:
- painkillers, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory;
- diuretics;
- antibiotics to exclude purulent infection;
- nootropic and vasotropic agents;
- drugs to improve cerebral circulation.
If the fracture is severe, for example, comminuted orpressed, with multiple damage to the bones, then surgical treatment is carried out. It is needed to remove fragments and areas of necrotic tissue, as well as accumulated blood. During the operation, damage to the nerves and blood vessels is also eliminated. Surgical treatment is used if purulent infection has begun, which cannot be eliminated with the help of conservative therapy.
Consequences of such injuries
If the skull fracture is linear, without displacement of the bonesand large hematomas, and if it was possible to avoid purulent infection, the prognosis for cure is usually favorable. But not always without complications goes skull fracture. The consequences of such an injury can be very serious:
- meningitis, encephalitis;
- intracerebral hematomas can lead to encephalopathy;
- heavy bleeding often ends in death;
- paralysis of the whole body may develop after a fragmentary fracture of the skull base;
- often patients suffer from psychological and emotional disorders, mental decline.
Rehabilitation after skull fractures
With minor injuries patient recoverypasses quickly. Rehabilitation is mainly carried out at home and includes rest, walks in the fresh air, taking nootropic and sedative preparations, and a special diet. Heavier injuries rarely do without consequences. Rehabilitation of such patients is long, sometimes takes years. But still, many remain disabled and cannot return to their normal life.