Infectious endocarditis is called valvular lesion of the heart and endocardium. The cause of it is bacteria. As a rule, it is streptococci. But sometimes the causative agents are fungi.
Etiology and pathogenesis
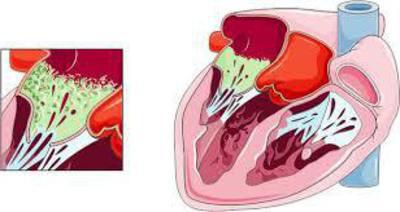
The most common pathogens fallto the heart chambers along with the bloodstream. However, there are cases when infective endocarditis becomes ill due to the fact that the infection is carried out during open-heart surgery. Microbes settle on the valves and infect the endocardium. Tissues with anatomical defects or lesions are most susceptible to infection. However, normal heart valves are also affected by some types of microorganisms, especially against the background of a general decrease in immunity. It happens that the colonies of bacteria and accumulations of blood clots are destroyed and enter the other organs with the bloodstream. They can infect them or provoke blockages in their arteries. Because of this, the patient may begin an inflammatory process in the zone of accumulation of pathogens, a heart attack or stroke.
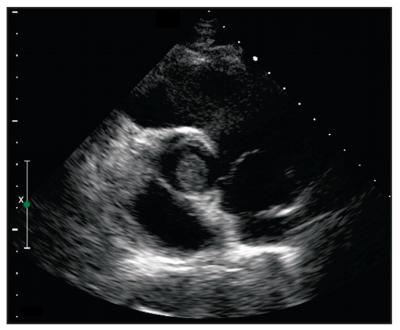
Infective endocarditis: classification
This disease is acute and subacute.Acute infective endocarditis is a disease that begins suddenly (up to several days) and is life threatening. The temperature of a person’s body rises to 40 ° C, the rate of heart contractions greatly increases, fatigue quickly increases and there is extensive valve damage. Emboli (endocardial vegetations) break away from it, which are carried by the bloodstream through the body, entering other organs, which can cause inflammation and blockage of important vessels. Within a few days, severe heart failure, shock, and septic syndrome with internal organ failure may develop. Artery weakened by inflammation can rupture. With this form of the disease is fatal.
Subacute infective endocarditis is calleda disease that develops gradually. Its imperceptible course can last from several weeks to several months. Without a special examination, only serious valve damage or embolism can diagnose endocarditis. In unexpressed cases, the symptoms may be as follows: a slight increase in temperature (usually not more than 38 ° C), persistently increased sweating, weight loss, anemia, and high fatigue.

Заподозрить, что человек болен инфекционным endocarditis, it is possible, if his temperature lasts for a long time without an obvious source of infection, an inflammatory process; existing heart sounds appear or change; spleen is enlarged. Often on the skin of a person there are small spots that resemble freckles. They may appear under the nails and on the whites of the eyes. These are small hemorrhages that are provoked by the entry of detached emboli into small vessels. Larger blood clots can cause large arteries in the arms or legs to clog, cause abdominal pain, stroke, or heart attack. Methods of treating diseases - antibiotic therapy, surgery (if necessary, remove bacterial vegetations or valve replacement).
Secondary endocarditis
The disease may develop again after alreadythe disease or for the first time against the background of existing ailments (heart defects and abnormalities, atherosclerosis, rheumatism, etc.). This pathology is called "secondary infective endocarditis."