The most common problem encountered withteeth, is caries. Therefore, most people assume that caries is the only reason why teeth can decay. But in fact, there are diseases that are not carious in nature, in which the damage and destruction of teeth occurs not under the influence of environmental factors, but because of the peculiarities of their structure.
These problems include enamel hypoplasia.teeth. This disease carries a serious danger, and the damage to the tooth caused by this disease cannot be treated or fully restored. However, the timely identification of the problem can significantly change the situation. Accordingly, it is very important to detect the disease at its early stage, as well as to establish the reasons for which it arose. Symptoms and diagnostics help the dentists with this.

Concept of hypoplasia
A layer of enamel that covers a healthy toothhuman, has a fairly strong structure, because its main purpose is to protect the internal structures of the tooth from the negative effects of the external environment. However, there may be situations in which the problem arises due to internal problems in the body. For example, hypoplasia of tooth enamel is a disease that can damage all tooth tissues without exception.
The most common variant of the disease ishypoplasia of tooth enamel. When this disease occurs, the tooth damage is of a non-carious nature. Causes of hypoplasia are considered deviations that have arisen in the process of formation and formation of enamel. As a result of this pathology, a layer of enamel is thinning, and the pathology may have a different form of severity.
Types of hypoplasia
Dentists note that enamel damage whenThe mild form of hypoplasia may be minimal, but the disease has a severe form. In this case, the tooth does not have a protective layer at all. This form is called aplasia.
The development of this disease can begin inany age. Although hypoplasia of tooth enamel is most common in children who still have milk teeth, there is no guarantee that the same symptoms will not occur in an adult.
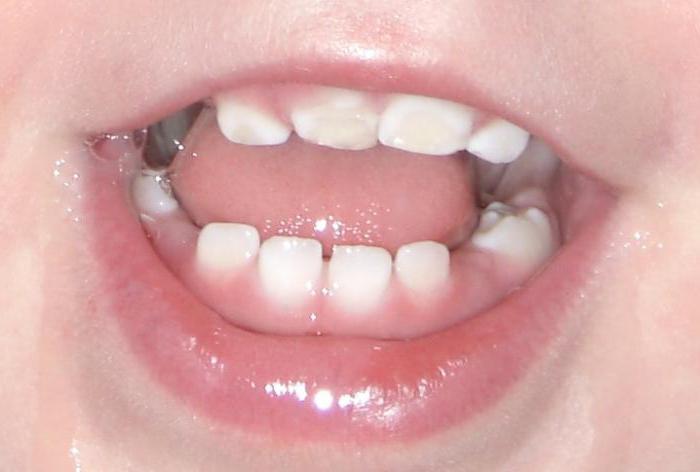
If you stick to the main classification,the disease can be divided into two types - systemic hypoplasia and local hypoplasia. When a systemic form of the disease occurs, the greatest threat appears, since in this case the entire enamel layer of the tooth is affected. The systemic form of hypoplasia in serious condition implies not so much the thinning of the enamel layer, but its serious underdevelopment, which manifests itself in the form of the formation of waves, grooves and points. Hypoplasia in the local form often affects the molars, which have undergone any damage at the stage of formation.
Tooth enamel hypoplasia isquite a serious problem, as a result of it there is a general weakness of the tooth and its protective layer, which, in turn, is a favorable environment for the emergence of other pathologies and diseases.
Causes
Currently, doctors adhere to twothe main theories regarding the nature of hypoplasia. The first group of experts believes that the beginning of the process that destroys the enamel, can be triggered by impaired mineralization. The other group of experts is of the opinion that such a cause is not of a single character, and the delayed function of epithelial cells in the tooth germ also influences the development of hypoplasia. However, it is worth noting that, along with physiological reasons, other factors are also of great importance, under which a favorable environment and conditions are created for the further development of enamel hypoplasia of permanent teeth.
Dental teeth diseases
Due to the fact that the formation of milk teethoccurs at the stage of intrauterine development of the infant, their general condition largely depends on how the pregnancy proceeded, as well as on the state of health of the mother of the child.
- diseases of the digestive system of the mother;
- infectious diseases that were carried by the mother during pregnancy;
- deviations in the position of the fetus;
- congenital diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- the influence of factors such as chemicals or dangerous temperatures;
- artificial feeding of the child;
- prematurityExperts are of the opinion that the latter reason has become relevant not so long ago and has led to an increase in the number of children suffering from hypoplasia. The situation is such that modern technologies allow even too premature babies to be cared for, but these children have not yet completed the development of tissues and organs. In this regard, premature babies and subsequently suffer from the hypoplasia of the enamel of milk teeth, since there was a violation of the process of its formation, or it was completely interrupted;
- lack of water;
- severe toxicosis;
- traumatic injuries. These include injuries from childbirth;
- bad habits during pregnancy.
All of these factors cause an early age hypoplasia of the enamel of milk teeth in a child.

Pathology of molars
Such pathology may begin to develop in earlyage in the first years of a child’s life. The formation and development of the molar embryos begins to occur at about six months of age. Therefore, it is quite logical to assume that the impairment of health at this age can trigger the process of impaired development of tooth enamel. In this regard, the hypoplasia of the molars can often be found in those people who in childhood suffered from such diseases as:
- severe forms of infectious diseases;
- rachites;
- kidney diseases, as well as disorders in the endocrine system;
- syphilis;
- serious disorders in the digestive system;
- anemia due to iron deficiency;
- brain dysfunction.
Tooth enamel hypoplasia will develop andappear on the molars depending on the age at which the child suffered this or that disease. For example, if the disease was transferred at the initial pores of life, then damage to the tooth enamel can be observed along the edges of the central incisors and the first large permanent teeth. The disease in the ninth month of life can provoke a lesion of enamel on the second and third order incisors on both sides, as well as on the central incisors and large chewing in the area of their crown.

Symptoms of hypoplasia
The diagnosis of this disease is notis a complex procedure for a competent specialist, for it has specific symptoms. But patients should still independently monitor the state of the enamel of their teeth. Only this will make it possible to timely detect the problem at the stage of its early development.
Systemic form of hypoplasia
As we have noted, the systemic form of the diseasemay manifest in varying degrees of severity. So, with the appearance of a light form, a partial change in the color of the tooth enamel is observed - on its surface, yellowish areas are formed, which have clearly defined boundaries. Such defects can be seen in the photo with hypoplasia of tooth enamel. The specificity of this form lies in the fact that the lesions in the form of spots have exactly the same size and are arranged symmetrically - on the same teeth on both sides of the jaw. Most often, this form of the disease affects the front side of the teeth, therefore, if you pay due attention to the state of your teeth, then the development of the disease at an early stage is absolutely not difficult to notice. In this form of hypoplasia, pain is not felt, and the thickness of the tooth enamel on the affected and healthy areas of the tooth is the same.
When the second degree of difficulty occursunderdevelopment of tooth enamel, which can be characterized by the appearance of changes of different types. Wavy pattern can be identified visually and in the absence of additional devices. If the tooth is dried, then small rollers will be visible on its entire surface. Another manifestation is the grooves - they, as a rule, have a single location and are located across the tooth. Along with the wave-like manifestations, the grooves are arranged alternately with healthy areas of the tooth enamel. The most common third type of manifestations - point. In this case, over the entire surface of the tooth are recesses, which eventually change their color to darker. Therefore, it is necessary to detect and start the treatment of tooth enamel hypoplasia in children in time.
Aplasia

The most dangerous stage of hypoplasia isaplasia, that is, a form in which tooth enamel is completely absent. Such a manifestation may be localized in a specific area of the tooth or may affect the entire tooth. In this form, there are significant pain sensations that occur as a reaction to environmental stimuli. A specific characteristic is that the painful sensation passes immediately after the external effect on the tooth has been stopped.
Local form
The main feature of the local form of enamel hypoplasiaPermanent teeth in children and adults is the process of the appearance of stains on the surface of the enamel coating, which may have different colors. Shades of such spots can range from pale yellow to dark brown. Such a defeat of the tooth enamel is manifested by the formation of recesses of a point character, which are everywhere located on the entire surface. It should be noted that this form can occur only on the molars.
Diagnosis of hypoplasia
Inherited tooth enamel hypoplasia as coupledwith the X chromosome dominant trait. As a rule, the diagnosis of hypoplasia does not cause difficulties for dentists due to the fact that the disease has visual symptoms that can be easily noticed. The main task of the dentist is to differentiate hypoplasia from a lesion of carious nature. In order to perform such an examination, doctors use three main methods:
- visual assessment of the enamel surface. With carious manifestations, the tooth enamel has a rough surface, and with hypoplasia, it remains smooth;
- assessment of the number of spots (hypoplasia is characterized by multiple manifestations);
- staining of the enamel affected areas with methylene blue solution. Spots characteristic of hypoplasia do not stain with this solution, in contrast to carious lesions.
Treatment of enamel hypoplasia of permanent teeth
The method of treatment of the disease depends on the clinical manifestations, that is, on the form and severity of the pathology, as well as on the nature of the changes.
В случае если гипоплазия проявляется путем the appearance on the enamel of light spots in small quantities, which are located on such parts of the teeth that are not too visible, the treatment of this manifestation is optional.
In the event that the spots are located on the frontthe surfaces of the incisors are noticeable, the defect can be repaired. Unfortunately, it is not possible to restore the affected enamel, so the doctor can apply various filling materials, as well as veneers or crowns.

What to do if hypoplasia in the form of grooves and strips?
If the disease manifests itself in the form of depressions, grooves, or strips, then the tooth filling according to the classical scenario may be effective.
If the teeth restored in this way are treated with care, then they will be functional and aesthetic for a long enough period.
Veneers are plates thatThe dentist attaches to the outer surface of the tooth. This type of crowns has a flawless appearance, but the inner side of the teeth still has a not quite attractive appearance. But because of its invisibility, veneers can be an excellent solution for treating hypoplasia.
If the tooth has a sufficiently modified shape,resulting from pathology, the dentists tend to use orthopedic crowns. Installing such a crown is a rather complicated job. Therefore, if there is an alternative opportunity to restore the aesthetic appearance of the teeth, then it is necessary to delay the installation of an orthopedic crown.






