Особенностью синхронных электродвигателей is that the magnetic flux and the rotor rotation speed are the same. For this reason, the rotor of an electric motor does not change its speed with increasing load. On the rotor there is a winding that creates a magnetic field.
Powerful permanent magnets are sometimes used.Usually in synchronous machines on the rotor there are as many windings as on the stator. So it turns out to align the speed of rotation of the magnetic flux and the rotor. The load that is connected to the motor does not affect the speed at all.
Construction of the electric motor

The synchronous motor device consists of the following elements:
- The stationary part is the stator on which the windings are located.
- The movable rotor, it is sometimes called the inductor or anchor.
- Front and rear covers.
- Bearings mounted on the rotor.
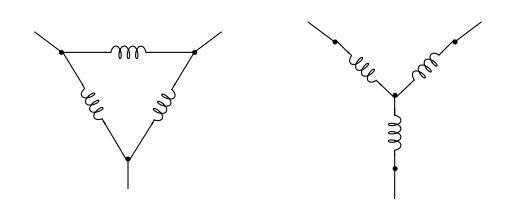
Between anchor and stator there is freespace. The windings are laid in the slots; they are connected into a star. As soon as the motor is energized, a current flows through the armature winding. Formed magnetic field around the inductor. But voltage is also applied to the stator. And here a magnetic flux occurs. These fields are offset from each other.
How does a synchronous motor work
In synchronous machines, the electromagnets on the stator are poles, as they operate on direct current. In total there are two schemes by which the stator windings are connected:
- Pole pole.
- Implicit pole.
In order to reduce the magnetic resistance and optimize the conditions of the passage of the field, apply the cores made of ferromagnetic. They are both in the stator and in the rotor.

They are made from special varietieselectrical steel, which contains a huge amount of such an element as silicon. With this, it is possible to significantly reduce the eddy current, as well as to increase the electrical resistance of the metal.
The basis of the synchronous motorslies the interaction of the poles of the stator and the rotor. At start-up, acceleration occurs up to the speed of the flow. It is in such conditions that the electric motor operates in synchronous mode.
Starting method with optional electric motor
Previously used special engines forstart-up, which are connected to the motor using mechanical devices (belt drive, chain, etc.). During start-up, the rotor began to rotate and, gradually accelerating, reached the value of synchronous speed. After that, the electric motor itself began to work. This is the principle of operation of a synchronous motor, regardless of the design and manufacturer.

The prerequisite is that the launcherthe electric motor should have a power of about 15% of the similar characteristics of the accelerated motor. This power is quite enough to start any synchronous motor, even if a small load is connected to it. This method is quite complicated, and the cost of all equipment is significantly increased.
Modern launch method
Modern designs of synchronous electric motors are not equipped with such schemes for overclocking. Another launch system is used. Approximately the synchronous machine is activated:
- With the help of a rheostat, the rotor windings are closed. As a result, the anchor becomes short-circuited, as on simple asynchronous electric motors.
- There is also a short-circuited winding on the rotor, which is soothing, it prevents the armature from swinging during synchronization.
- As soon as the anchor reaches the minimum rotational speed, a direct current is connected to its windings.
- If permanent magnets are used, then it is necessary to use external starting motors.
There are cryogenic synchronous electric motors that use a reversed type design. Excitation windings are made of superconducting materials.
The advantages of synchronous machines

Asynchronous and synchronous motors havevery similar constructions, but differences still exist. In the latter, there is a clear advantage in that excitation from a constant current source occurs. In this case, the motor can work with a very large power factor. There are also other advantages of synchronous motors:
- They work with an overestimated coefficient.This allows to reduce power consumption, and also significantly reduces the loss of current. The efficiency of a synchronous machine will be much higher than that of an asynchronous motor with the same power.
- Torque depends on the voltage in the supply network. Even if the voltage in the network decreases, the power will remain.
But still, asynchronous machines are used much more often than synchronous ones. The fact is that they have greater reliability, simple construction, do not require additional maintenance.
Disadvantages of synchronous motors

It turns out that the disadvantages of synchronous machines are much greater. Here are the main ones:
- The scheme of a synchronous motor is quite complicated, it consists of a large number of elements. For this reason, the cost of the device is very high.
- Be sure to use to power the inductor DC source. This greatly complicates the entire structure.
- The procedure for starting an electric motor is quite complicated than that of asynchronous machines.
- Adjusting the rotor speed is possible only by using frequency converters.
In general, the advantages significantly overlapdisadvantages of synchronous motors. For this reason, they are very often used where it is necessary to conduct a continuous continuous production process, where it is not necessary to frequently stop and start equipment. Synchronous machines can be found in mills, crushers, pumps, compressors. They rarely turn off, work almost constantly. Through the use of such motors can be achieved significant energy savings.