What are natural complexes?This is a geographical concept, which denotes a series of interrelated components of nature. They can cover both vast areas and completely small areas of the Earth. What are natural complexes? What is the difference? What is characterized? Let's find out.
Geographic shell
Telling what natural complexes are,It is impossible not to mention the geographical envelope. This is a conditional concept that unites several spheres of the Earth at once, which intersect and interact with each other, forming a single system. In fact, it is the largest natural complex on the planet.
The boundaries of the geographical envelope almost repeatedge of the biosphere. It includes the hydrosphere, the biosphere, the anthroposphere, the upper part of the lithosphere (the earth's crust), and the lower atmosphere (troposphere and stratosphere).

The shell is one-piece and continuous.Each of its components (terrestrial spheres) has its own patterns of development and features, but at the same time it is influenced by other spheres and influences them. They constantly participate in the cycles of substances in nature, exchanging energy, water, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, etc.
Natural complex and its types
The geographical envelope is the largest, butnot the only natural complex. There are a lot of them on the globe. What are natural complexes? These are certain parts of the planet that have a uniform geological structure, soil, vegetation, animal world, climatic conditions and the same water character.
Natural complexes are also called landscapesor geosystems. They differ in vertical and horizontal directions. Proceeding from this, the complexes are divided into zonal and azonal complexes. The main reason for their diversity is the heterogeneity of the geographical envelope.

First of all, differences in natural conditionsprovide an uneven distribution of solar heat on Earth. This is due to the elliptical shape of the planet, the unequal relationship between land and water, the location of mountains (which hold up air masses), etc.
Zonal natural complexes
Zonal natural complexes representmainly horizontal division of the planet. The largest of these are the geographical belts. Their location is consistent and regular. The emergence of these complexes is directly related to the climatic conditions of the area.
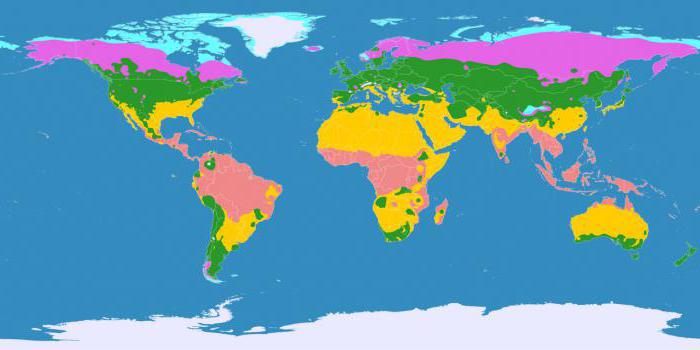
The nature of the geographical belts varies fromequator to the poles. Each of them has its own temperature and weather conditions, as well as the nature of soils, underground and surface waters. There are such belts:
- arctic;
- subarctic;
- Antarctic;
- subantarctic;
- northern and southern temperate;
- northern and southern subtropical;
- northern and southern subequatorial;
- equatorial.
The next largest zonal complexesare natural zones, which are divided according to the nature of moistening, that is, the number and frequency of precipitation. They do not always have a purely latitudinal distribution. And depend on the height of the terrain, as well as proximity to the ocean. Isolate the arctic desert, steppe, tundra, taiga, savannah and other natural areas.
Azonal natural complexes
Azonal complexes are not connected with latitudinaldivision of the planet. Their formation is associated primarily with the relief and formation of the earth's crust. The largest azonal natural complexes are the oceans and continents, which differ significantly in geological history and structure.
The continents and oceans are divided into smaller complexes -natural countries. They consist of large mountain and lowland formations. For example, the natural complexes of the Far East include the Central Kamchatka Plain, the Sikhote-Alin Mountains and the Khingano-Bureya Mountains, and others.

The natural countries of the world include the desertSahara, the Ural Mountains, the East European Plain. They can be divided into narrower and more homogeneous areas. For example, gallery forests, located on the outskirts of the steppes and savannas, mangrove forests located along the coast of the seas and in the mouths of rivers. The smallest natural complexes include river floodplains, hills, ridges, uremas, swamps, etc.
Components of natural complexes
The main constituent parts of anyThe geographical landscape is relief, water, soil, flora and fauna, climate. The interconnection of the components of the natural complex is very close. Each of them creates certain conditions for the existence of others. Rivers affect the condition of soils, soils and climate - on the appearance of certain plants, and plants attract certain animals.

Changing even a single component can lead tocomplete change of the whole complex. Drainage of the river will lead to the disappearance of vegetation characteristic of river terrain, to a change in soil quality. This will certainly affect animals that leave the geosystem in search of their usual conditions.
Чрезмерное размножение какого-либо вида животных can lead to the extermination of the plants that they consume for food. There are cases when huge swarms of locusts completely destroyed meadows or fields. This development of events does not remain inconspicuous for the natural complex and provokes changes in the soil, water, and then the climate regime.
Conclusion
So what are natural complexes?This is a natural-territorial system, the components of which are homogeneous in their origin and composition. The complexes are divided into two main groups: azonal and zonal. Within each group there is a separation from large to smaller areas.
The largest natural complex isgeographic envelope, which includes part of the lithosphere and atmosphere, the biosphere and hydrosphere of the Earth. The smallest complexes are individual hills, small forests, estuaries, marshes.











