The second largest continent in the world (after Eurasia) is Africa. Its subregions (their economy, population, nature, and states) will be discussed in this article.
Variants of division of the continent

The territory of Africa is the largest geographicalregion of our planet. Therefore, the desire to divide it into parts is quite natural. The following two major areas are distinguished: Tropical and North Africa (or Africa north of the Sahara). Between these parts there are quite large natural, ethnic, historical and socio-economic differences.
Tropical Africa is the most backward regiondeveloping world. And nowadays, the share of agriculture in its GDP is higher than the share of industrial production. 28 out of 47 least developed countries of the world are located in Tropical Africa. Also here is the maximum number of countries that do not have access to the sea (there are 15 such states in this region).
There is another option for dividing Africa into regions. According to him, its parts are South, Tropical and North Africa.

We now turn to the consideration of the actualregionalization, that is, the allocation of large macroregions (subregions) of the continent of interest. At present, it is considered that there are only five of them. Africa subregions has the following: South, Eastern, Central, West and North Africa (on the map above). At the same time, each of them has specific features of the economy, population and nature.
North Africa

North Africa goes to the Red and Mediterraneanthe sea as well as the Atlantic Ocean. Due to this, its relations with Western Asia and Europe have been established since ancient times. Its total area is about 10 million km2, на которых проживают около 170 млн человек.The Mediterranean "facade" defines the position of this subregion. Thanks to him, North Africa is adjacent to South-West Asia and Southern Europe. It has access to the main sea route, which runs from Europe to Asia.
Cradle of civilization, Arab colonization
Low-habitable Sahara desert spaces form"rear" of the region. North Africa is the cradle of the civilization of ancient Egypt, who made a great contribution to culture. The Mediterranean part of the continent in ancient times was considered the breadbasket of Rome. To this day, among the lifeless sea of stone and sand, one can find the remains of underground drainage galleries, as well as other ancient structures. Many cities located on the coast, originate from the Carthaginian and Roman settlements.
Arab colonization, which took place in 7-12 centuries., had a huge impact on the culture of the population, its ethnic composition and lifestyle. And nowadays, the northern part of Africa is considered Arabic: almost the entire local population is Muslim and speaks Arabic.
Economic life and population of North Africa
In the coastal strip is concentrated economicthe life of this subregion. Here are the main manufacturing enterprises, as well as the main areas of agriculture. Naturally, it is here that almost the entire population of the subregion lives. Pise houses with earth floors and flat roofs prevail in rural areas. Cities also have a very distinctive appearance. Therefore, ethnographers and geographers distinguish the Arabic type of city as a separate type. It is characterized by the division into the old and the new part. North Africa is sometimes called Maghreb, but this is not entirely accurate.
Economy
Currently located in this subregion15 independent states. Republics are 13 of them. Most states of North America are underdeveloped. In Libya and Algeria, the economy is somewhat better developed. These countries have a significant supply of natural gas and oil, which today are a hot commodity on the world market. Phosphorites used in the production of fertilizers are mined by Morocco. Niger is a major producer of uranium, but remains one of the poorest countries in North Africa.
The southern part of this area is very poorly populated.subregion. The agricultural population lives in oases where the date palm is the main commodity and consumer culture. Only nomad camels can be found throughout the rest of this region, and even then not everywhere. In the Libyan and Algerian parts of the Sahara there are gas and oil fields.
Narrow "life band" only along the Nile Valleywedged into the desert far to the south. For the development of Upper Egypt, the construction on the Nile of the Asuan hydroelectric complex with technical and economic assistance from the USSR was very important.
West Africa

The subregions of the continent of interest to us are a rather extensive topic, so we will limit ourselves to their brief description. Moving on to the next subregion - West Africa.
Here are the areas of savanna, tropical desertsand wet equatorial forests, which are located between the Gulf of Guinea and the Sahara Desert. It is the largest subregion of the continent in terms of population and one of the largest in terms of area. The natural conditions here are very diverse, and the ethnic composition of the local population is the most complex - various peoples of Africa are represented. This subregion in the past was the main area of the slave trade. Currently, agriculture is developed here, represented by the production of various plantation consumer and commercial crops. Available in the subregion and industry. Its most developed industry is mining.
West African population
According to 2006 data, the population of West Africa is280 million people. In composition, it is multi-ethnic. The largest ethnic groups are wolof, mande, serer, mossi, songai, fulani and hausa. The indigenous population is divided by language into 3 metagroups - Nilo-Saharan, Niger-Congo and Afro-Asian. English and French are common in European languages in this subregion. The main religious groups are Muslims, Christians and animists.
West African Economy

All states here are -developing countries. As we have said, the economic subregions of Africa are significantly different. The table presented above gives a description of such an important economic indicator of the countries of the continent of interest as the gold reserves (2015 data). West African countries in this table include Nigeria, Ghana, Mauritania and Cameroon.
Leading role in creating GDP in this subregionplays agriculture, as well as the mining industry. The minerals found in West Africa are oil, iron ore, bauxite, gold, manganese, phosphates and diamonds.
Central Africa
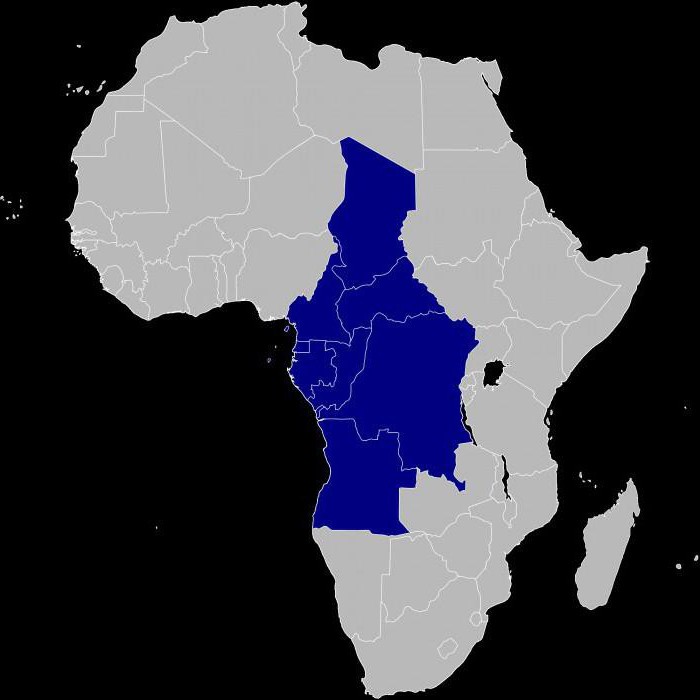
From the very name of this subregion, it is clear that it occupies the central part of the continent (equatorial). The total area of the region is 6613 thousand km2. A total of 9 countries are located in Central Africa:Gabon, Angola, Cameroon, Congo and the Democratic Republic of Congo (these are two different states), Sao Tome and Principe, Chad, Central African Republic and Equatorial Guinea. Also here is the island of St. Helena, which is an overseas territory of the United Kingdom.
The states of Central Africa are located inzones of savannas and humid equatorial forests, which greatly influenced their economic development. This subregion is one of the most mineral-rich areas, not only in Africa, but in the world. The ethnic composition of the local population, in contrast to the previous region, is homogeneous. Nine-tenths of it are the Bantu peoples of Africa who are related to each other.
Subregion economy
All countries of the subregionUN classifications are developing. In the creation of GDP, agriculture plays a major role, as well as the mining industry. In this respect, West and Central Africa are similar. The minerals mined here are cobalt, manganese, copper, diamonds, gold, natural gas, and oil. The subregion has good hydropower potential. In addition, significant forest resources are located here.
These are the main features of Africa Central.
East Africa

It is located in tropical andsubequatorial climate. East Africa goes to the Indian Ocean, so it has long had trade relations with Arab countries and India. The mineral wealth of this subregion is less significant, but the diversity of natural resources in general is very high. This is what largely determines the various options for their economic use.
East African Population
East Africa is a highly mosaic subregion inethnic relation. The borders of many countries were set arbitrarily by the former colonial powers. At the same time, cultural and ethnic differences, which the population of East Africa has, were not taken into account. Due to significant differences in social and cultural terms, this subregion has significant conflict potential. Often there were wars, including civil ones.
South Africa

It is located on the southern part of the continent, whichmost remote from Asia, America and Europe, but it goes to the sea route, which goes around the southern tip of Africa. This subregion is located in the subtropical and tropical latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere. There is a significant amount of natural resources, especially the mineral ones are highlighted. The Republic of South Africa (South Africa) is the main “core” of the subregion. This is the only economically developed state on the continent.
The population and economy of South Africa
A significant amount of the population of South Africa hasEuropean origin. The Bantu peoples constitute the overwhelming majority of the inhabitants of this subregion. The local population as a whole is poor, but in South Africa there is a network of roads, air traffic is effective, and there is a good tourist infrastructure. Mining, as well as deposits of gold, platinum, diamonds and other minerals form the basis of the economy. In addition, southern Africa is increasingly developing technology, tourism and manufacturing.
Finally
Как вы видите, в целом материк не очень развит в economically. Its population is unevenly distributed. Currently, about a billion people live on a continent like Africa. We have briefly characterized its subregions. In conclusion, I would like to note that this continent is considered the ancestral home of humanity: the oldest remains of the early hominids, as well as their probable ancestors, were found here. There is a special science of African studies that studies the cultural, political, economic and social problems of Africa.