HUNDRED, TOE - under these abbreviations hidesfamiliar to almost all the term "theory of relativity." In a simple language, you can explain everything, even the statement of a genius, so don’t despair if you don’t remember a school course in physics, because in fact everything is much simpler than it seems.
The origin of the theory
So, let's start the course "Theory of Relativity forteapots ". Albert Einstein published his work in 1905, and it caused a resonance among scientists. This theory almost completely covered many gaps and inconsistencies in the physics of the last century, but also, among other things, turned the idea of space and time. In many statements Einstein's contemporaries were hard to believe, but experiments and research only confirmed the words of the great scientist.
Einstein's theory of relativity in simple languageexplained what people have been fighting for centuries. It can be called the basis of all modern physics. However, before continuing the discussion on the theory of relativity, the question of terms should be clarified. Surely many, reading non-fiction articles, faced with two abbreviations: SRT and GRT. In fact, they imply several different concepts. The first is the special theory of relativity, and the second is deciphered as the "general theory of relativity."

Just about the complex
SRT is an older theory, which thenbecame part of GR. It can only consider physical processes for objects moving at a uniform speed. The general theory can describe what happens with accelerating objects, and also explain why there are particles of gravitons and gravity.
If you want to describe the motion and laws of mechanics, andalso relations of space and time when approaching the speed of light - this can be done by the special theory of relativity. Simple words can be explained as follows: for example, friends from the future gave you a spaceship that can fly at high speed. On the nose of the spacecraft is a gun that can shoot photons everything that comes in front.
When a shot is made, it is relativespaceships these particles fly at the speed of light, but, logically, a fixed observer should see the sum of two speeds (the photons and the ship themselves). But nothing like that. The observer will see photons moving at a speed of 300,000 m / s, as if the speed of the ship was zero.
The thing is that no matter how fast an object moves, the speed of light for it is the same.
This statement is basically astoundinglogical conclusions like deceleration and time distortion, depending on the mass and speed of the object. The plots of many science fiction films and TV shows are based on this.

General theory of relativity
Простым языком можно объяснить и более объемную GRT. To begin with, we must take into account the fact that our space is four-dimensional. Time and space are combined in such a "subject" as the "space-time continuum". In our space there are four coordinate axes: x, y, z and t.
But people can not perceive directlyfour dimensions, just like a hypothetical flat man living in a two-dimensional world, are not able to look up. In fact, our world is only a projection of four-dimensional space into three-dimensional.
An interesting fact is that, according togeneral theory of relativity, the body does not change when moving. The objects of the four-dimensional world are in fact always unchanged, and when moving, only their projections change, which we perceive as a distortion of time, a reduction or increase in size, and so on.

Experiment with elevator
On the theory of relativity in simple language cantell through a little thought experiment. Imagine you are in the elevator. The booth began to move, and you were in a state of weightlessness. What happened? There can be two reasons: either the elevator is in space, or it is in free fall under the influence of the planet’s gravity. The most interesting thing is that it is impossible to find out the cause of weightlessness if it is not possible to look out of the elevator car, that is, both processes look the same.
Perhaps by doing a similar thought experiment,Albert Einstein came to the conclusion that if these two situations are indistinguishable from each other, it means that in fact the body does not accelerate under the influence of gravity, this is a uniform movement that is bent under the influence of a massive body (in this case, the planet). Thus, accelerated motion is only a projection of uniform motion into three-dimensional space.

A good example
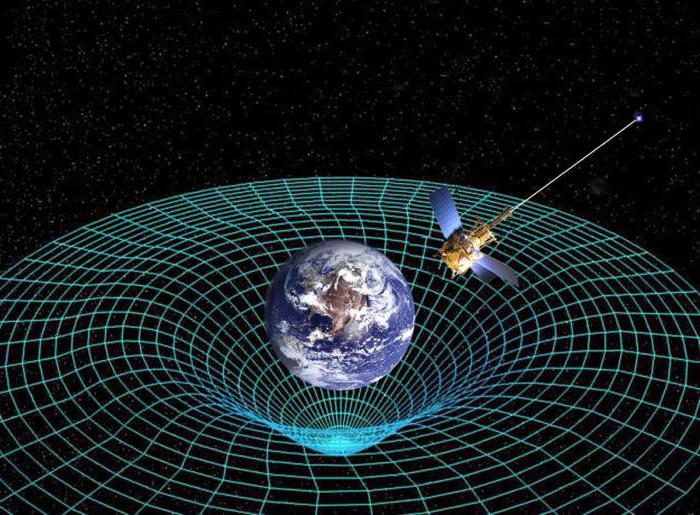
Another good example on "Theoryrelativity for teapots ". It is not entirely correct, but very simple and vivid. If you put an object on a stretched fabric, it forms a" deflection "and" funnel "under it. All smaller bodies will have to distort their trajectory according to the new bend of space , and if the body has a little energy, it may not overcome this funnel at all. However, from the point of view of the moving object itself, the trajectory remains straight, they will not feel the bending of space.
Gravity "lowered in rank"
With the advent of the general theory of relativitygravity has ceased to be a force and is now content with the position of a simple consequence of the curvature of time and space. GRT may seem fantastic, but is a working version and is confirmed by experiments.
A lot of seemingly incredible in our worldthings can explain the theory of relativity. In simple terms, such things are called consequences of GR. For example, rays of light, flying at close range from massive bodies, are bent. Moreover, many objects from far space are hidden one after another, but due to the fact that rays of light bend around other bodies, invisible objects appear to be visible to our eyes (more precisely, to the telescope). This is like looking through walls.
The more gravity, the slower onthe surface of an object flows time. This applies not only to massive bodies like neutron stars or black holes. The effect of time dilation can be observed even on Earth. For example, instruments for satellite navigation are equipped with the most accurate atomic clocks. They are in the orbit of our planet, and time is ticking a little faster there. The hundredths of a second in a day will add up to a figure that will give up to 10 km error in the calculations of the route on Earth. Calculate this error allows the theory of relativity.
In simple terms, one can put it this way: UTO is the basis of many modern technologies, and thanks to Einstein we can easily find a pizzeria and a library in an unfamiliar area.










