In nature, there are no flowers per se.Each shade that we see, sets one or another wavelength. Red color is formed under the influence of the longest waves and represents one of the two faces of the visible spectrum.
About the nature of color
The emergence of a color canexplain thanks to the laws of physics. All colors and shades are the results of processing by the brain of information coming through the eyes in the form of light waves of various lengths. In the absence of waves, people see black, and with one-time exposure of the entire spectrum, white.
The colors of objects are determined by their abilitysurfaces to absorb waves of a certain length and repel all others. Illumination also matters: the brighter the light, the more intensely the waves are reflected, and the brighter the object looks.

People are able to distinguish more than one hundred thousand colors.Loved by many scarlet, burgundy and cherry hues are formed by the longest waves. However, in order for the human eye to see red, the wavelength should not exceed 700 nanometers. Behind this threshold begins the infrared spectrum invisible to people. The opposite border separating the violet hues from the ultraviolet spectrum is about 400 nm.
Color spectrum
The range of colors as some combination of them,distributed in ascending order of wavelength, was discovered by Newton in the course of his famous experiments with a prism. He singled out 7 clearly distinguishable colors, and among them - 3 main ones. Red color refers to both distinguishable and basic. All shades that people distinguish are the visible region of the vast electromagnetic spectrum. Thus, a color is an electromagnetic wave of a certain length, not shorter than 400, but not longer than 700 nm.
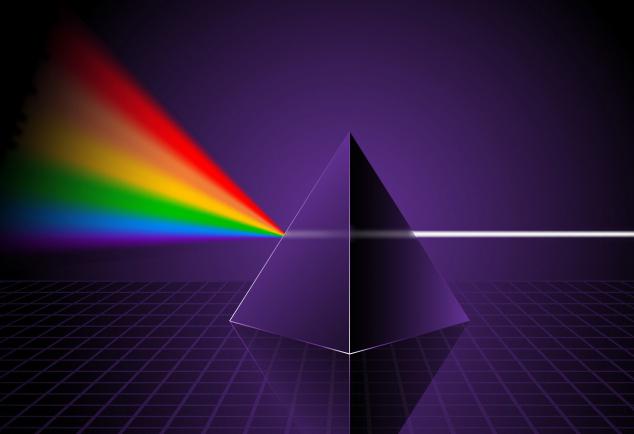
Newton noticed that beams of light of different colorshad different degrees of refraction. If expressed more correctly, the glass refracted them in different ways. The maximum speed of passage of rays through matter and, as a result, the longest refractivity was due to the longest wavelength. Red is the visible display of the least refracted rays.
Red Waves
Electromagnetic wave is characterized by suchparameters like length, frequency and photon energy. Under the wavelength (λ) is commonly understood as the smallest distance between its points, which oscillate in the same phases. Basic units of wavelength measurement:
- micron (1/1000000 meter);
- millimicron or nanometer (1/1000 micron);
- angstroms (1/10 nanometer).
The maximum possible red wavelength is 780 μmk (7800 angstroms) when passing through a vacuum. The minimum wavelength of this spectrum is 625 mmk (6250 angstroms).

Another significant indicator is the frequencyfluctuations. It is interconnected with the length, so the wave can be set to any of these values. The frequency of the red waves is in the range from 400 to 480 Hz. In this case, the photon energy forms a range from 1.68 to 1.98 eV.
Red color temperature
Shades that man subconsciouslyperceived as warm or cold, from a scientific point of view, as a rule, have the opposite temperature. The colors associated with sunlight — red, orange, yellow — are usually considered as warm, and the opposite to them - as cold.
However, radiation theory proves the opposite:red shades have a much lower color temperature than blue ones. In fact, it is easy to confirm: hot young stars have a bluish light, and dying away ones are red; when heated, the metal becomes red first, then yellow, and then white.
According to the law of wine, there is a reversethe relationship between the degree of wave heating and its length. The more the object heats up, the greater the power that comes from radiation from the region of short waves, and vice versa. It only remains to recall where in the visible spectrum there is the longest wavelength: the red color occupies a position that contrasts with the blue tones, and is the least warm.
Shades of red
Depending on the specific value, which has a wavelength, red gets different shades: scarlet, crimson, burgundy, brick, cherry, etc.

Hue is characterized by 4 parameters. These are such as:
- Tone is the place that color occupies in the spectrum among 7 visible colors. The length of the electromagnetic wave sets the tone.
- Brightness - determined by the power of the radiation energya certain color tone. The extreme decrease in brightness leads to the fact that a person sees black. With a gradual increase in brightness, a brown color will appear, followed by a burgundy, after - scarlet, and with a maximum increase in energy - bright red.
- Serene - characterizes the proximity of shade towhite. White color is the result of mixing waves of different spectra. With a consistent increase of this effect, the red color will turn into crimson, after - in pink, then - in light pink and, finally, in white.
- Saturation - determines the distance of color from gray. Gray in nature - these are the three primary colors, mixed in different quantities with a decrease in the brightness of the light emission to 50%.










