Much in quantum mechanics remains beyond the boundsmany things seem fantastic. The same applies to quantum numbers, the nature of which is still mysterious today. The article describes the concept, types and general principles of working with them.
general characteristics

Целые или полуцелые квантовые числа у физических quantities determine all possible discrete values that characterize the systems of quanta (molecule, atom, nucleus) and elementary particles. Their application is closely related to the existence of Planck's constant. Discreteness, flowing in the microcosm of processes, reflect quantum numbers and their physical meaning. They were introduced for the first time in order to describe the regularities of the atomic spectra. But the physical meaning and discreteness of the individual quantities were revealed only in quantum mechanics.
A set that defines an exhaustive stateof this system, called full. All states responsible for possible values from such a set form a complete system of states. Quantum numbers in chemistry with the degrees of freedom of an electron determine it in three spatial coordinates and the internal degree of freedom - spin.
The configurations of electrons and atoms
In the atom are the nucleus and electrons, betweenforces of electrostatic nature. Energy will increase as the distance between the nucleus and the electron decreases. It is believed that the potential energy will be zero if it is removed from the nucleus indefinitely. This state is used as the origin. Thus, the relative energy of the electron is determined.
The electron shell is a set of energy levels. Belonging to one of them is expressed by the principal quantum number n.

Main number
It refers to a certain level of energy witha set of orbitals with similar values consisting of natural numbers: n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ... When an electron moves from one level to another, the principal quantum number changes. It should be borne in mind that not all levels are filled with electrons. When filling the shell of an atom, the principle of least energy is realized. His condition in this case is called unexcited or primary.
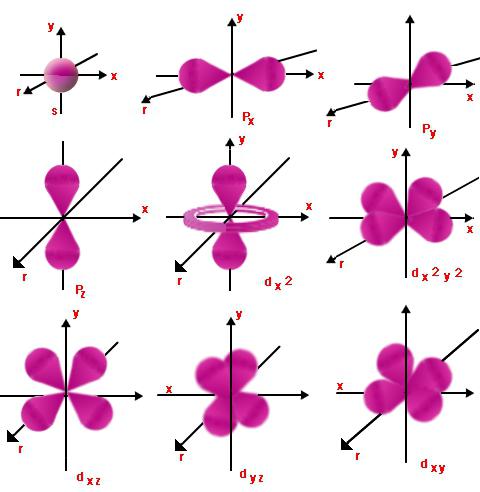
Orbital numbers
Each level has orbitals.Those of them who have similar energy form a sublevel. Such assignment is made using the orbital (or as it is also called - side) quantum number l, which takes integer values from zero to n - 1. So the electron having the principal and orbital quantum numbers n and l can be equal, starting l = 0 and ending with l = n - 1.
This shows the nature of the movementsublevel and energy level. When l = 0 and any value of n, the electron cloud will have the shape of a sphere. Its radius will be directly proportional to n. When l = 1, the electron cloud will take the form of infinity or figure eight. The greater the value of l, the more difficult the shape becomes, and the electron energy increases.
Magnetic numbers
Ml is a projection of the orbital (side)angular momentum to one or another direction of the magnetic field. It shows the spatial orientation of those orbitals, in which the number l is the same. Ml can have different values of 2l + 1, from -l to + l.
Another magnetic quantum number is calledspin is ms, which is its own moment of the number of motion. To understand this, one can imagine the rotation of the electron as it were around its own axis. Ms can be -1/2, +1/2, 1.
In general, for any electron, the absolute value of the spin is s = 1/2, and ms means its projection on the axis.
The Pauli principle: an atom cannot have two electrons with 4 similar quantum numbers. At least one of them should be excellent.
The rule of making the formulas of atoms.
- The principle of minimum energy. According to it, the levels and sublevels that are located closer to the core are first filled according to the Klechkovsky rules.
- The position of an element indicates how electrons are distributed across energy levels and sublevels:
- the number coincides with the charge of the atom and the number of its electrons;
- the periodic number corresponds to the number of energy levels;
- the group number is the same as the number of valence electrons in the atom;
- subgroup shows their distribution.

Elementary particles and nuclei
Квантовые числа в физике элементарных частиц are their internal characteristics that determine the interactions and patterns of transformations. In addition to the spin s, it is the electric charge Q, which for all elementary particles is zero or an integer, negative or positive; baryon charge B (in a particle, zero or one, in an antiparticle, zero or minus one); lepton charges, where Le and Lm are equal to zero, one, and in the antiparticle - zero and minus one; isotopic spin with integer or half integer; strangeness s and others. All these quantum numbers are applied both to elementary particles and to atomic nuclei.
In a broad sense, they are called physicalquantities that determine the motion of a particle or system and which are saved. However, it is not necessary that they belong to the discrete spectrum of all possible values.









