Гинекологические заболевания вряд ли можно considered a rarity. And not least among them is cervical hypertrophy. This is a rather unpleasant and dangerous pathology, which is accompanied by an increase in the size of the neck. Such a disease can lead to a lot of complications, and the quality of life of a woman is significantly worsened due to constant discomfort and soreness.

Вполне естественно, что многие женщины They are interested in additional information about this ailment. Why does hypertrophy develop, what are the symptoms of cervical enlargement? What methods of treatment does modern medicine offer? What are the projections for patients and are there ways to prevent the development of pathology? Answers to these questions will be useful to every woman.
Cervical hypertrophy: what is it? Photo and short description
Cervical hypertrophy - a pathological conditionwhich is accompanied by an increase in the size of this part of the female genital system. It should be understood that there are two main types of pathological increase. Hyperplasia is a condition that is accompanied by an increase in the number of cells. At the same time, with hypertrophy, cell size increases, but their quantitative ratio remains normal.
The increase in the size of the cervix may be different- sometimes the tissues are enlarged to such an extent that it falls out of the outside of the labia majora. Pathology may be to some extent associated with lengthening of the vagina or omission of the pelvic organs. However, sometimes cervical hypertrophy is not accompanied by comorbidities.
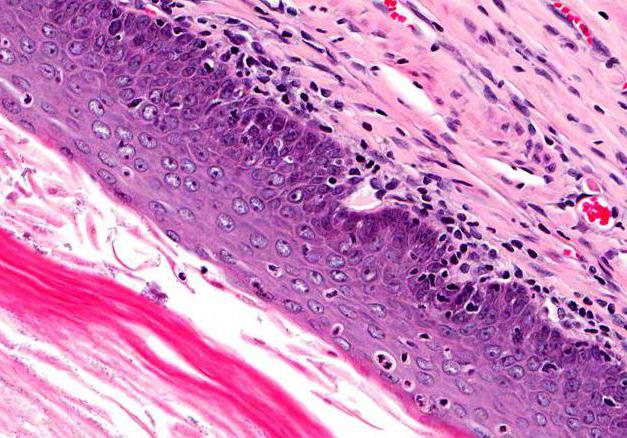
What are the causes of the development of pathology?
Naturally, many people firstThey are interested in the question of why cervical hypertrophy develops. The reasons may be different, and therefore it is worth considering a list of the main risk factors:
- Injuries and damage to the epithelium of the endocervix(channel inside the cervix). Hypertrophy can be the result of abortion, difficult labor, diagnostic curettage. Normally, with injury, the epithelial cells of the mucous membrane begin to actively divide, ensuring complete tissue regeneration. However, repeated damage may result in a thickening.
- Не последнее место среди факторов риска занимает and hormonal imbalance. The fact is that the state and function of the tissues of the cervix of the uterus are directly dependent on the level of progesterone and estrogen. Changes in the level of these hormones can lead to increased activity of the cervical epithelium, the consequence of which is often hypertrophy.
- Infectious diseases can also cause the development of this pathology, especially if we are talking about a chronic inflammatory process.
- Some types of pathology, in particular muscularcervical hypertrophy, develop on the background of changes in the muscle layer, for example, when the pelvic organs are lengthened or lowered. Quite often, hypertrophy is diagnosed in elderly patients, as well as in women who have often given birth, because their pelvic muscles are weakened, as a result of which the genitals are shifted towards the vagina. To the same result can lead heavy exercise.
- Sometimes hypertrophy develops on the background of uterine fibroids, especially if myomatous nodes are located close to the cervix.
- There is also a genetic factor, as it is not uncommon for women in the genus to find women who have suffered from the same pathology.

The main symptoms of hypertrophy
Today, many patients are interested in the question ofthat is a cervical hypertrophy. The causes, treatment and prevention of the disease also need to know. No less important are the symptoms that accompany the pathology. Immediately it should be said that in the initial stages of hypertrophy rarely causes any serious complications and discomfort, and therefore is diagnosed by chance.
Also, the symptoms of the disease are directly dependent oncauses of hypertrophy. For example, in the glandular form of the disease, women often complain of the appearance of abundant mucous discharge. Symptoms also include menstrual disorders, the appearance of bleeding and even uterine bleeding, although such violations in most cases are associated with hormonal disruptions.
The hypertrophy caused by the inflammatory process is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of the infection, in particular itching, pain in the lower abdomen, uncharacteristic discharge with an unpleasant smell.
In the event that the disease is caused by the omission of the pelvic organs, women complain of pulling pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort, a certain soreness, which may increase during intercourse.
Follicular hypertrophy and its features
Фолликулярная гипертрофия шейки матки, как и some other forms of this pathology are associated with blockage and increase in size of secretory cells of the mucous epithelium. Violation of the outflow leads to stagnation of secretion, and the formed follicles go deep into the tissues. Due to this, the size of the cervix increases, and the contours become more rigid. Sometimes formed follicles become inflamed, which leads to accumulation of purulent masses inside. This complication can be very dangerous.

Muscle hypertrophy
Muscular hypertrophy of the cervix is usually associatedwith a change in size or omission of the pelvic organs. That is why it is most often diagnosed in giving birth, as well as older women, because in these cases muscle weakness often develops.
Depending on the bias, it is customary to distinguish three main stages in the development of pathology:
- In the first stage, the cervix is slightly lowered into the vaginal cavity. With a visual examination, the pathology is not visible, but it can be easily detected by vaginal examination.
- As the disease develops, the cervix shifts lower, almost reaches the genital slit, but does not go beyond its borders.
- The third stage of the development of the disease is accompanied by a strong omission of the cervix, which is already extending beyond the edges of the genital slit, out.
Often, together with the cervix, the uterus itself falls.By the way, talking about the omission in the event that the internal genital organs are displaced into the cavity of the vagina. If they completely go outside, then we are talking about a fallout.

Glandular form of the disease
Glandular cervical hypertrophy in mostcases develops against a background of chronic inflammation. The fact is that in the mucous layer lining the cervix, there are many glandular structures that, when exposed to certain factors, can expand. This is how hypertrophy develops. Cysts of the cervix with this disease can also develop - in such cases, doctors talk about a glandular-cystic form of pathology.
Cystic hypertrophy and its features
Cystic form of hypertrophy - quitecommon problem. It is associated with the formation of cysts, which are benign formations with a clearly defined membrane and liquid contents. This form of the disease develops with blockage of the mucous glands in the tissues of the cervix. Due to the violation of the outflow, the secret begins to accumulate in the cavity of the gland - this is how nabotov cysts are formed. In most cases, they are small and multiple, but sometimes they can merge into one large structure.
As a rule, the cause of cyst formation iseither chronic inflammation or hormonal disorders. If cystic hypertrophy is diagnosed in time, medication can be effective.
Cicatricial hypertrophy
Cicatricial hypertrophy of the cervix for the most partis the result of injuries of the mucous membrane of the cervix. The causes include childbirth (with rupture of perineal tissues), curettage and abortion. For one reason or another, habitual tissue regeneration does not occur. Instead, the scarring process starts. Due to the formation of scars (scars), the size of the uterine neck also increases.

Modern diagnostic methods
In the presence of discomfort and anyalarming symptoms should consult a doctor. By the way, cervical hypertrophy is often detected by chance. Suspicions for the presence of this pathology, as a rule, arise at the doctor during a planned gynecological examination using mirrors.
In the future, of course, additionalexaminations to make an accurate diagnosis. In most cases, an ultrasound scan is indicated, which helps to determine whether an increase in the volume of the cervix is the result of a pathological process or pregnancy.
Sometimes additionally carried outX-ray examination using a contrast agent. Colposcopy is considered a very informative method, since the doctor has the opportunity to examine the tissues of the cervix uterus well, as well as take samples for analysis, which are then sent to the laboratory (this can, for example, exclude the possibility of malignant cell degeneration).
Cervical hypertrophy: treatment
After determining the exact diagnosis, the doctor will be able toto make a competent treatment regimen. What measures does cervical hypertrophy require? Treatment depends on the form and causes of the development of pathology. It can be conservative or surgical (by the way, quite often, patients are prescribed combination therapy, which involves taking medications and surgical intervention). In turn, surgical procedures can be minimally invasive.
Conservative therapy is necessary ifif, for example, the cause of hypertrophy is an inflammatory process. In such cases, patients are prescribed antibacterial (antiviral, antifungal) drugs, vitamin complexes, immunomodulators to strengthen the immune system. If the pathology develops against a background of hormonal imbalance, hormonal medication will be effective.
Quite often, the patient needs surgicaltreatment, the purpose of which is to restore the normal structure and functioning of the internal genital organs. In the initial stages, minimally invasive procedures are possible. For example, thermocoagulation of nabot cysts may be performed. Sometimes excess muscle mass is dissected using electric current or destroyed by treating with liquid nitrogen.
In more severe cases, excision is performed.plot of cervix with a scalpel. A fairly new but promising method is radio wave conization, in which the doctor removes excess tissue mass with a radio wave knife. By the way, the removed tissues are then sent for laboratory research to determine the exact cause of the development of the pathology and check for the presence of cancer cells.
Amputation of the cervix is sometimes necessary. If a woman does not plan to give birth anymore, the doctor may recommend removal of the uterus and appendages.
Patient forecasts
Cervical hypertrophy is a dangerous disease,which in no case can be ignored. If the patient underwent treatment on time, the prognosis for her is positive, since in most cases it is possible to completely restore the structure and functioning of the reproductive system.
However, in the absence of qualifiedRelief The disease becomes more severe. Missed cases are fraught with infertility. The fact is that due to the increase and swelling of the cervix, spermatozoa simply cannot penetrate the uterus and fallopian tube for fertilization. Often, against the background of hypertrophy, a change in the hormonal background is observed, which also leads to infertility and more fundamental changes in the body of a woman.
Помимо этого, возможны и другие осложнения.In particular, cystic hypertrophy of the cervix may be accompanied by rupture of the cyst. Against the background of uterine fibroids, intense bleeding can be observed. With this pathology, the risk of developing a myomatous node, leukoplakia and other diseases, up to precancerous conditions, is increased. In addition, against the background of the disease, inflammatory processes and cicatricial tissue changes occur, and after that it is much more difficult to normalize the reproductive system, even taking into account the possibilities of modern medicine.
Are there any prevention methods?
К сожалению, на сегодняшний день не существует really effective ways to prevent a disease like cervical hypertrophy. The causes of the pathology are known, and therefore prevention comes down to avoiding risk factors. In particular, it is not recommended to begin sexual activity in early adolescence. It is also worth avoiding frequent changes of partners, since in this case the probability of infection with various pathogenic microorganisms, including the human papillomavirus, increases.
Women are recommended at least every sixmonths to undergo a gynecological examination, do vaginal smears, take tests. The sooner the disease is detected, the greater the chance of a quick and successful treatment.




