Today, no one will be surprised by this methodtreatments like surgery. But a few centuries ago, the operation was equated with death: the majority of patients died of painful shock or sepsis. For a long time, the introduction of a person into a surgical sleep remained the most difficult task of medicine. With the study of chemistry, the process went faster. More perfect mixtures and preparations for anesthesia were created, which, moreover, are now carried out in different ways. One of these is endotracheal anesthesia. What it is? How is it used and in what cases is it necessary? These and many other questions will be answered in the article.
From the history of endotracheal anesthesia
For the first time this type of anesthesia was tried in XIV – XVcenturies, when the doctor Paracelsus from Switzerland inserted a tube into the human trachea, which saved his life. Three centuries later, in this way they saved people from lack of air. In 1942, an anesthesiologist from Canada first applied muscle relaxants - substances that reduce the tone of skeletal muscles, up to complete immobilization. Thanks to this discovery, anesthesia has become safer and more perfect, allowing specialists to fully control the course of surgical sleep during surgery.
In the middle of the 20th century, endotracheal anesthesia becamerapid development, helped by the Soviet physicians. Today it is the most common method of general anesthesia used in most operations.
Endotracheal anesthesia: what is it?
In order to protect the body from hugestress during surgery, use pain relief. It may be local, regional or general. The latter type is called anesthesia. It is characterized by the complete “turning off” of the patient’s consciousness with the onset of surgical sleep. In modern anesthesiology, intravenous, mask or combined anesthesia is used. The latter combines two methods: the substances enter both the blood and the respiratory tract. This type is called endotracheal anesthesia.

Специалисты по праву считают его самым безопасным and an effective method of anesthesia: it allows you to fully control the patient’s condition, achieve deep surgical sleep and relaxation of skeletal muscles, as well as avoid such unpleasant complications as aspiration and respiratory failure.
Indications
Endotracheal anesthesia protects the patient frompain shock and respiratory failure, which allows its use during operations and resuscitation. Among the indications for combined anesthesia may be:
- operations on the mediastinum, pharynx, inner ear, mouth and head;
- interventions for which you need to use muscle relaxants;
- disruption of the nervous system;
- full stomach syndrome;
- risk of airway obstruction.
Endotracheal general anesthesia is more commonly used.for the long operations which term makes more than 30 minutes. It can be used at any age with different conditions of the patient, since it does not burden the heart and is much less toxic by other methods of anesthesia.
Contraindications
Routine surgical treatment (e.g.surgery to remove a mediastinal tumor) is accompanied by a thorough study of the patient’s condition. The doctor has the necessary time to familiarize with the medical card of the patient, managing to calculate the possible risks and identify contraindications to a particular method of anesthesia. Combined anesthesia is not recommended for the following conditions:
- infectious diseases;
- pathology of the liver, kidneys;
- suspected myocardial infarction;
- airway pathology;
- physiological features of the pharynx structure;
- severe endocrine disorders.
Especially dangerous is the use of endotracheal anesthesia for infections of the upper respiratory tract, because the risk of infection of the lungs is high.
Stages of combined anesthesia
Итак, эндотрахеальный наркоз.What is it for the doctor? The anesthesiologist performs three successive stages of action: the introduction into a surgical sleep, the maintenance of a stable state and the awakening. The first stage is the implementation of a light introductory anesthesia. The patient receives intravenous drugs or inhales a mixture of gases. When the muscles are completely relaxed, the anesthesiologist enters the endotracheal tube into the lumen of the trachea. It provides ventilation of the lungs with oxygen and inhalation with gaseous anesthetics.

After the surgeons finished their work,the crucial moment for the anesthesiologist comes - the patient's withdrawal from anesthesia. The dosage of drugs is gradually reduced. After the restoration of spontaneous breathing, extubation is performed — removal of the endotracheal tube from the trachea. The patient is transported to the intensive care unit, observing vital signs and the process of postoperative recovery.
Induction anesthesia
Easy initial anesthesia is necessary forpainless and safe intubation, without which endotracheal anesthesia is impossible. To achieve this state, use inhalation or intravenous pain medication. In the first case, the patient breathes through a mask in vapors of Etran, Foran, Ftorotan or other similar mixtures of anesthetics. Sometimes it is enough nitrous oxide with oxygen.
As intravenous medicationsbarbiturates and neuroleptics (droperidol, fentanyl) are commonly used. They are used in the form of a solution (no more than 1%). The dose of the drug is selected by the anesthesiologist individually for each patient.

After the light anesthesia worked,perform tracheal intubation. For this, muscle relaxants are used to relax the muscles of the neck. The tube is inserted using a laryngoscope, after which the patient is transferred to artificial lung ventilation. The stage of deep anesthesia begins.
Droperidol: instruction
Droperidol is a neuroleptic commonly usedwith endotracheal anesthesia. By chemical structure, this substance is a tertiary amine. It has a sedative effect after 3 minutes after administration. Blocks dopamine receptors, which causes neurovegetative inhibition. In addition, it has antiemetic and hypothermic effects. Influences the breath slightly.
Назначается при премедикации, вводной анестезии, myocardial infarction, shock condition, severe angina pectoris, pulmonary edema, and hypertensive crisis. Recommended as a drug that eliminates nausea and vomiting. It has low toxicity, which allows its use in pediatric surgery and obstetrics.
Methods of using neuroleptics with induction anesthesia
There are several options for performingneyroleptanalgezii. Introduction anesthesia is usually carried out according to this scheme: droperidol, the instruction of which was discussed above, in the amount of 2-5 ml with 6-14 ml of fentanyl is administered intravenously to the patient. At the same time serves a mask with a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen in the ratio of 2: 1 or 3: 1. After the depression of consciousness, muscle relaxants are administered and intubation is initiated.

Droperidol has a neuroleptic effect in4-5 hours, so it is administered at the beginning of the anesthesia. Calculate it based on body weight: 0.25-0.5 mg / kg. Repeated administration of the drug is necessary only for long operations.
Fentanyl in the amount of 0.1 mg is administered every 20 minutes and stops its delivery 30-40 minutes before the end of the surgery. The initial dose is 5-7 mcg / kg.
Intubation
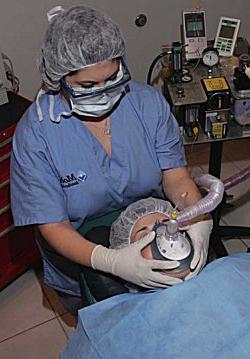
After the depression of consciousness, an artificialoxygen ventilation of the lungs using an anesthetic mask. Then the doctor performs intubation through the mouth (less often through the nose). The head is thrown back, the mouth is opened. A laryngoscope with a straight blade is inserted in the midline between the sky and the tongue, pressing the latter upwards. Moving the instrument further, lift the tip of the epiglottis. The glottis is shown in which the endotracheal tube is inserted. She should go into the trachea by about 2-3 cm. After successful intubation, the tube is fixed and the patient is connected to the ventilator.

Less commonly used laryngoscope with a curved blade.It is inserted between the base of the epiglottis and the root of the tongue, squeezing the latter upwards from itself. If it is impossible to insert the tube through the mouth, use the lower nasal passage. For example, an operation is performed to remove a cyst of the oral cavity.
Maintenance and recovery from anesthesia
After intubation and connecting the patient to the deviceIVL comes the main period. Surgeons are actively working, the anesthesiologist is closely monitoring livelihoods. Every 15 minutes check the heart rate, blood pressure, with the help of monitors monitor the patient's heart activity.
General anesthesia is maintained byadditional doses of neuroleptics, muscle relaxants or inhalations with mixtures of anesthetics. The operation under combined anesthesia allows the anesthesiologist to adapt to the body's need for anesthesia, ensuring an optimal level of safety.
After the end of surgical proceduresthere comes the last stage - out of narcotic sleep. Before the onset of this point smoothly reduce the dosage of drugs. Atropine and prozerin are administered at 5-minute intervals to restore breathing. Making sure that the patient is able to breathe on their own, they carry out extubation. To do this, clear the area of the tracheobronchial tree. After removal of the tube, a similar procedure is performed with the oral cavity.

Postoperative observation
After leaving the operating room, the patient is placed inintensive care unit, where it is carefully monitored for its condition. After general anesthesia, discomfort develops, less often complications. Usually, postoperative patients complain of:
- pain;
- feeling of discomfort in the throat;
- nausea;
- weakness and muscle fatigue;
- drowsiness;
- confusion of consciousness;
- chills;
- thirst and lack of appetite.
These symptoms usually disappear within the first 2–48 hours after surgery. To eliminate the pain prescribed analgesics.

So let's summarize.Endotracheal anesthesia - what is it? This is a method of introducing a person into a surgical sleep, allowing to perform complex operations, controlling the activity of the respiratory system. Combined anesthesia is less toxic, and the depth of anesthesia is easy to control during the entire period of intervention. By endotracheal anesthesia primarily imply intubation followed by connecting the patient to the ventilator. It uses both inhaled and medical anesthetics, which are usually combined.