Renal colic is a very serious condition,which is accompanied by acute pain associated with renal ischemia or impaired urine flow. In this case, the correct diagnosis is very important. Timely treatment of renal colic will help prevent very dangerous complications.
Of course, many people are looking for additional information.Why does a pain attack occur? What symptoms should I pay attention to? How to remove attacks of renal colic and whether it is possible to do it at home? What are the complications of the disease? What code gave the kidney colic ICD-10? Answers to these questions should be studied.
General information about the disease

To begin with it is necessary to understand the maininformation about renal colic. ICD-10 assigned the code No. 23 to this pathology. This is a complex of symptoms that arise against the background of urinary diversion from the kidneys (it may be disturbed or absent altogether).
In the cavity of the renal pelvis begins to accumulateurine, as a result of which the pressure inside the kidney increases. The walls of the pelvis stretch, resulting in a spasm (contraction) of the smooth muscle fibers. The tissues of the kidney become swollen, which leads to the squeezing of the blood vessels and the disturbance of normal trophism. The kidney and other organs of the excretory system do not receive enough oxygen, which only aggravates the situation. Colic is accompanied by acute, severe pains - they are so intense that the patient sometimes loses consciousness.
Of course, it is very important to notice the alarming symptoms in time and to see a doctor. The sooner the treatment of renal colic is started, the more chances for complete recovery without complications.
The main causes of the appearance of the disease
Treatment of renal colic directly depends on the causes of the syndrome. In fact, colic is not an independent disease - it's just a symptom of other pathologies.
- As already mentioned, renal colic developsas a result of a violation of the diversion of urine, which may be due to the squeezing of the urinary tract or their obstruction. Violation of the passage of urine is often associated with the formation of a mechanical obstacle. According to statistics, in 57-58% of cases, renal colic develops against a background of urolithiasis - the calculus blocks the lumen of the ureter.
- It is impossible not to mention pyelonephritis, because against the background of the inflammatory process in the ureter may accumulate mucous clots and pus.
- Renal colic may indicate tuberculosis of the kidney - in this case, there is a blockage of the ureter with detached narcotized tissues and caseous masses.
- Torsion or kink of the ureter can also lead to the appearance of renal colic. This is often observed, for example, against the background of kidney dystopia, as well as with nephroptosis.
- To the list of reasons carry tumors of kidneys, adenoma or prostate cancer, posttraumatic hematomas. The appearance and growth of such formations often leads to compression of the urinary tract.
- An attack of renal colic can be associated withstagnant phenomena and an actively occurring inflammatory process. The cause of the appearance of symptoms may be prostatitis, urethritis, hydronephrosis, venous phlebostasis of the small pelvis.
- The reason for the violation of the passage of urine is sometimes associated with a disease of the vessels that feed the organs of the excretory system. For example, colic is observed with kidney infarction, embolism and thrombosis of renal veins.
- This symptomatology is sometimes associated with some congenital disorders of urodynamics (dyskinesia, spongy kidney, achalasia, dyskinesia of the urinary tract).
Are there risk factors?
Of course, there are some factors, their presence increases the likelihood of developing renal colic (if there are other prerequisites, of course). The list of them is as follows:
- it is proved that there is a hereditary predisposition;
- increased physical activity;
- prolonged, systematic overheating;
- increased fluid loss;
- the presence of a person with diseases that predispose to the development of concrements (sarcoidosis, polycystic kidney disease, tubular renal acidosis);
- taking medications that are poorly soluble (especially when it comes to unauthorized use of the drug, incorrect dosage, etc.).
Potentially dangerous is the presence in the patient's anamnesis of urolithiasis. According to statistics, the probability of a re-episode is 60%.
What symptoms should I pay attention to?

How is renal colic manifested? Signs largely depend on the severity of the pathology and the stage of its development. It is accepted to distinguish three phases, each of which is accompanied by certain violations.
- The acute phase is the initial phase of renal colic.Suddenly, there is a sharp pain. If at this time a person is awake, then he can name the exact time of the onset of symptoms. If soreness appears at night, the patient suddenly wakes up. According to the results of the research, physical activity does not affect the appearance of symptoms. Nevertheless, to intensify and accelerate the appearance of pain can stress, abundant food or drink the day before, shaking while riding. The intensity of unpleasant sensations constantly increases. Unpleasant sensations are localized in the lower back, side, sometimes under the ribs.
- A few hours later, a constant phase occurs.The pain reaches its apogee and becomes almost unbearable. The patient can not eat, talk, find a comfortable position for the body. From such unpleasant sensations a person can lose consciousness. As a rule, it is at this time that patients get to the hospital. This period lasts from 4 to 12 hours.
- Then the attenuation phase follows.Unpleasant sensations disappear just as quickly as they appeared. As a rule, it is at this time that the bladder empties (urine is released in large amounts and often contains impurities of blood).
- Of course, there are other symptoms.For example, some patients complain of frequent urge to urinate, with little urine. Possible the appearance of cutting pain in the urethra and in the bladder.
- Other symptoms include nausea, dry mouth, vomiting, which, alas, does not bring relief to the patient.
- In the human intestine, gases accumulate, resulting in bloating and constant urge to empty (although defecation itself may not occur).
- Sometimes there may be a slight increase in body temperature, the appearance of chills, the rapidity of contractions of the heart, hypertension.
In the absence of treatment, renal colic can lead to pain shock - the frequency of heart beats decreases, blood pressure drops, the patient's skin pales and cold sweat appears on it.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis in this case is extremely important, because it is necessary to determine the cause of colic, as well as the presence of concomitant complications. The patient needs a complete examination.
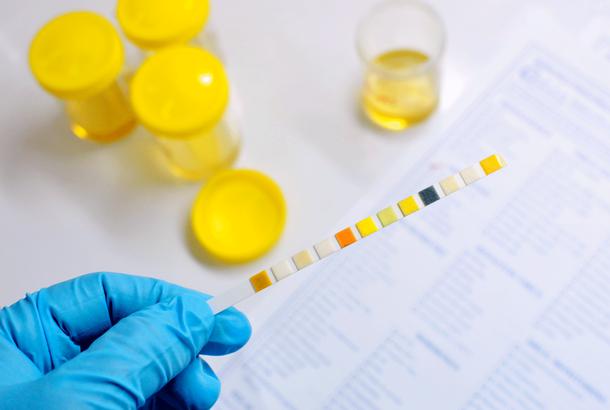
- An important is the blood test. Against the background of renal colic, the level of urea sharply increases (this often indicates a blockage of the upper urinary tract).
- A mass of useful information can be obtained by examining the urine test. In renal colic, an increase in the amount of salt, proteins, erythrocytes and leukocytes can be observed. Sometimes in the urine there are clots of blood.
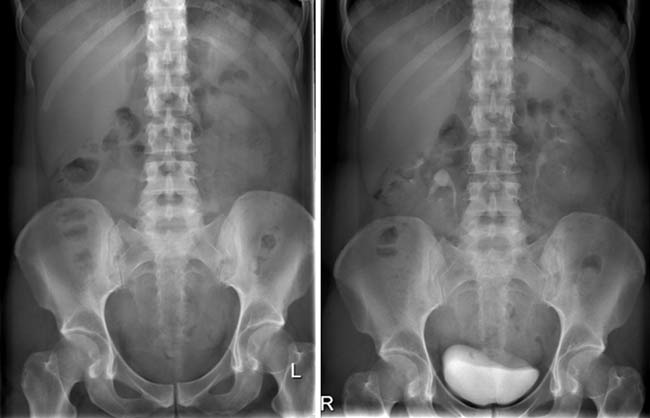
- An X-ray of the abdominal cavity and the area of the small pelvis is necessarily performed. During the procedure, you can determine the presence of edema of the kidneys, see large concrements, check the state of the intestine.
- Intravenous urography allows assessing the degreekidney function. The patient is given a contrast agent, followed by a series of X-rays - so the doctor can track the movement of the contract.
- Chromocystoscopy is a procedure that allowsthe doctor to examine the internal surface of the urinary tract, the mucous membranes of the bladder and ureters. During the inspection, a special contrast solution is used.
- Computed tomography is performed in the case,if ultrasound diagnosis did not provide an opportunity to find out the cause of colic. This procedure is mandatory if the patient is to undergo surgery.
Based on the findings, the doctor can assess the patient's condition, pick up medicines and draw up a scheme for further treatment.
Renal colic: an algorithm for emergency care

At the first symptoms it is necessary to call a brigadeAmbulance. Only the doctor knows about what treatment requires renal colic. First aid at home is limited to the following recommendations:
- put the patient in bed (the patient should remain in peace until the arrival of specialists);
- To cope with pains help thermal procedures,for example, you can put a warm water bottle on your stomach (it is worth noting that if colic is associated with inflammation, then heat is contraindicated, since it can only aggravate the patient's condition);
- if the patient wants to drink, then he can give warm water (coffee, tea, carbonated drinks are contraindicated);
- Strong pain can be removed with the help of antispasmodics.
The standard of treatment of renal colic in hospital

Treatment for a similar disease shouldis carried out in a hospital - the patient must be constantly under supervision. How to anesthetize renal colic? What should be the therapy? It depends on the intensity of the symptoms and the root cause of their appearance.
- If during the diagnosis it was revealed thatthe appearance of colic is not associated with an inflammatory process, then a warm water bottle is placed on the patient's stomach or crotch area. This helps to ease the patient's condition.
- Spasmolytics in kidney colic also help. The pain does not completely disappear.
- Typically, analgesics are used andnonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Opiates are used only in extreme cases, although sometimes pain can only be removed with their help. Anesthetics are prescribed by a doctor for renal colic. In the event that the patient is unable to take the pill, the painkillers are administered intravenously or intramuscularly.
- Killing of renal colic in the event thatthe above drugs do not help, is carried out by introducing novocaine directly into the area of the round ligament of the uterus or spermatic cord. The introduction of an anesthetic into perinephricous tissue is not recommended - it can only further injure the kidney.
- If the pain was not removed with the help ofmedicines, the doctor decides to install the catheter into the ureter. This procedure helps to remove urine, which, as a rule, instantly alleviates the condition of the patient.
Eliminate the cause: primary disease therapy

It should immediately be clarified that the aboveactivities can only relieve colic and ease the patient's condition, but do not guarantee that the symptoms will not appear again. It is very important to determine the nature of the primary disease, the therapy should be directed precisely at its elimination.
- If the cause of colic was a blockage of the ureterstone, then the obstacle must be removed. The method in this case is selected individually. Sometimes the concrement can be dissolved with the help of medicines. But in most cases, lithotripsy is performed by remote (stones are destroyed, acting on them by ultrasonic waves) or contact (stones are removed with an endoscope).
- If there is an initial stage of omission of the kidney,then patients are selected special exercises to strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor. It also helps to wear a special bandage, which prevents further displacement of the kidney.
- With severe nephroptosis or ureteral excess, the situation can be corrected surgically.
- Indication for surgical intervention is the presence of stricture (narrowing) of the ureter. If the stricture is small, then it is eliminated by means of an endoscopic procedure.
- In the event that twisting or bendingureter is caused by tumor growth, surgical excision is performed. If the neoplasm is benign, then the operation is sufficient. In the presence of a malignant tumor, surgical procedures are combined with radiation or chemotherapy.
The right diet for kidney colic
A very important part of the treatment is proper nutrition. Diet not only helps to speed up the healing process, but also prevents the development of complications in the future. The principles of nutrition are simple:
- First of all it is necessary to give up spices and salt;
- from the diet you need to exclude sweets, pastries and other simple carbohydrates, which are quickly absorbed;
- contraindicated fats, smoked products, conservation, semi-finished products;
- will be useful lactic acid products (whole milk can be added to tea);
- It is worth including in the diet vegetables, but they are better to boil or bake;
- useful are low-fat varieties of fish and meat (you can not fry them);
- it is very important to increase the daily amount of liquid to 3 liters.
Possible complications of the disease
You already know how and whyrenal colic. The algorithm of emergency care, effective therapeutic measures, the main symptoms are, of course, important information. But it is worth considering that in the absence of proper treatment this pathology can result in dangerous complications. These include acute obstructive pyelonephritis, as well as the formation of strictures in the ureter. Violation of the diversion of urine can result in renal failure, sepsis or bacteremic shock. That's why it's so important to ask for help in time.









