Such a complex feeling as vision has a peculiar structure. The eye consists of a vitreous, watery and crystalline lens. And what is stored this body, we will consider further.
Anatomy of the eye
Bone sphere in the eye socket is the paired partThe skull, which contains the eye organ. The orbital cavity forms a model of the broken pyramid with its four walls. The anatomy of the orbit keeps an eyeball with a circulatory system, nerve endings, a fatty layer and a lacrimal gland. From the front, the eye socket has a large opening, which is the backbone of the irregular pyramid, bordered by the bone of the orbital margin.
В строении глазницы имеется наиболее расширенный entrance, gradually tapering towards the center. Also, there are axes that run along and across one of the orbits. Their optic nerves are connected in the middle of the eye. The walls of the eye socket border on the nasal cavity. And with the front part of the forehead, the bones forming the eye socket are connected. Along the edges they are adjacent to the temporal fossa.
The structure of the eye socket has the form of a square withrounded edges. Above the orbit cavity extends the supraorbital nerve, which connects the frontal bone and the procession of the cheekbone. From the inside, the entrance to the opening of the skull is closed by the medial edge formed by the frontal bone of the nose and the skeleton of the maxilla. At the bottom of the path into the orbit passes the infraorbital nerve, connecting with the upper jaw and the malar portion. The lateral edge of the structure of the eye socket frames the zygomatic part.
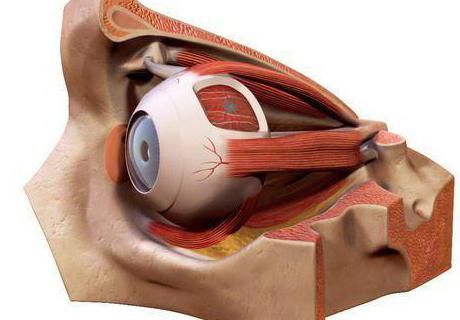
Full image of the eye sockets
The facial skull consists of a series of holes. One of which is the eye sockets. Its walls are very fragile.
Top of the wall
It consists of the orbital plane of the frontal boneand a small portion of the sphenoid bone. This bone separates the orbital walls from the intracranial fossa and brain of the head. And on the outside, the upper wall borders on the temporal cavity.
Bottom wall
It connects with the facial part of the upper jaw. This wall also borders on the malar bone. The lower wall is above the maxillary sinus, which should be known for medical purposes.
Medial wall
It connects with the upper jaw and with an insertfrom the latticed bone. The medial wall is very thin. It has holes for the passage of nerve endings and vessels. This factor explains the occurrence of pathological processes through this lattice in the eye and back.
Lateral wall
It is formed from the orbital cavity of the sphenoid bone and part of the cheekbones of the skull, as well as the frontal bone. The lateral wall separates the edges of the eye from the temporal part.
At the very opening for the eye there are many cracks and strokes with which the eye socket joins with other facial skull formations:
1. visual channel of the nerve end;
2. lower lacrimal fissure;
3. the upper slit of the eye;
4. the zygomatic opening;
5. nasolacrimal passage;
6. Lattice cells.
The structure of the orbit will give us a detailed answer to all the questions of interest about the location of the eye.
Inside the orbit, along the lateral and upper edgeswalls, there is a gap, which on one side is closed by a wedge-shaped bone, and on the other by its wing. It unites the orbital aperture with the median fossa of the facial skull. The motor eye nerves slip through the upper orbital entrance. The collection of such important nerve endings in the outskirts of the ophthalmic entrance explains the formation of such symptoms, in which the defeat of a healthy site with the syndrome of the "orbital fissure" is possible.
The medial wall consists of a lacrimal cavityskull, trellised cells and part of the skull of the sphenoid bone. A teardrop path follows from the front, which follows into the lacrimal sac. In it is a pit, which rests against the nasolacrimal duct.
Two cracks run from the top of the medial wall.The first is the latticed entrance, which is located at the initial edge of the frontal suture, and the second gap extends along the last edge of the frontal sulcus. The anatomy of the orbit seems to be a very complex choice of viewing angles. A full view of the facial skull from the inside will help us cut it across and along.

Structure of the eye socket
1. Cheek bone segment of the forehead.
2. The wide part of the sphenoid bone.
3. Cavity of the cheek surface.
4. Frontal process.
5. The main orbital output.
6. Skull and facial plexus.
7. Part of the cheekbones of the skull.
8. The infraorbital path.
9. Part of the upper jaw.
10. The glaucous gap.
11. Nasal passage.
12. Palatine segment of the skull.
13. Part of the tear sulcus.
14. The glabellar band of the trellised link.
15. Lacrimal path along the skull.
16. Back tear febrinum.
17. Maxillary frontal segment.
18. The first latticed window.
19. The last latticed window.
20. Supraorbital cleft.
21. The visual passage.
22. A small wing of the wedge-shaped surface of the skull.
23. The ornate aperture from above.
In ordinary adults, the volume of the orbit is approximately 30 ml, the eye - 6.5 ml.
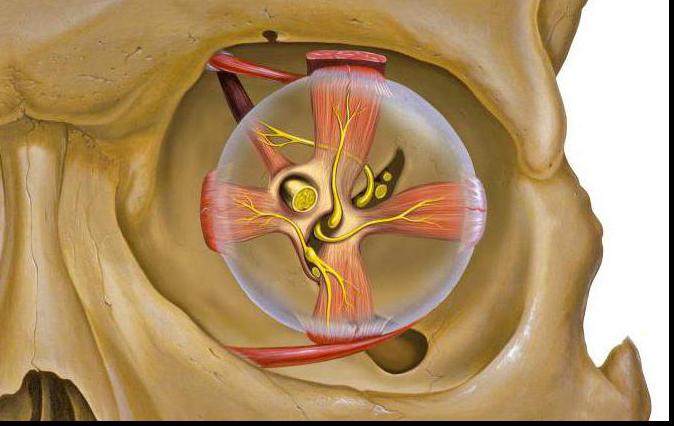
Anatomy of the orbit
Сфера орбиты глазницы – две впадины в виде pyramids, which have a base, four walls and a top. The base, which is located inside the skull, is formed by four corners. The bones forming the eye socket are connected to the extreme angle of the frontal bone, and the angle from below is connected with the maxillary bone. The medial margin borders on the frontal, lacrimal and maxillary bone. The lateral corner joins with the jaw.
The apex of the orbit passes at the medial angle of the orbital aperture from above and smoothly passes into the channel of the nerve end of the eye.

Combining the orbital aperture with the skull
At the top of the orbit there is an impressive opening,along which the visual canal and the artery of the eye pass. In the anterior protuberances of the medial margin, there is a fossa of the lacrimal sac, which continues with a nasolacrimal canal extending into the nasal cavity.
The orbital entrance below passes through the lateraland the lower edge of the orbit. Further it goes to the palate-like and temporal fossa. Along it, the lower vein of the eye passes into the upper artery. It connects to the venous plexus and passes through the nerves and artery located at the bottom of the eye socket.
Through the upper hole that goes into thethe middle cranial fossa, the oculomotor nerve plexuses arrive, as well as the trigeminal nerve. Immediately the upper vein of the eye flows, which is the main collector of the veins of the eyeball.

Structure of the orbit
The sphere contains the eyeball with itssprouts, apparatus for communication with the facial skull, vessels, nerve plexuses, muscles and lacrimal glands, surrounded by fatty margins at the edges. Ahead of the sphere of the orbit is limited to the orbital fascia, interwoven into the cartilage of the eyelids. It fuses with the periosteum in the corners of the sphere. The lacrimal sac passes in front of the orbital fascia and lies outside the cavity of the orbit. This is how the anatomy of the eye socket looks in the facial section.

Value in medicine
At the site of the plexus neurovascular endingsOphthalmic fissure in the event of the occurrence of various pathological processes in this area may occur syndrome "upper orbital fissure." With this disease, an upper eyelid prolapse may appear. Also with this syndrome, complete immobility of the eye may appear, the pupil gradually expands.
In the place of occurrence of pathology observeddisorder of sensitivity, and in the place of distribution of the trigeminal plexus there can be a stupor of nerve endings and veins of the initial section of the eye. Given the various difficulties that follow after treatment or after surgery, it is necessary first to consult several doctors at once: a neuropathologist, an ophthalmologist, an endocrinologist, a therapist. It is necessary to pass all the required tests, diagnose, tonometry, biomicroscopy. Then mozhena carry out medical intervention.









