Dielectrics in an electric field behaveaccording to its internal structure. They are also called nonconductors, since, as is known, they are substances that do not conduct almost electric current. They do not contain free charge carriers, which would be able to move inside this dielectric.
A molecule is a tiny particle of matter,which retains its chemical properties. It, in turn, itself consists of atoms with a positively charged core and negatively charged electrons. Molecules in general are neutral. As the theory of covalent bonds says, one or several pairs of electrons formed in them, becoming common for connecting atoms, ensure the stability of molecules.
For each type of charge - positive(nuclei) and negative (electrons) - there is a point, which is like for them a "center of gravity" (electrical). These points are called the poles of the molecule. In the case of coincidence in the molecule of electric centers of gravity of charges of opposite charges: positive and negative - it will be nonpolar (not having a dipole moment).
The structure of the molecule can be asymmetric,say, there can be two heterogeneous atoms in it, then to some extent there must be a displacement of the total pair of electrons in the direction of one of the atoms. It is clear that in this case the uneven distribution of unlike charges (positive and negative) inside the molecule will lead to a mismatch of their electrical centers of gravity. The resulting molecule is called polar or has a dipole moment.
The main property of dielectrics is their ability to polarize.
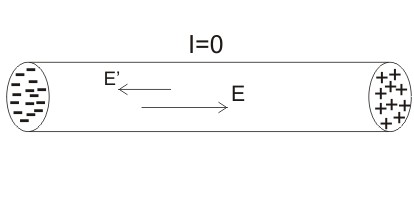
Диэлектрики в электрическом поле поляризуются.This means that in their atoms the electrons begin to move along elongated orbits. As a result, some of their surfaces are negatively charged, others - positively. Thus, an electric field appears in dielectrics, which, accordingly, is called internal. That is, dielectrics are simultaneously affected by electric fields (external and internal), which are opposite in this case.
The resulting electric field hasThe intensity equal to the difference in the strengths of the larger and smaller of the fields. It should be noted that the field strength in a dielectric, regardless of its type, is always less than the electric field strength that caused its polarization.
The intensity of the polarization is in the straightproportional to the dielectric constant of the dielectric. The smaller it is, the less intense is the polarization in the dielectric and the stronger the electric field in it.
Charges appear not only on the surface, but also at the ends of the dielectric, but their transition upon contact with the electrode is impossible, since the nonconductor is attracted to the electrode by Coulomb forces.
Dielectrics in an electric field, if itstrong and its tension can be increased, for certain values of the tension will begin to break through, that is, from the atom will begin to break off the electrons. This will lead to a process of ionization of dielectrics, as a result of which they become conductors.
The magnitude of the strength of the external field, whichleads to breakdown of the dielectric, called its breakdown tension. And the corresponding limiting voltage at which the dielectric breaks through is the breakdown voltage. Another name for the limiting voltage is known - the dielectric strength.
It should be noted that only dielectrics in an electric field have an internal field, which basically disappears if the external one is removed.