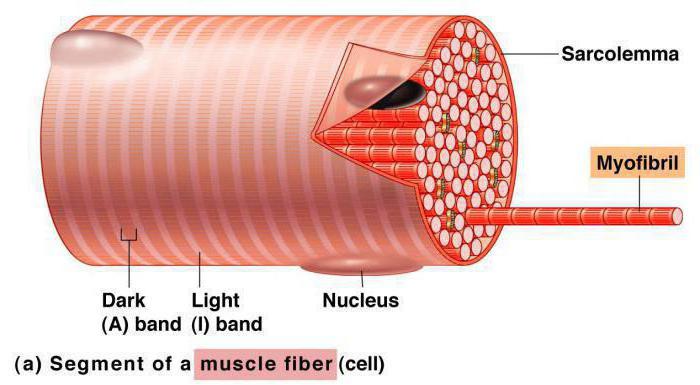
Thin muscle fibers form eachskeletal muscle. Their thickness is only about 0.05-0.11 mm, and their length reaches 15 cm. Muscle fibers of the striated muscle tissue are collected in bundles, which include 10-50 fibers. These bundles are surrounded by connective tissue (fascia).

The muscle itself is also surrounded by fascia.About 85-90% of its volume is muscle fibers. The rest are the nerves and blood vessels that pass between them. At the ends, the muscle fibers of the striated muscle tissue gradually pass into the tendons. The latter are attached to the bones.
Mitochondria and myofibrils in the muscles

Consider the structure of the muscle fiber.In the cytoplasm (sarcoplasm) it contains a large number of mitochondria. They play the role of power plants, in which there is a metabolism and accumulate energy-rich substances, as well as those that are needed to meet energy needs. As part of any muscle cell there are several thousand mitochondria. They occupy about 30-35% of its total mass.
The structure of the muscle fiber is such that the chain ofmitochondria line up along the myofibrils. These are the thin threads providing reduction and relaxation of our muscles. Usually there are several dozens of myofibrils in one cell, and the length of each can reach several centimeters. If you add up the mass of all myofibrils that make up a muscle cell, then its percentage of the total mass will be about 50%. The fiber thickness, therefore, depends primarily on the number of myofibrils located in it, as well as on their transverse structure. In turn, the myofibrils consist of a large number of tiny sarcomeres.
Поперечно-полосатые волокна свойственны мышечным tissues of both women and men. However, their structure is somewhat different depending on the floor. Based on the results of muscle biopsy, it was concluded that the percentage of myofibrils in women’s muscle fibers is lower than that of men. This applies even to high-level athletes.
By the way, the muscle mass itself is distributedunequal body in women and men. The overwhelming part of it in women is in the lower part of the body. In the upper volumes of the muscles are small, but they themselves are small and often completely untrained.
Red fibers
Depending on fatigue, histochemicalcolor and contractile properties of muscle fibers are divided into the following two groups: white and red. Reds are slow fibers with a small diameter. In order to get energy, they use the oxidation of fatty acids and carbohydrates (such an energy-formation system is called aerobic). These fibers are also called slow or slow-reducing. Sometimes they are called type 1 fibers.
Why red fiber got its name

They are called red because they havered histochemical color. This is due to the fact that these fibers contain a lot of myoglobin. Myoglobin is a special pigment protein that has a red color. Its function is that it delivers oxygen deep into the muscle fiber from the blood capillaries.
Red fiber features
Slow muscle fibers have manymitochondria. They carry out the oxidation process, which is necessary for energy. Red fibers are surrounded by a large network of capillaries. They are needed to deliver a large amount of oxygen along with blood.
Slow muscle fibers are well adapted tothe implementation of an aerobic energy generation system. The strength of their contractions is relatively small. The speed at which they consume energy is sufficient to only manage aerobic metabolism. Red fibers are excellent for non-intensive and long-term work, such as walking and easy running, distance rides in swimming, aerobics, etc.

Muscle fiber contraction providesperforming movements that do not require much effort. Thanks to him, posture is also supported. These striated fibers are characteristic of muscle tissue, which are included in the work under loads that are in the range from 20 to 25% of the maximum possible force. They are characterized by excellent endurance. However, red fibers do not work in sprint distances, heavy weight lifting, etc., since these types of loads imply fairly rapid consumption and energy production. For this purpose are white fibers, which we now talk.
White fibers
They are also called fast, fast-moving.type 2 fibers. Their diameter is larger compared to red. For energy, they mainly use glycolysis (that is, their energy-generating system is anaerobic). In fast fibers there is a smaller amount of myoglobin. That is why they are white.
ATP cleavage
Fast fiber is characterized by high activity.ATphase enzyme. This means that the splitting of ATP occurs quickly, while producing a large amount of energy, which is necessary for intensive work. Since white fibers are characterized by a high rate of energy consumption, they also need a high rate of reduction of ATP molecules. And it is able to provide only the process of glycolysis, since, unlike oxidation, it occurs in the sarcoplasm of muscle fibers. Therefore, the delivery of oxygen to the mitochondria is not required, as is the delivery of energy from the latter to the myofibrils.
Why white fibers get tired quickly
Glycolysis causes the formation oflactate (lactic acid), rapidly accumulating. Because of this, white fibers get tired quickly enough, which ultimately stops muscle work. In red fibers, aerobic formation does not produce lactic acid. That is why they can maintain moderate tension for a long time.
White fiber features
Белые волокна характеризуются большим диаметром relatively red. In addition, they contain much more glycogen and myofibrils, but they contain less mitochondria. The cell of a muscle fiber of this type incorporates also creatine phosphate (CF). It is required at the initial stage of the implementation of high-intensity work.

Most of all white fibers are adapted formaking powerful, fast, but short-term efforts, because they have low endurance. Fast fibers, as compared to slow fibers, are able to shrink 2 times faster, and also to develop a force that is 10 times greater. A person develops maximum speed and strength precisely because of them. If the work requires 25-30% of maximum effort and higher, it means that white fibers take part in it. They are divided by the method of obtaining energy into the following 2 types.
Fast glycolytic muscle fibers
The first type is fast glycolytic fibers.The process of glycolysis is used by them for energy. In other words, they are able to use only an anaerobic energy-formation system that promotes the formation of lactic acid (lactate). Accordingly, these fibers do not produce energy with the participation of oxygen, that is, by an aerobic route. Fast glycolytic fibers are characterized by maximum contraction speed and strength. They play a major role in weight gain among athletes-bodybuilders, as well as provide maximum speed for runners and swimmers performing at sprint distances.
Fast oxidative glycolytic fibers
The second type - fast oxidative-glycolyticthe fibers. They are also called transient or intermediate. These fibers are a kind of intermediate type between slow and fast muscle fibers. They are characterized by a powerful system of energy formation (anaerobic), but they are also adapted to the implementation of a rather intense aerobic exercise. In other words, these fibers can develop large forces and a high rate of contraction. In this case, the main source of energy is glycolysis. At the same time, if the intensity of the reduction becomes low, they are able to use oxidation sufficiently effectively. This type of fibers is involved in the work, if the load is from 20 to 40% of the maximum. However, when it is about 40%, the human body immediately completely switches to the use of fast glycolytic fibers.
The ratio of fast and slow fibers in the body
Studies have been conducted, during whichit was established that the ratio of fast and slow fibers in the human body is genetically determined. If we talk about the average person, he has about 40-50% slow and about 50-60% fast. However, each of us is individual. In the body of a particular person, both white and red fibers may prevail.
The proportion of them in differentbody muscles are also not the same. This is because the muscles and their groups in the body perform various functions. Because of this, the transverse muscle fibers are quite different in their composition. For example, in the triceps and biceps are about 70% of white fibers. A little less than them in the thigh (about 50%). But in the gastrocnemius muscle of these fibers is only 16%. That is, if the functional task of a muscle includes more dynamic work, it will have more fast, not slow ones.
Communication potential in sports with muscle fiber types

We already know that the total ratiored and white fibers in the human body laid genetically. Because of this, different people have different potential in sports activities. Some people are better given sports that require endurance, and someone - strength. If slow fibers prevail, skis, marathon run, long-distance swims, etc., that is, sports that involve mainly the aerobic energy-formation system, are much more suitable for a person. If the body has more fast muscle fibers, it is possible to achieve good results in bodybuilding, sprint, sprint swimming, weightlifting, powerlifting and other types, where the main importance belongs to explosive energy. And as you already know, only white muscle fibers can provide it. Great sprinter athletes are always dominated by them. Their number in the leg muscles reaches 85%. If there is an approximately equal ratio of different types of fibers, the average distance in running and swimming is excellent for a person. However, the foregoing does not at all mean that if fast fibers prevail, such a person will never be able to run a marathon. He will run it, but he will definitely not become a champion in this sport. Conversely, if the body has much more red fibers, the bodybuilding results will be worse for such a person than for the average person, the ratio of red and white fibers is approximately equal.






