Potato in the human diet isalmost the main place, yielding to consumption except that bread. But few people think how difficult this plant is from a scientific point of view. It has unique features that are unique to it.
Biological features
Potato is one of the leadingfood crops. It occupies not only the first place among agricultural crops for the production of protein, but also has one of the highest levels of fitness.
The homeland of potatoes is the tropical zone of the continentSouth America. The first centers of origin are located in Bolivia and Peru, in the highlands of the Andes (2000-4800 m above sea level), as well as in the temperate zones of Chile (0-250 m above sea level).
Man introduced potatoes into culture for more than 8000 yearsago. Originally, the territories on which it was cultivated were in South-Eastern Peru and North-West Bolivia. In Russia, this agricultural culture appeared during the reign of Peter I. It was this ruler that legalized the widespread cultivation of potatoes.

The above-ground part
A potato plant is a bush that consists of4-8 stems. Branchedness depends on the maturity period. In early maturing varieties, as a rule, a weak branching is observed at the base of the stem, and in late maturing varieties, a strong one. A large seed potato, or rather a tuber, forms an escape with a greater number of stems than a small one.
По количеству листьев растения картофеля тоже can be very different. Loneliness may be weak, but there are also shoots when the stems are almost not visible behind the numerous leaves. According to the shape of the bush, varieties are distinguished with shrub shrubs, spreading and semi-spread bushes. Based on the position of the stems, we distinguish erect, dilapidated and semidilute bushes.

Root system
As for the root system of potatoes, itgummy and in fact is a combination of the root systems of individual stalks. The penetration of the roots into the soil depends largely on its type. But on average, the depth of penetration ranges from 20 to 40 cm. In addition, in the topsoil, the roots expand by 50-60 cm.
Above-ground part of the plant: potato leaf and flower
Leaf simple single-pinnately dissected type.If we consider its components, then we can see several pairs of lobes, lobules and end segments, which are located in various combinations on the main petiole. And the potato sheet ends with one unpaired share. The characteristic features of the leaf (the degree of dissection, the size and shape of the lobes, the size and position of the stem) are important varietal characteristics. The leaf plate is always in the lowered position, the color varies from yellow green to dark green.

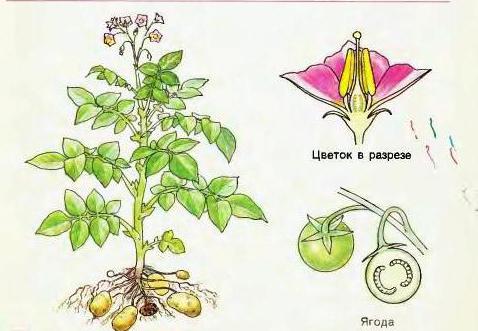
Tuber formation mechanism
Potato tuber - escape, but not aboveground, butunderground. Its formation is as follows. Due to the increased concentration of nutrients in the upper part of the tuber, the germination of the buds of not all of the eyes, but only those that are located in its upper part, is observed during planting. The color of sprouts depends on the variety and can be green, red-violet or blue-violet. When a plant reaches a height of 10-20 cm, the underground part of its stems gives shoots - stolons, the thickness and length of which are 2-3 mm and 5-15 cm, respectively. Their ends gradually thicken, thus turning into tubers.
Tuber structure
Клубень картофеля является укороченным утолщенным stem, as evidenced by numerous similarities, especially noticeable at an early stage of development. This, in particular, the presence of scaly leaves, in the axils of which resting buds are formed, the number of which varies from 2 to 4 in each eye. Also, the similarity consists in a similar alternation and arrangement of tissues and vascular bundles in tubers and stems. And the formation of chlorophyll in the tuber becomes apparent when it turns green when exposed to light. That is why in places of storage, poorly protected from light, there are often green potato tubers, which cannot be eaten.
Верхняя, наиболее молодая часть клубня содержит more eyes than the average, and even more so the oldest, lower, or umbilical cord part. Therefore, the buds of the apical part develop stronger and more viable. It is known that most often in a single eye, the central bud, which is the most developed, sprouts first. In the case of sprout removal, the spare buds start to grow and get stuck in growth, the plants of which will be weaker than from the central bud. Therefore, seed potatoes during winter storage should not be regularly exempt from sprouts. This may lead to the fact that plants will not be formed from the central bud, but from the spare, that is, they will be weaker.
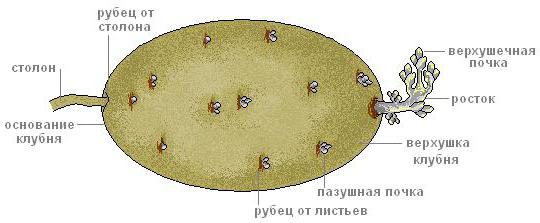
Tuber Breath and Moisture Evaporationwith the help of lentils. Their laying under the stomata of the developing tuber occurs simultaneously with the formation of periderm. It is through them that oxygen gets into the tuber and carbon dioxide and water vapor are removed.
Does the structure of the tuber depend on the potato variety?
The structure of potato tubers in early and late varieties may vary. For example, later varieties are characterized by the presence of more dense cork tissue in tubers.
Tubers can have a wide variety of forms, depending on the variety and conditions of cultivation. Variants of the form - round, elongated, oval, round-oval, shaped, barrel-shaped, etc.
The greatest economic valuepossess varieties with round tubers and surface eyes. This form is ideal for mechanized planting and harvesting, and the superficial arrangement of the peepholes facilitates mechanical peeling and washing.
The color of tubers is the most different - white,light yellow, pink, red, red and blue-violet. Thus, the external structure of the potato tuber is a variety. The flesh of the tubers is also different in shade: it can be white, yellow or light yellow.
Potato tuber: chemical composition
The deepest state of natural resttubers observed during the harvest period in the fall. As spring approaches, it gradually weakens, as growth inhibitors are no longer so active. At this time, the formation of substances that stimulate growth. They encourage the growth of the kidney.
In the winter in a dry room withthe air temperature is 1-3 ° C; potatoes are well kept, without germinating, for 6-7 months. After this time, when the air temperature rises to 10-12 ° C and a sufficient influx of oxygen, growth processes begin.
Tuber potato contains significant stocknutrients that are necessary for the growth and development of the plant in the initial period of life. In the composition of its dry matter has more than 26 different chemical elements. The composition may vary depending on the variety, soil, climatic conditions and fertilizer.
The average content in the chemical composition of tubers of various substances are: water 75%, starch 20.4%, sugar 0.3%, crude protein 2%, fat 0.1%, fiber 1.1%, ash 1.1%.
Starch in potato tubers affects tastequality. The more starch, the more tasty the potatoes. In the case of increasing the concentration of crude protein taste, by contrast, deteriorate. Starchiness is judged on the culinary properties of potatoes. Its increase causes an increase in the powderiness of the pulp, an improvement in the digestibility.

Reproduction
The multiplication of potatoes can be done in two ways - by vegetative and sexual means.
Vegetative breeding method - this ispotato growing from tubers. Also, this method includes reproduction using segments of stems, on which one apical or several lateral vegetative buds must necessarily be present.
The most common way is cultivation.potato tubers. And stem cuttings are planted in cases where the number of tubers is limited, and some new valuable variety requires a quick introduction into practice.









