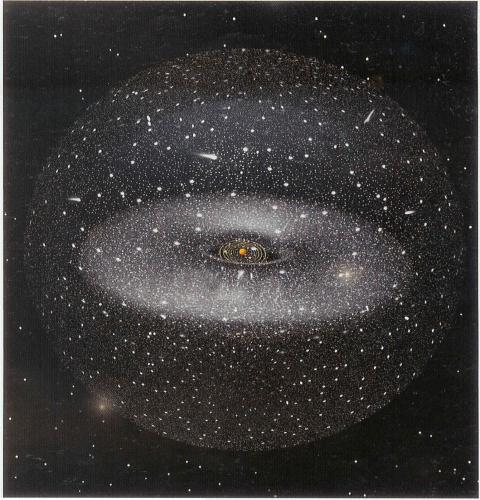
The Oort cloud is a hypothetical belt aroundSolar system, filled with asteroids and comets. At the moment, not a single telescope is able to detect such small objects at a considerable distance, but a lot of circumstantial evidence indicates that there is a similar formation at the far borders of our stellar system. However, do not confuse the Kuiper belt and the Oort cloud. The first is also similar to the asteroid belt and includes many
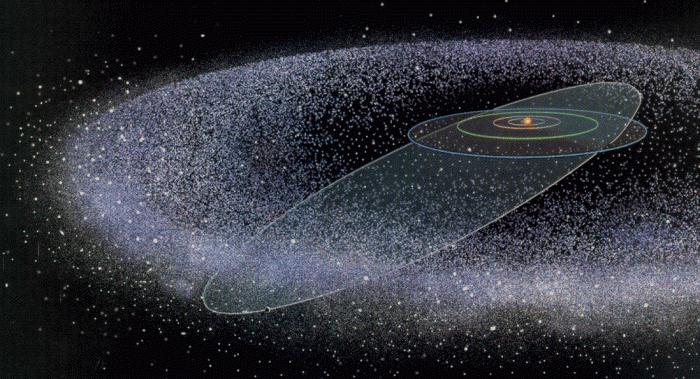

If Kuiper Belt Objects are Well Availableto modern telescopes, the bodies of this cloud are separated from the sun for a whole light year. It is rather difficult to examine them directly at telescopes at such a distance. At the same time, astrophysicists have already discovered dozens of planets, even in other star systems, but, firstly, these are almost all giant planets like Jupiter, and secondly, they are observed not by themselves, but due to the gravitational influence on their star. However, the Oort cloud literally sends us plenty of evidence of its existence. We are talking about comets, which with a constant frequency come to the solar system, being the envoys of this sphere. Perhaps the most famous example will be Halley's comet. The Oort cloud was named after the Dutch astrophysicist, who predicted its discovery in the middle of the 20th century, based on the observation of long-period comets. This sphere, as well as the Kuiper belt, consists of trans-Neptunian objects, which, in turn, consist mainly of ice, as well as methane, carbon monoxide, hydrogen cyanide, ethane and other substances. It is very likely that stone objects can also rotate there.

Origin of the sphere
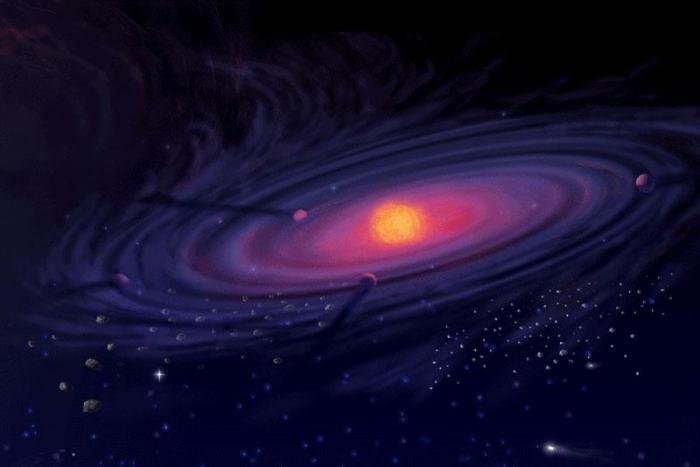
Modern astrophysicists believe that Kuiperthe belt, the Oort cloud - this is what remains of the substances that formed the solar system, but were not included in any planet. About five billion years ago, most of the substance of an exploding star of the first generation (that is, formed relatively soon after the Big Bang) due to gravity and millions of years of condensation transformed into a new star - the Sun. A small part of this protoplanetary rotating disk has gathered into huge boulders and formed the planets of our system. The rest of the dust and small objects of the nebula were thrown to the very edge of the solar system, forming the Kuiper belt and the very distant sphere of the Oort cloud.












